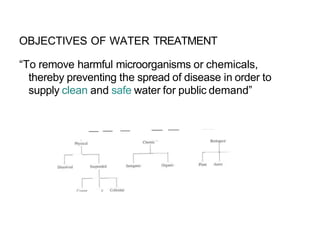
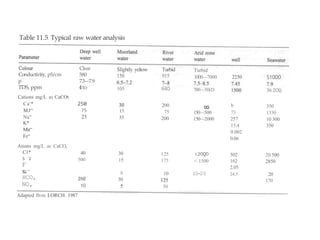
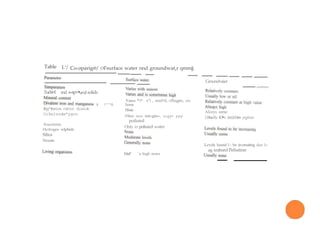
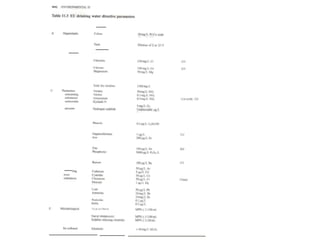
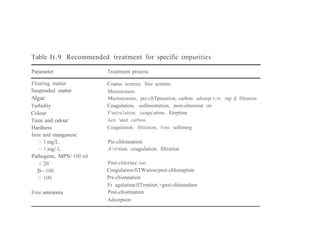
The document discusses the objectives and processes of water treatment, emphasizing the removal of harmful microorganisms and chemicals to provide safe drinking water. It compares the quality of surface and groundwater, outlining standard health effects associated with various chemical contaminants. It also details recommended treatment processes based on specific impurities and provides an overview of typical treatment plant operations for both surface and groundwater.