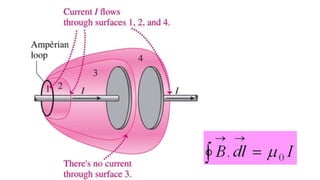
Maxwell developed a theory that unified electricity and magnetism and predicted electromagnetic waves. He corrected Ampere's law by including displacement current, which accounts for changing electric fields. Displacement current exists due to changing electric fields between capacitor plates. Maxwell's correction showed that magnetic fields can be produced by both conduction currents and time-varying electric fields, laying the foundation for understanding electromagnetic waves.