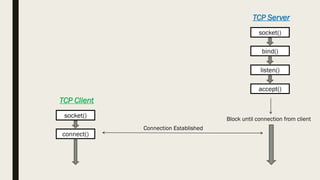
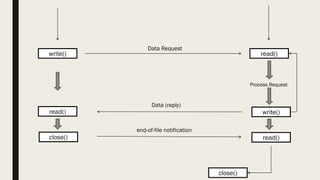
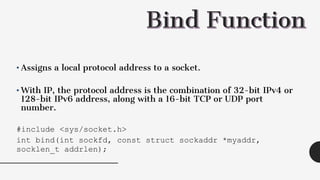
The document describes the functions used in TCP client-server communication. A TCP server uses socket(), bind(), listen(), and accept() to set up the server socket and accept connections. A TCP client uses socket() and connect() to establish a connection. Data can then be sent between client and server using read() and write() and the connection closed with close(). The server may fork() to handle multiple clients concurrently.