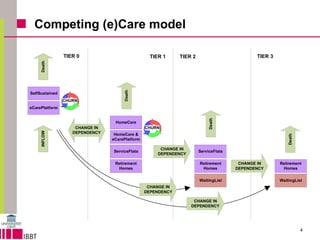
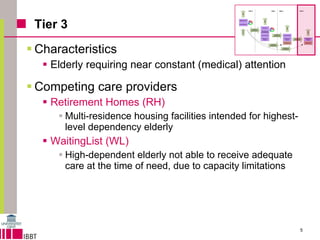
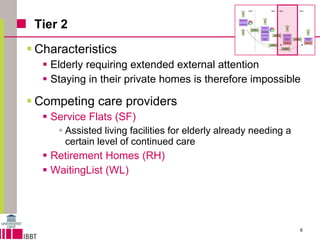
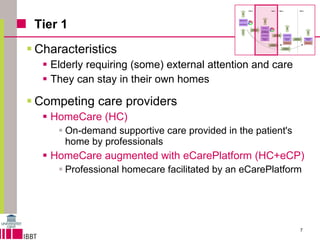
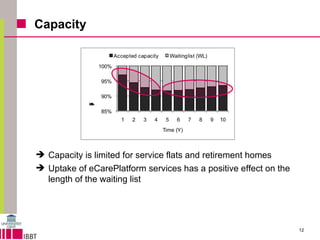
This document summarizes a model for predicting market shares of competing care providers for the elderly in Flanders over a 10-year period from 2010 to 2020. The model divides elderly care needs into 4 tiers based on level of dependency. It considers various care providers that compete within and between the tiers, including home care, assisted living facilities, retirement homes, and e-care platforms. The model mechanisms include patient flows between tiers and competition within tiers. Simulation results indicate trends in how competition may evolve and the impact of limited capacity on waiting lists. Conclusions discuss using the model to forecast market shares and further techno-economic analysis of e-care platforms.










![Thank you for your attention Questions ? Jan Van Ooteghem [email_address] www.ibcn.intec.ugent.be/te INTEC Broadband Communication Networks (IBCN) Department of Information Technology (INTEC) Ghent University - IBBT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ehealth2009vanooteghem-100924103122-phpapp01/85/Ehealth-2009-Van-Ooteghem-18-320.jpg)