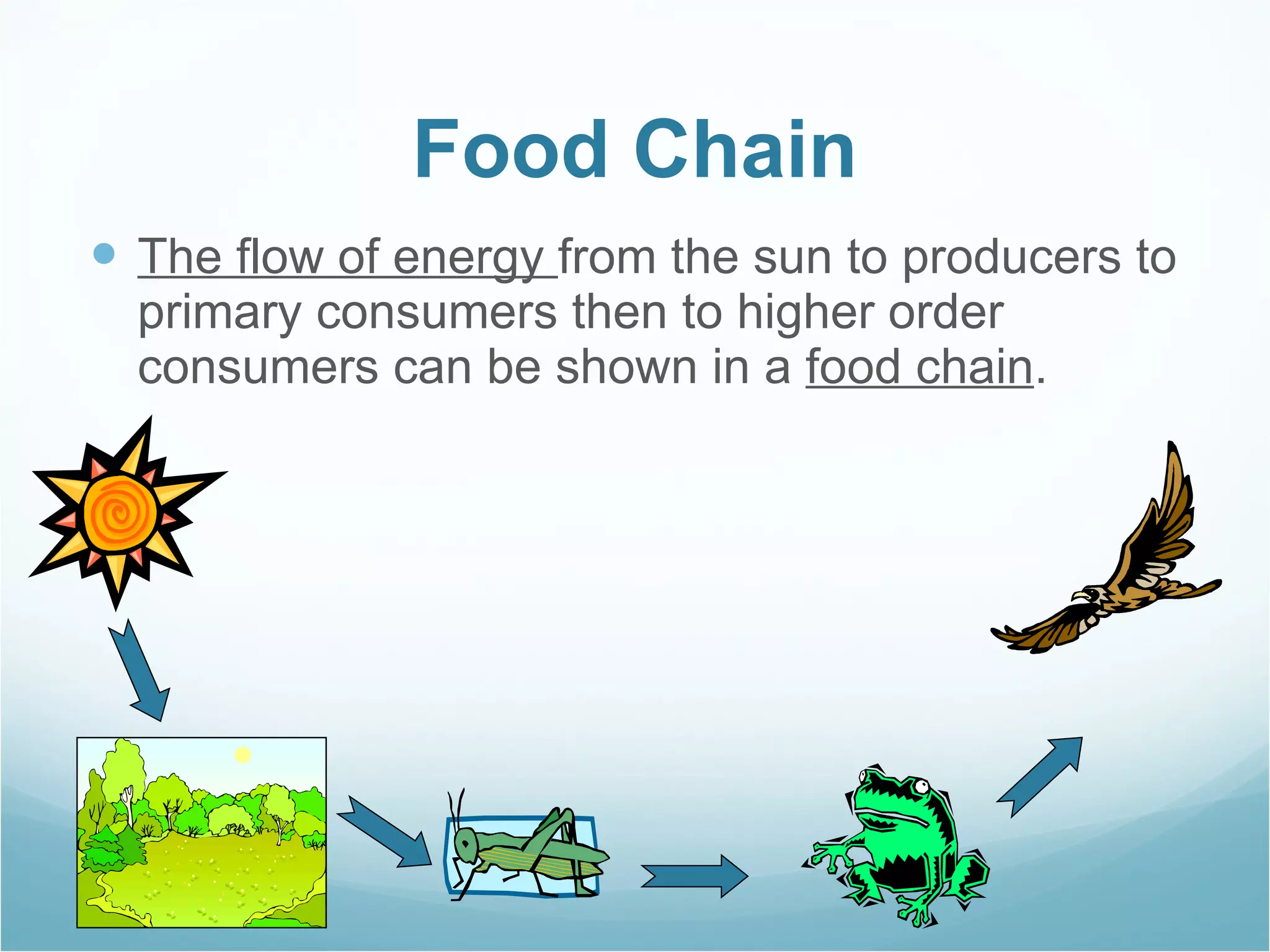
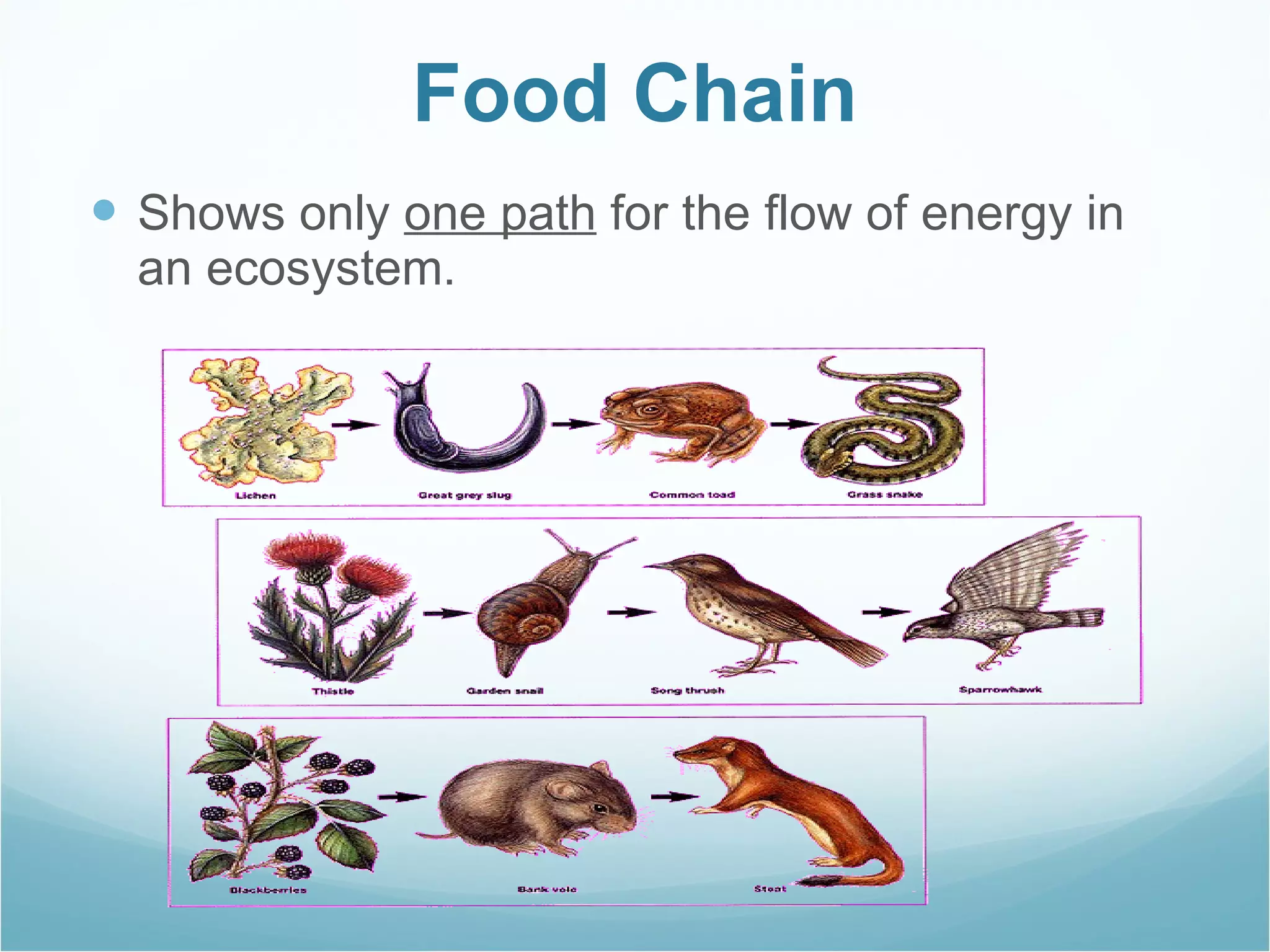
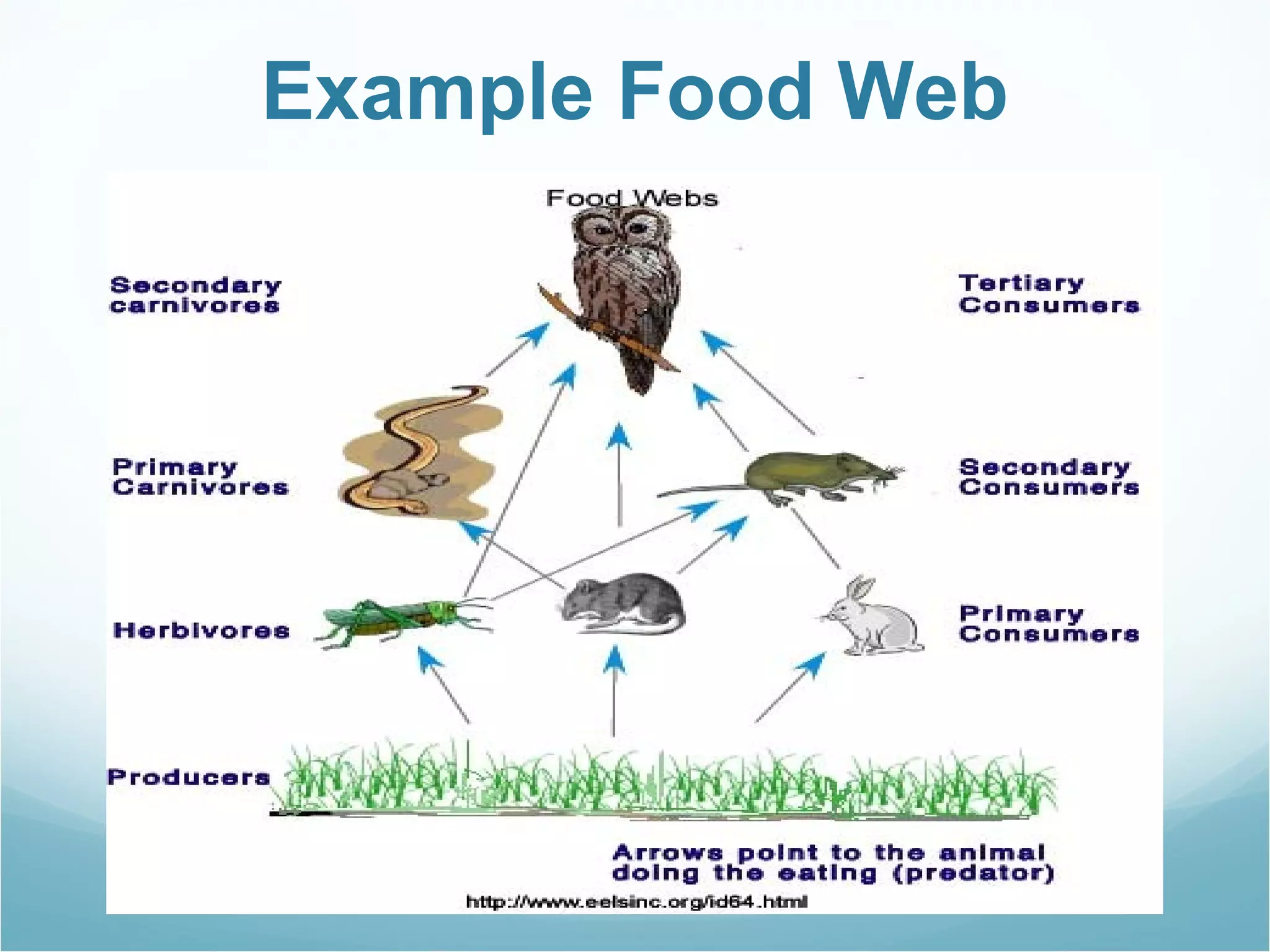
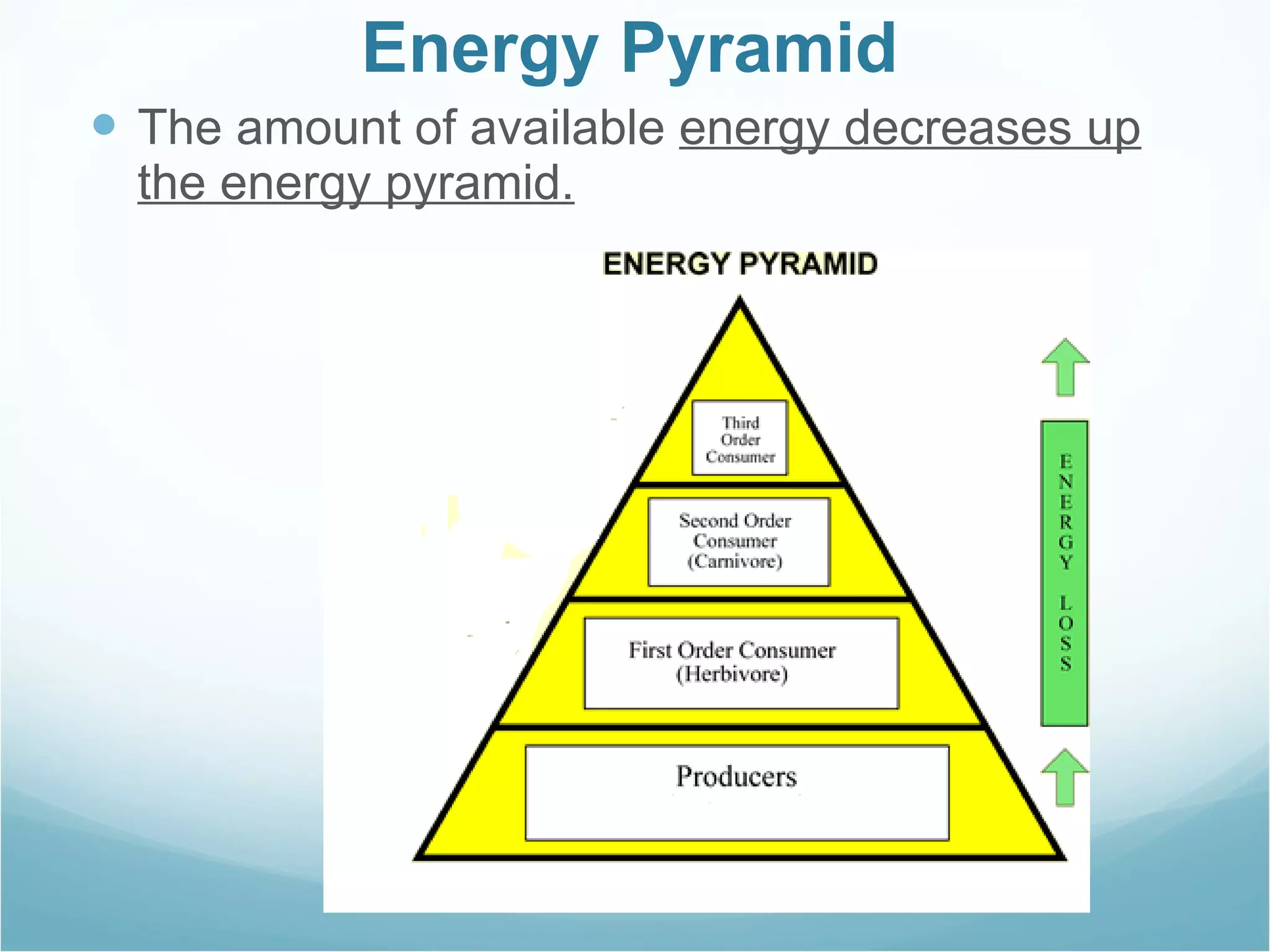
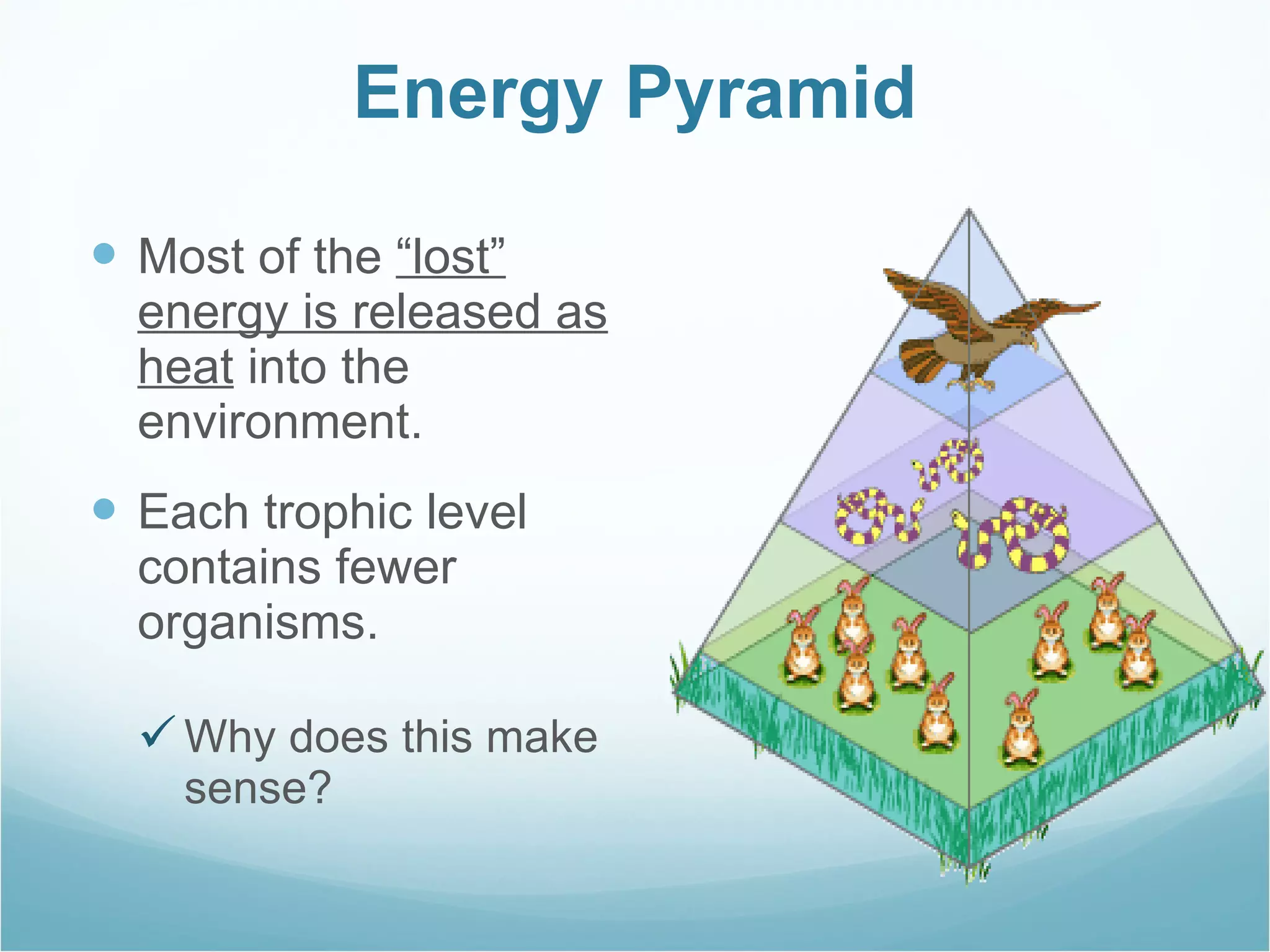
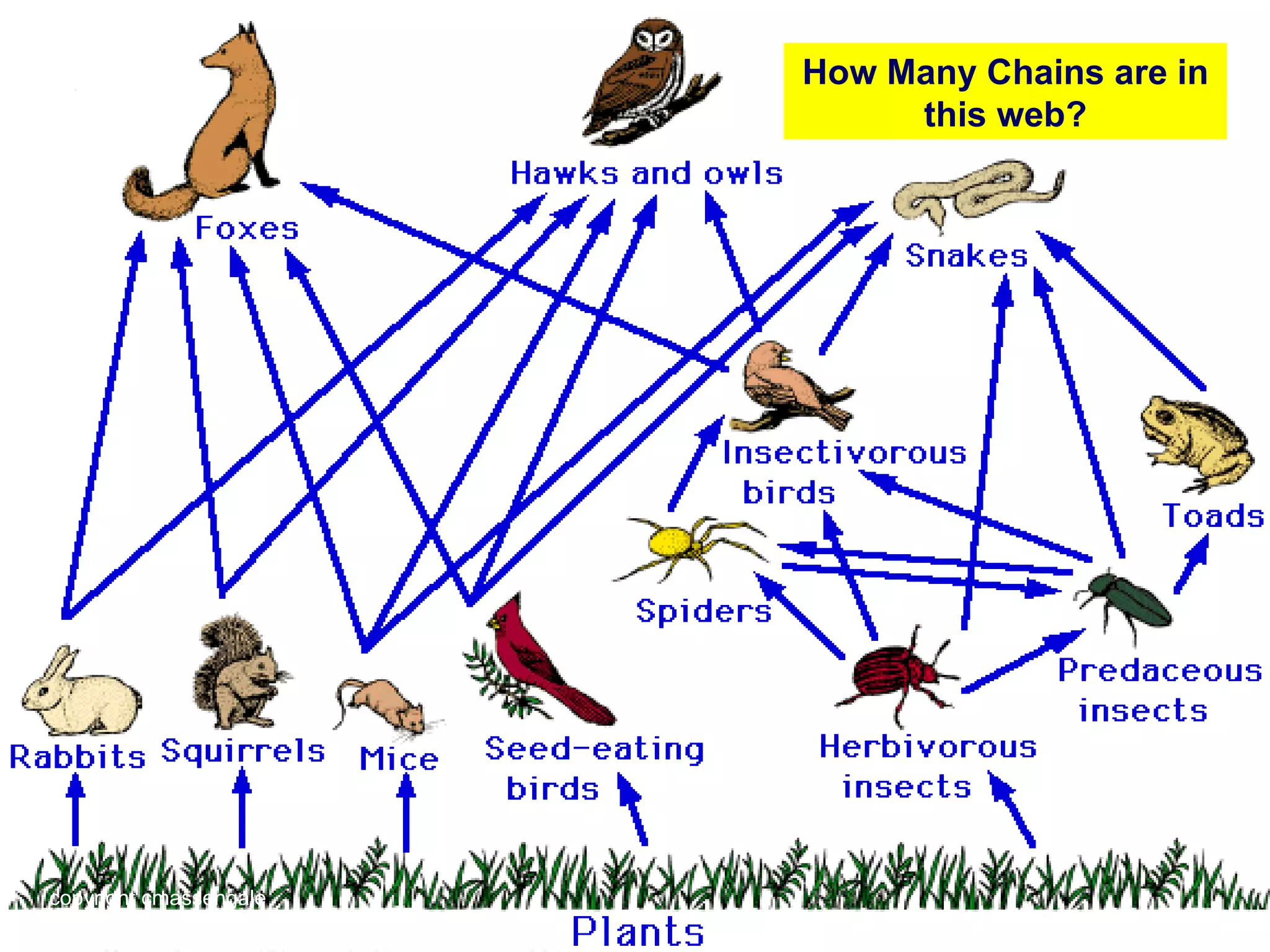
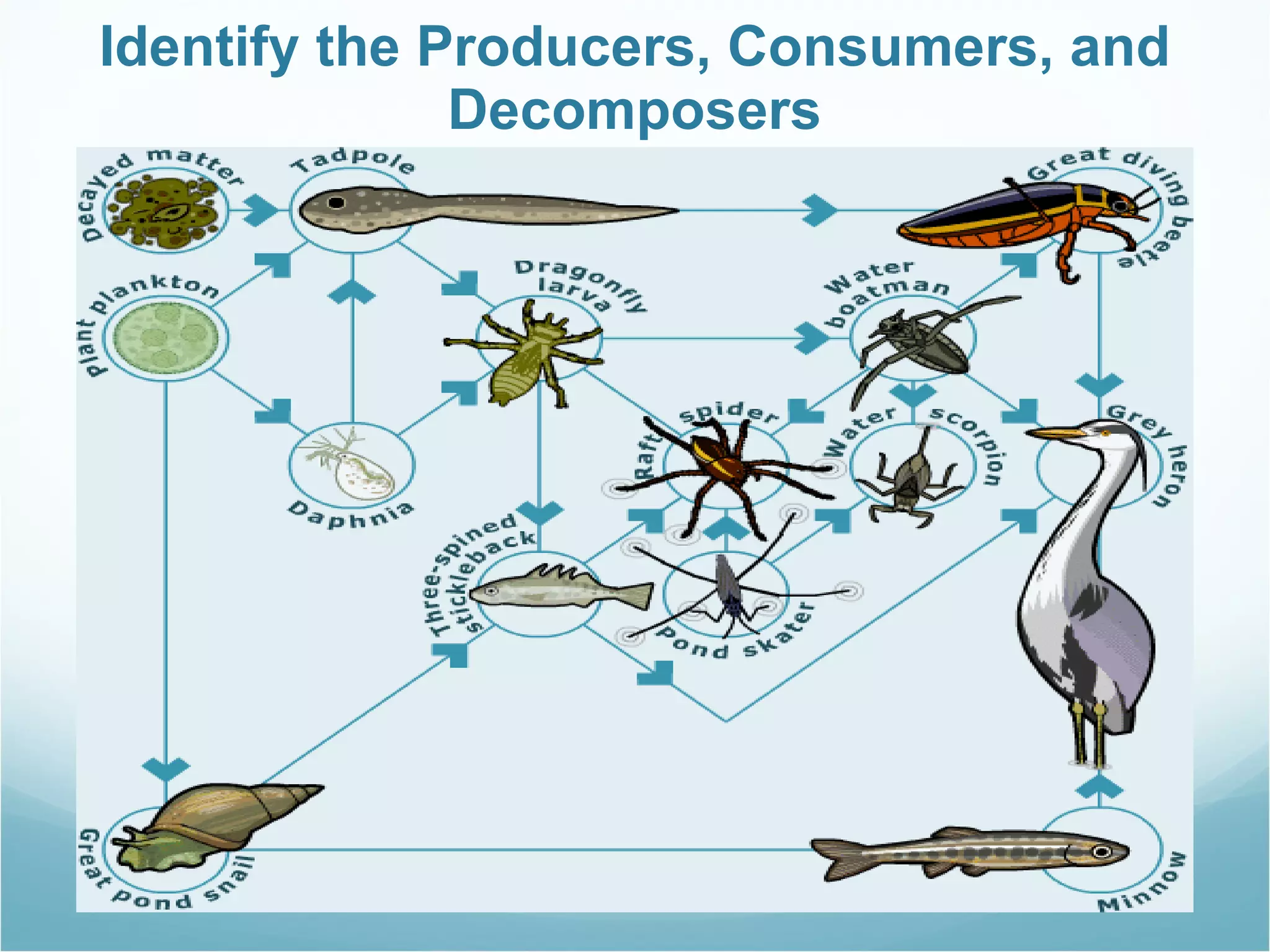
The document discusses key concepts about energy flow within ecosystems, including food chains, food webs, and energy pyramids. It defines producers as organisms at the first trophic level that convert sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis. Consumers are organisms at higher trophic levels that get energy by eating other organisms, including herbivores, omnivores, and carnivores. Decomposers break down dead organic matter and cycle nutrients. Food chains show a single path of energy transfer, while food webs illustrate the many interconnected food chains in an ecosystem. Energy pyramids demonstrate that the amount of available energy decreases at each trophic level as heat is lost during energy transfers between organisms.