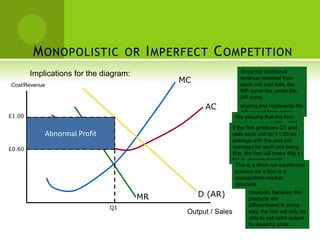
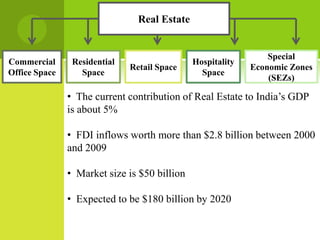
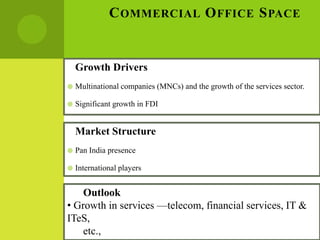
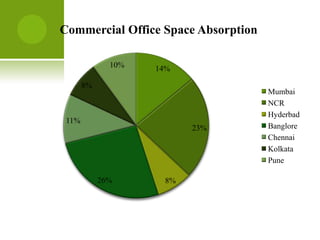
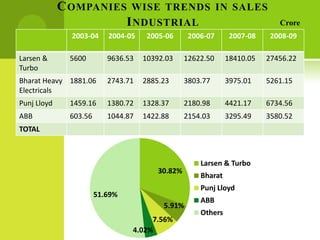
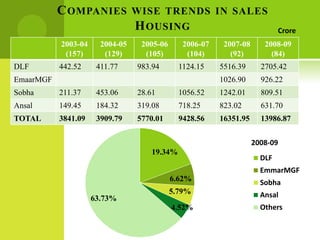
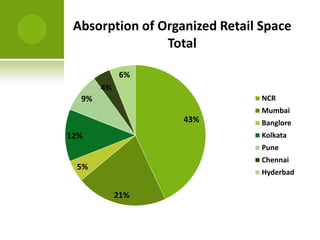
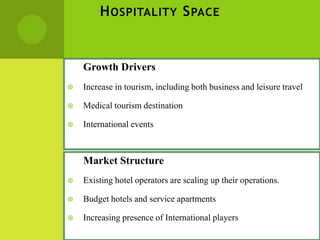
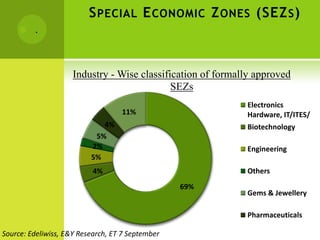
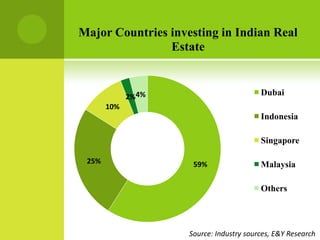
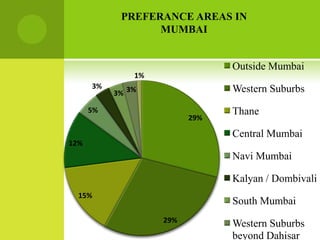
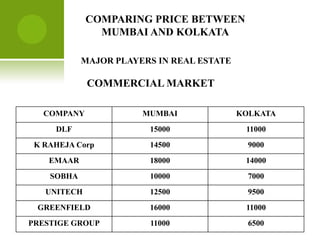
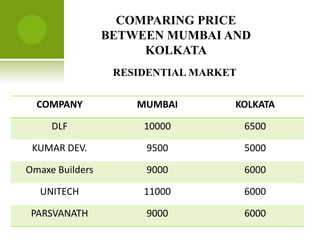
The real estate industry in India witnessed significant growth between 2002-2007 due to liberalization policies. Real estate became a major contributor to India's GDP and attracted billions in foreign investment. The major sectors within real estate are commercial office spaces, residential spaces, retail spaces, hospitality, and special economic zones. While the industry grew rapidly in the past, it is now expected to continue expanding to meet the needs of India's growing urban population in the coming years.