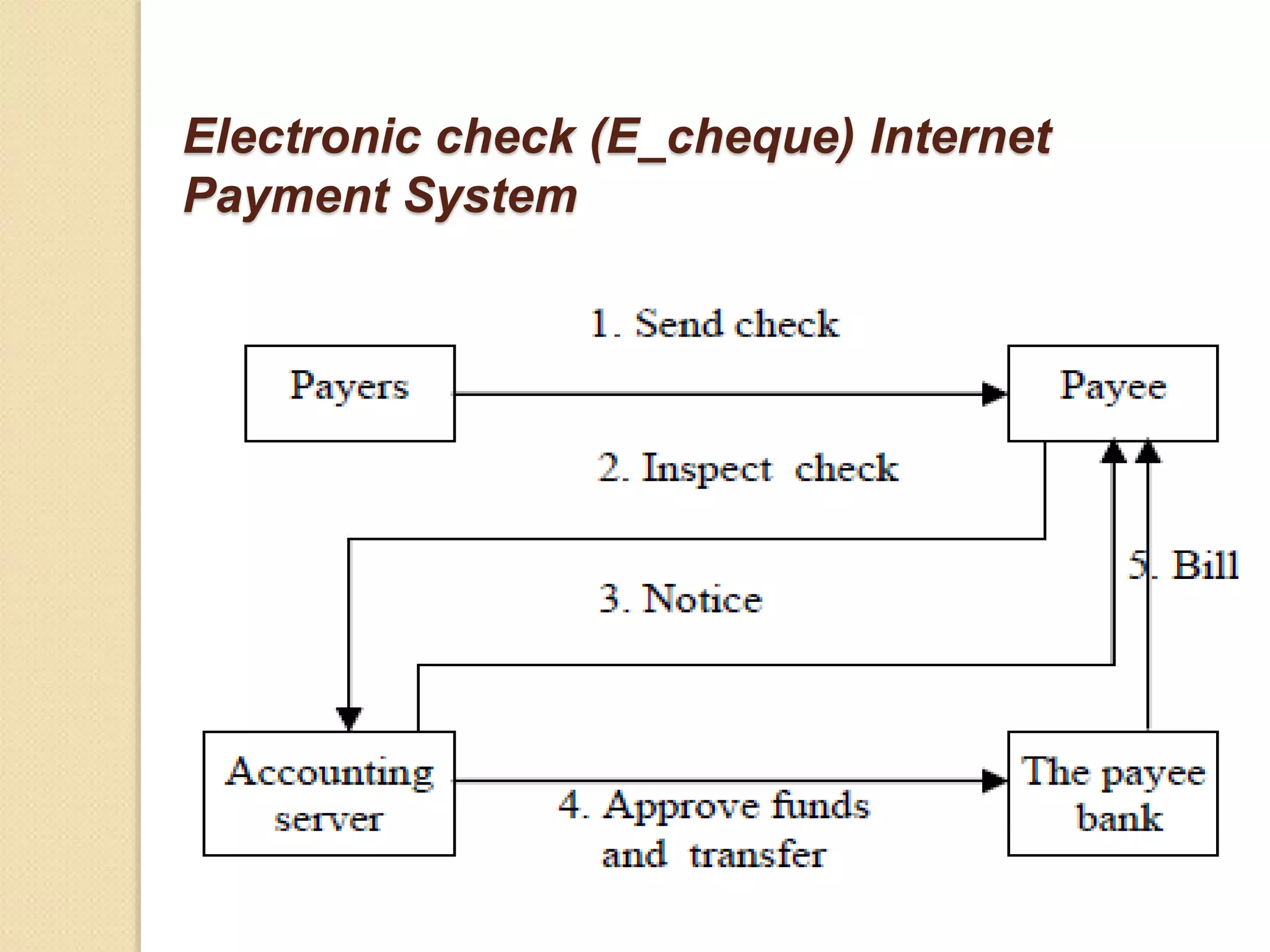
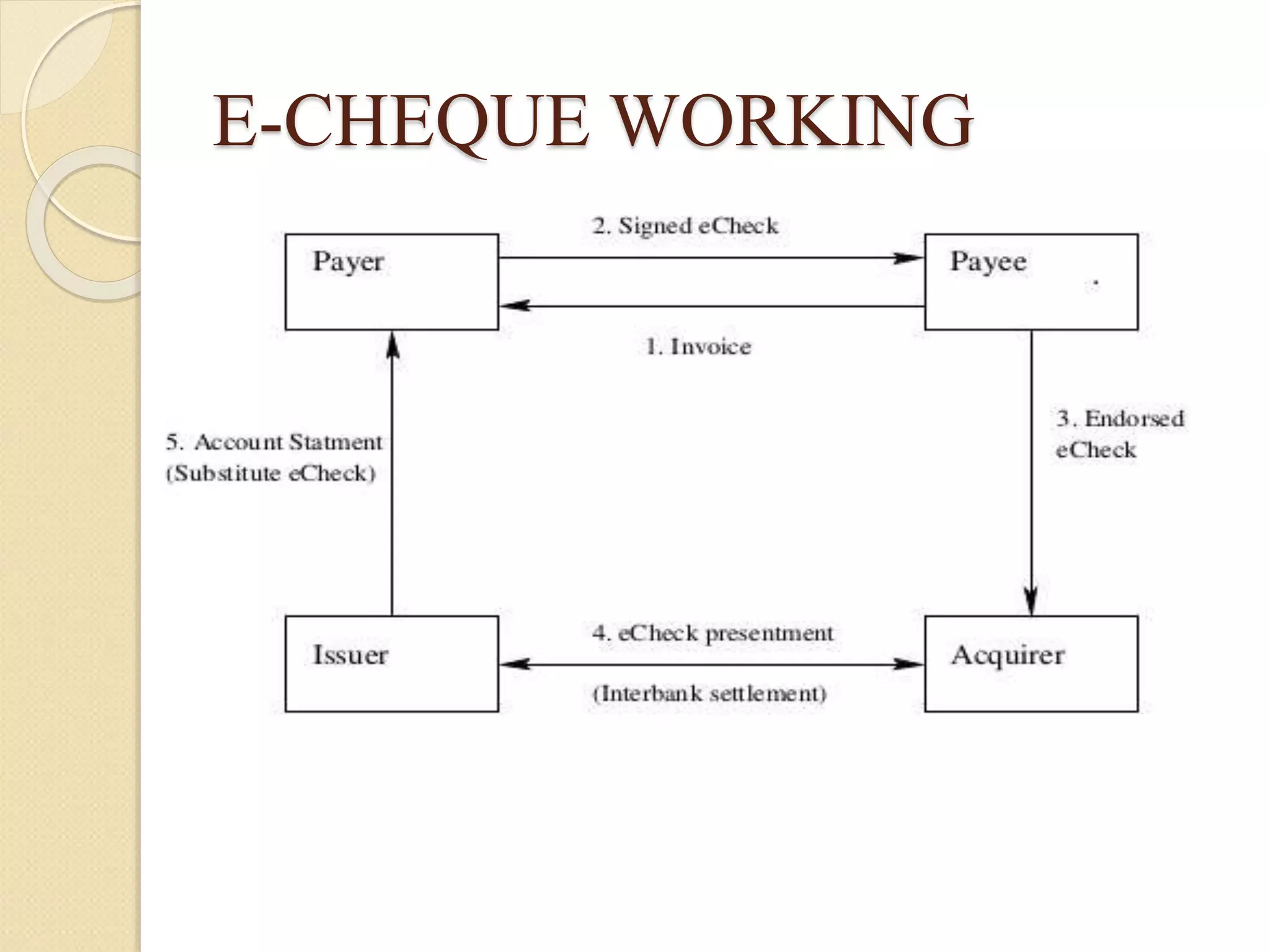
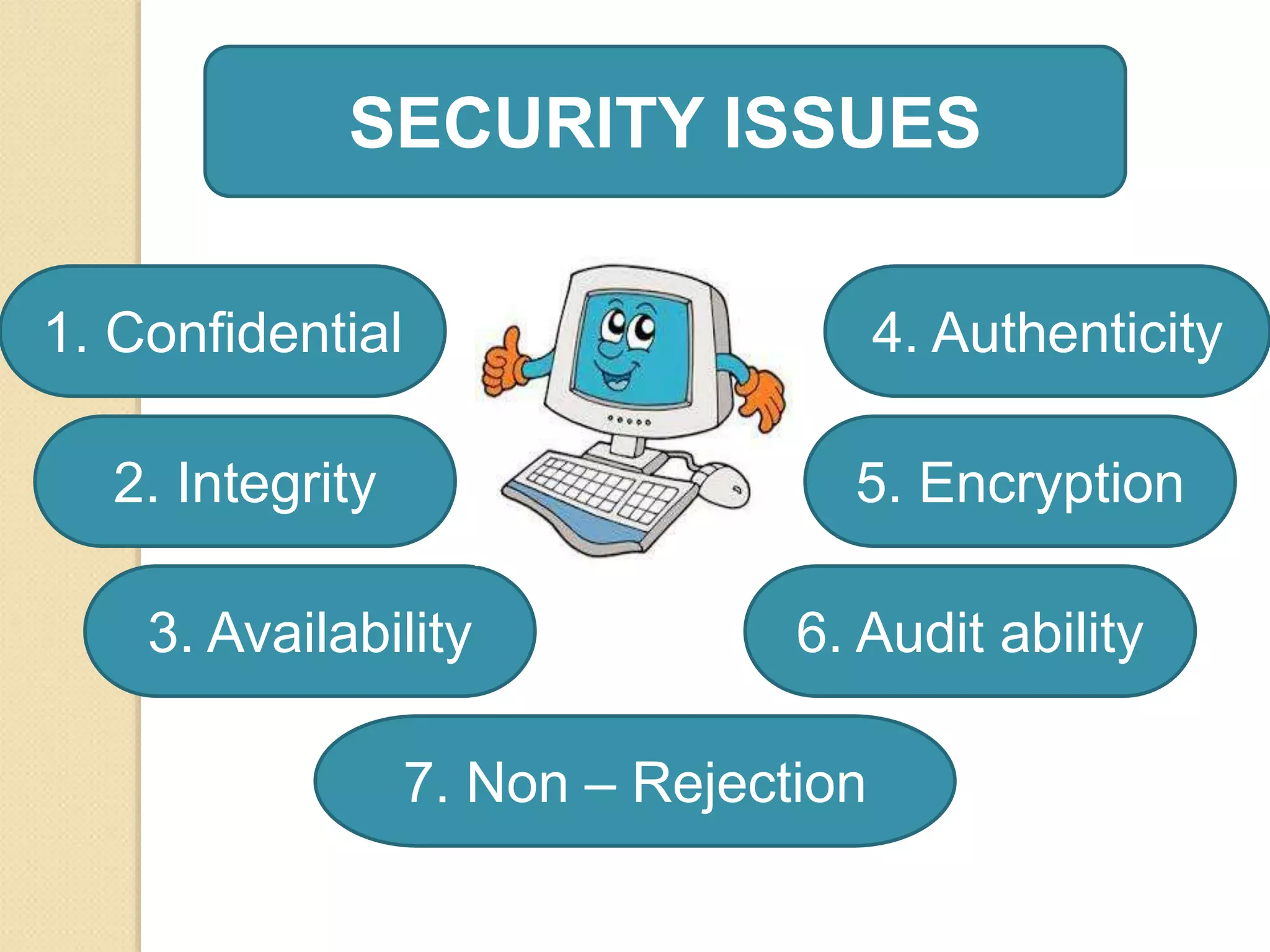
Electronic payment systems allow for online financial transactions between buyers and sellers. They use digital payment methods like encrypted credit/debit cards, e-checks, or digital cash backed by financial institutions. The main types of electronic payments discussed are credit cards, debit cards, smart cards, e-money, and electronic funds transfer. Electronic payments provide benefits like increased customer base, improved cash flow, reduced costs, and enhanced customer service for businesses. However, they also present risks like stolen credentials, fraudulent transactions, and insufficient customer funds that must be addressed.