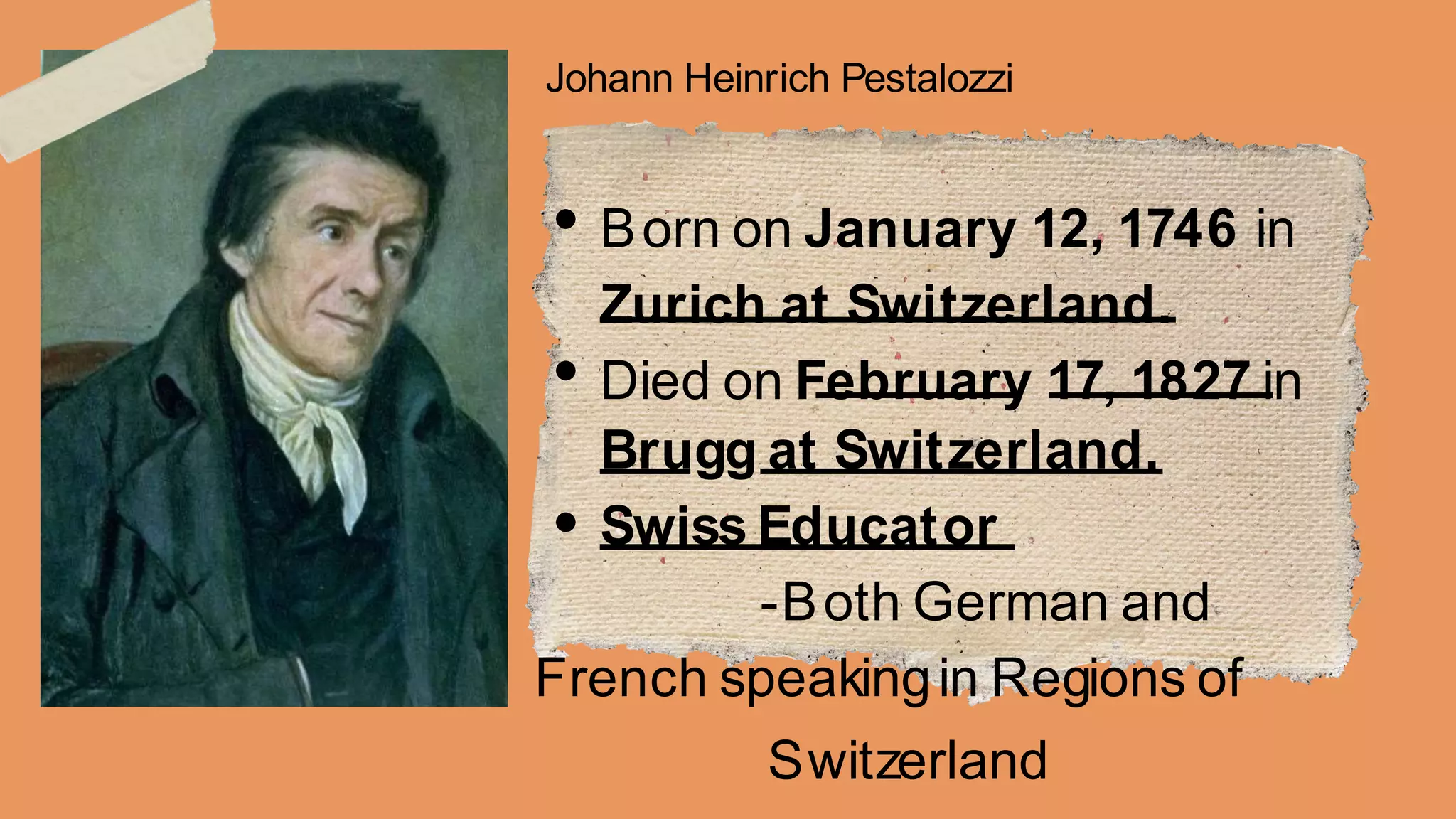
The document discusses the major proponents of early childhood philosophy including Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi, Friedrich Froebel, Maria Montessori, and Rudolf Steiner. It provides biographical information and outlines the key methodologies and principles of each proponent. Pestalozzi emphasized sensory learning and a nurturing environment. Froebel founded kindergarten and believed in learning through play and gifts. Montessori developed her method based on movement, choice, interest and order. Steiner advocated for Waldorf education based on stages of child development.