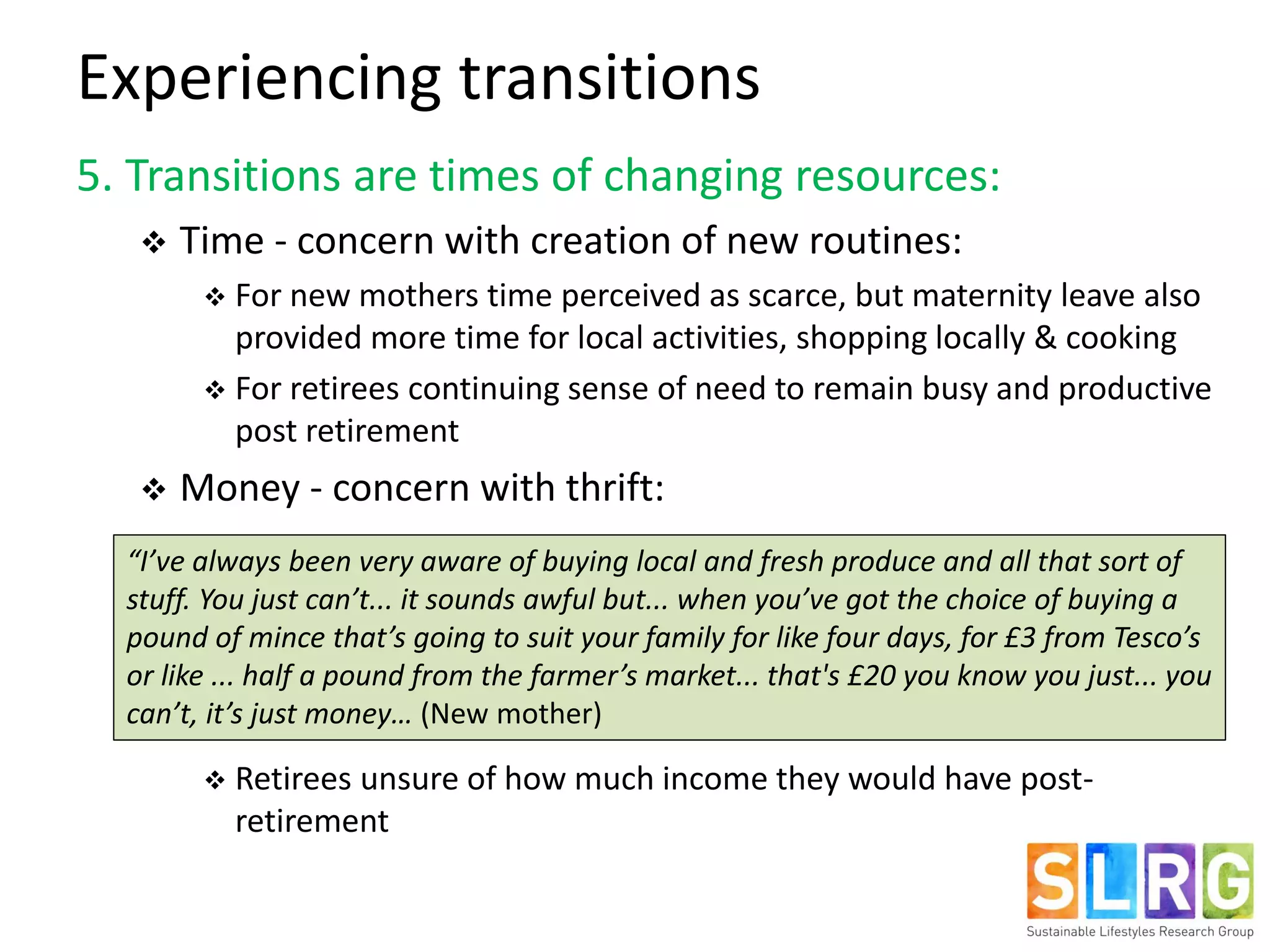
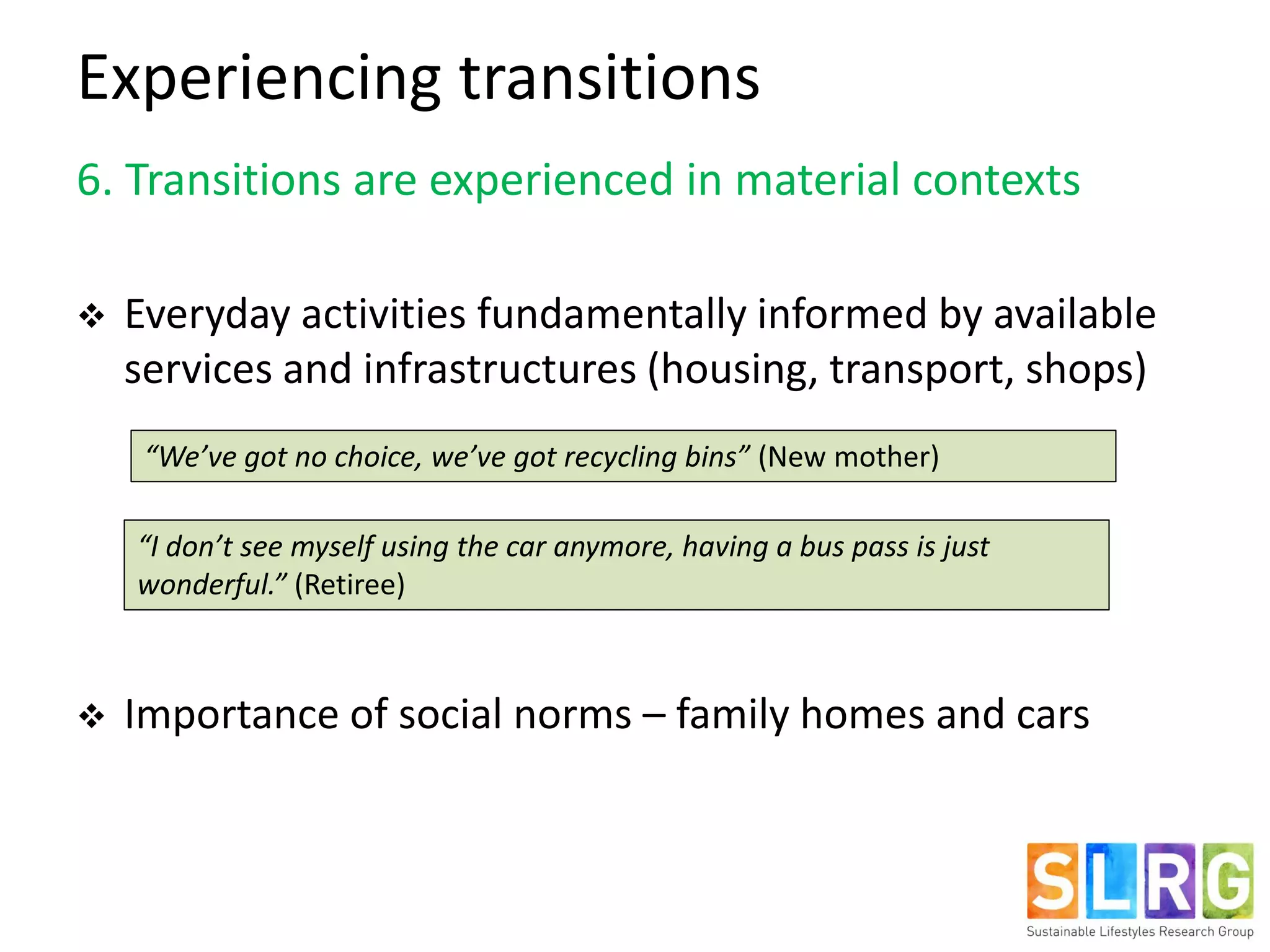
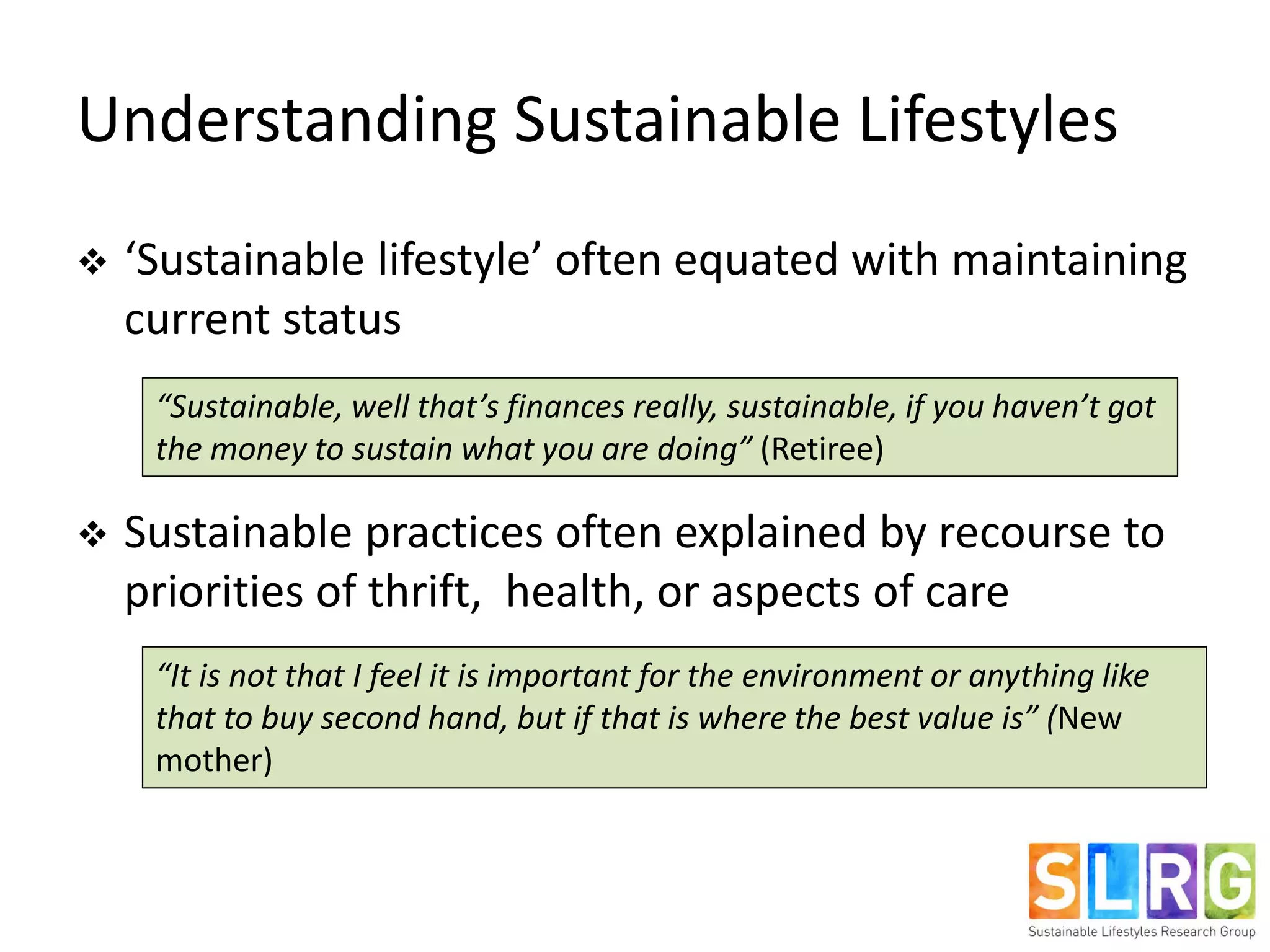
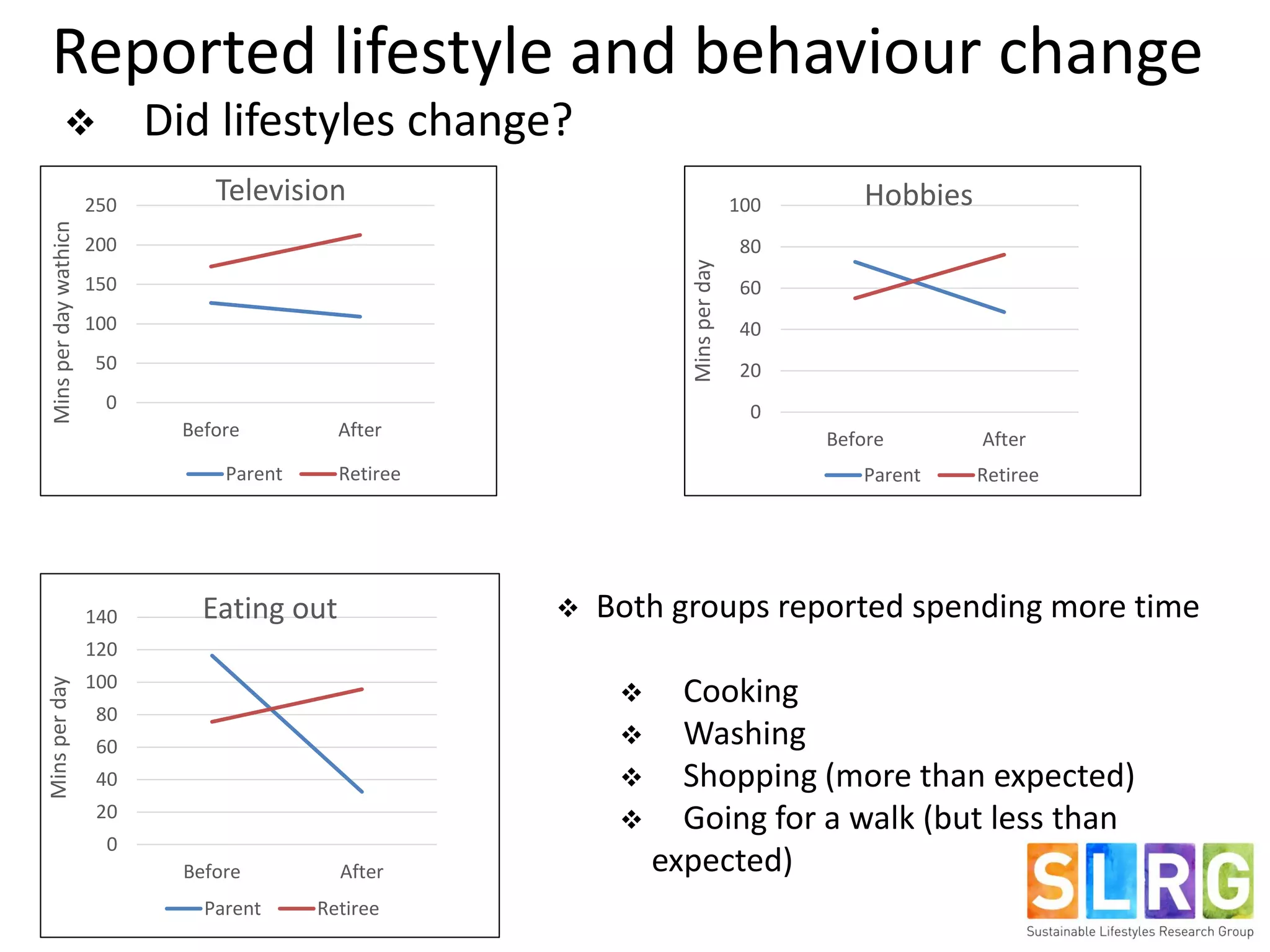
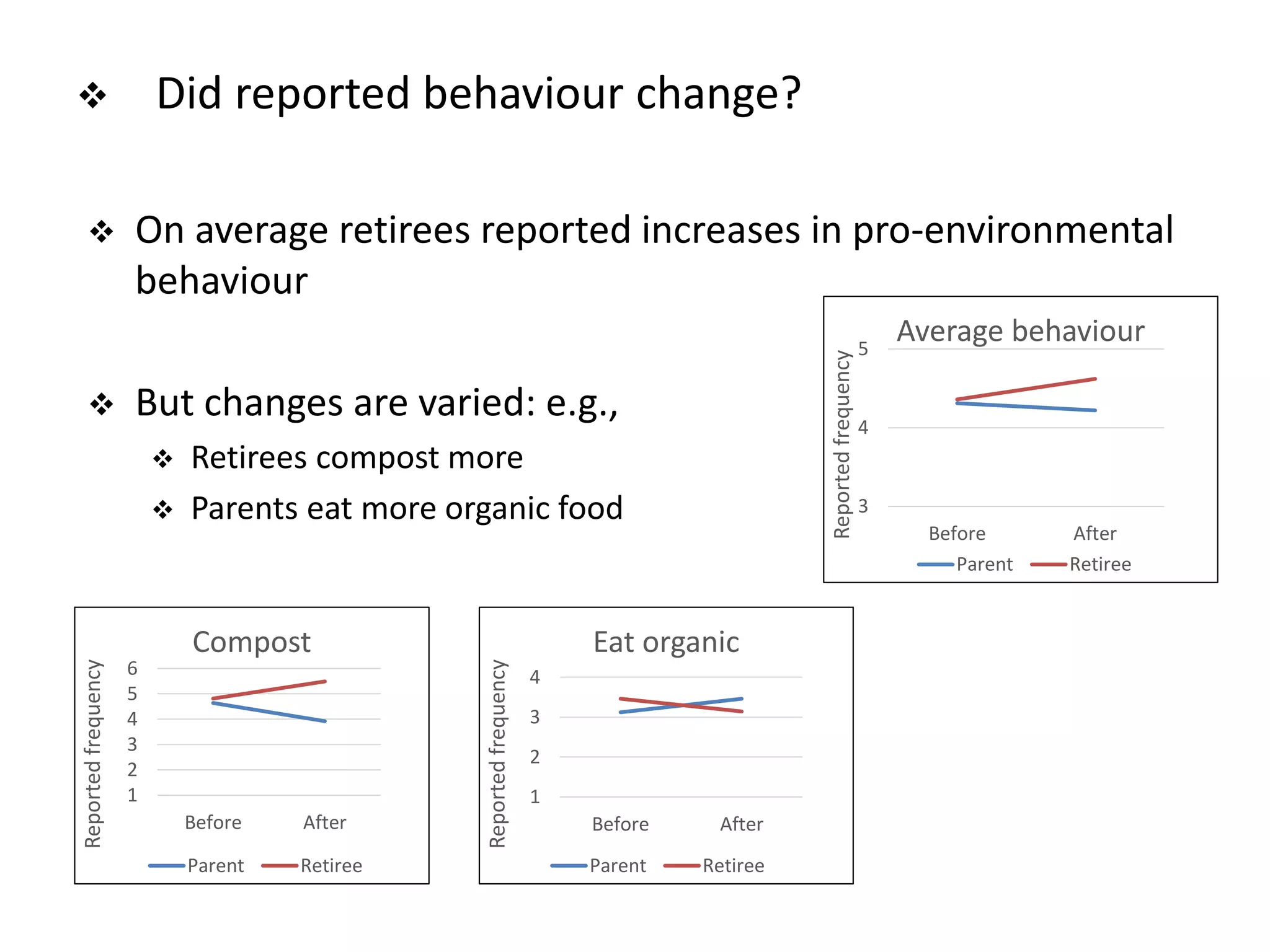
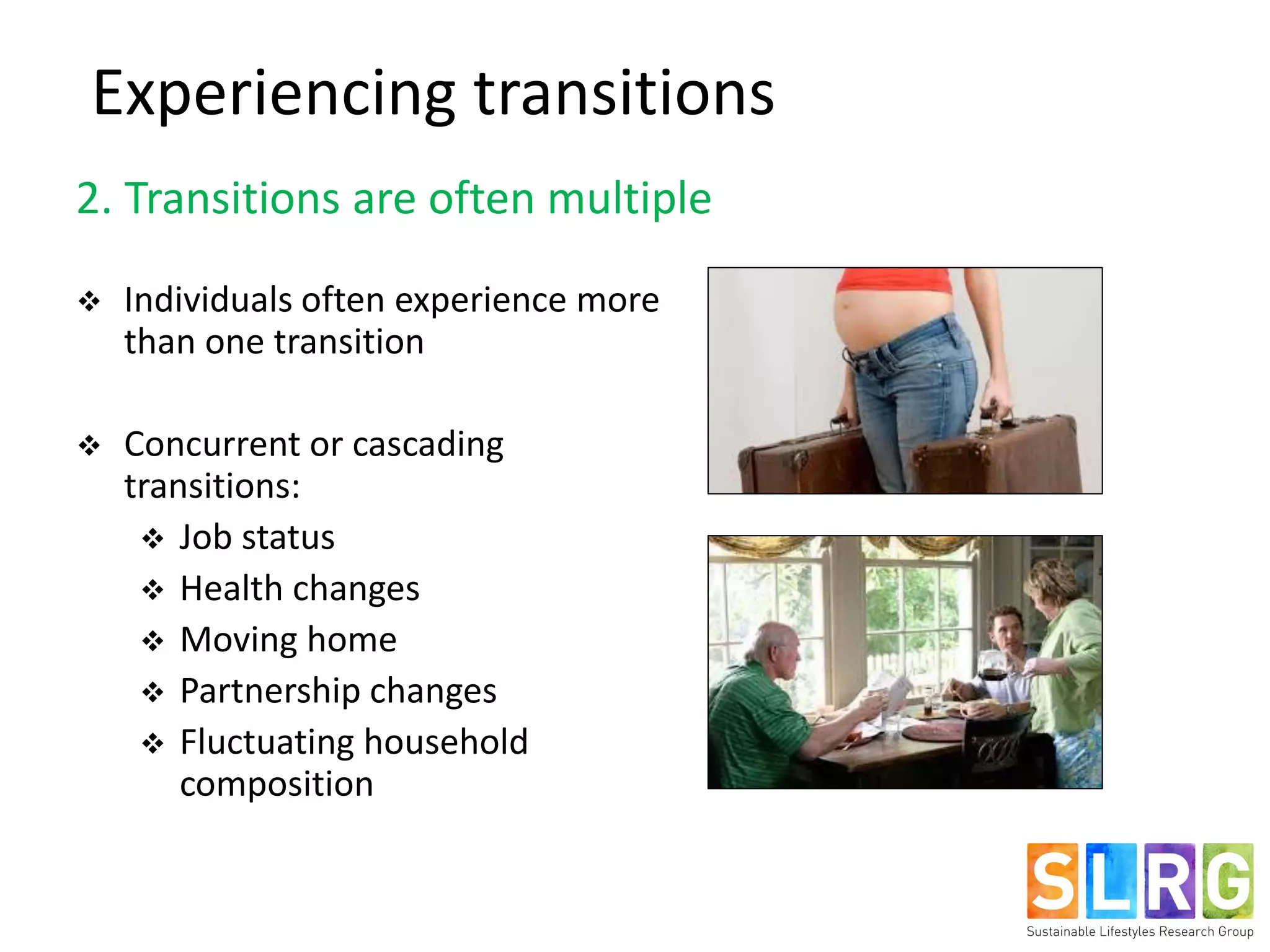
The document examines lifestyle changes during significant transitions, specifically focusing on new parents and retirees, through a longitudinal study involving interviews and journals. It reveals that transitions are complex processes that can impact household dynamics, identity, and consumption behaviors, often highlighting challenges in maintaining sustainable lifestyles. Results indicate that while some individuals reported increased pro-environmental behaviors, motivations were primarily driven by convenience and economic factors rather than environmental concerns.


![3. Transitions are experienced by households
‘Individual’ transitions affect other family members
Household negotiation of changes in everyday consumption
Change or stability in individual consumption practices often
reflect others’ preferences or needs
So how often does your husband eat meat?
R: “Probably only a couple of times a week actually. We were talking about
it to someone and he was saying before he used to eat meat every day and …
he does eat it a lot less” (New mother)
Experiencing transitions
“I’ll put a jumper on whereas [wife] will turn the central heating on… if she is
cold I will let her put the heating on” (Retiree)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elicit-140618035154-phpapp02/75/ELiCiT-Exploring-lifestyle-changes-in-transition-7-2048.jpg)
![4. Transitions are a time of reflection on identity and
priorities
Becoming a ‘good’ parent overrides everything else
Contested identities for retirees – ‘it’s time for me’ versus
caring for grandchildren or other relatives
Importance of family relationships
Experiencing transitions
“Every waking thought is her really and now we’re a family it’s changed all
sorts of things.” (New mother)
“I feel that I’ve done my bit and, …yeah, before it [work] kills me or you
know before I'm too old to do anything else. Yeah, no I actually feel now I
deserve it [retirement]” (Retiree)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elicit-140618035154-phpapp02/75/ELiCiT-Exploring-lifestyle-changes-in-transition-8-2048.jpg)