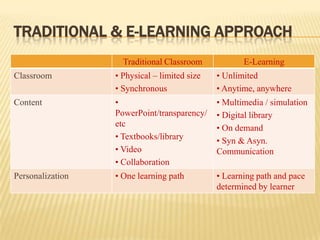
E-learning refers to the use of electronic media and information and communication technologies to enable learning. It allows people to learn anytime and anywhere. There are two main types of e-learning - synchronous which occurs in real-time, and asynchronous which allows learners more flexibility in their schedule. E-learning delivery methods include online lectures, prerecorded videos, online courses, and collaborative tools like blogs and forums. Benefits include convenience, cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and the ability to learn at one's own pace. However, some learners may feel isolated or lack motivation without in-person interaction and instruction.