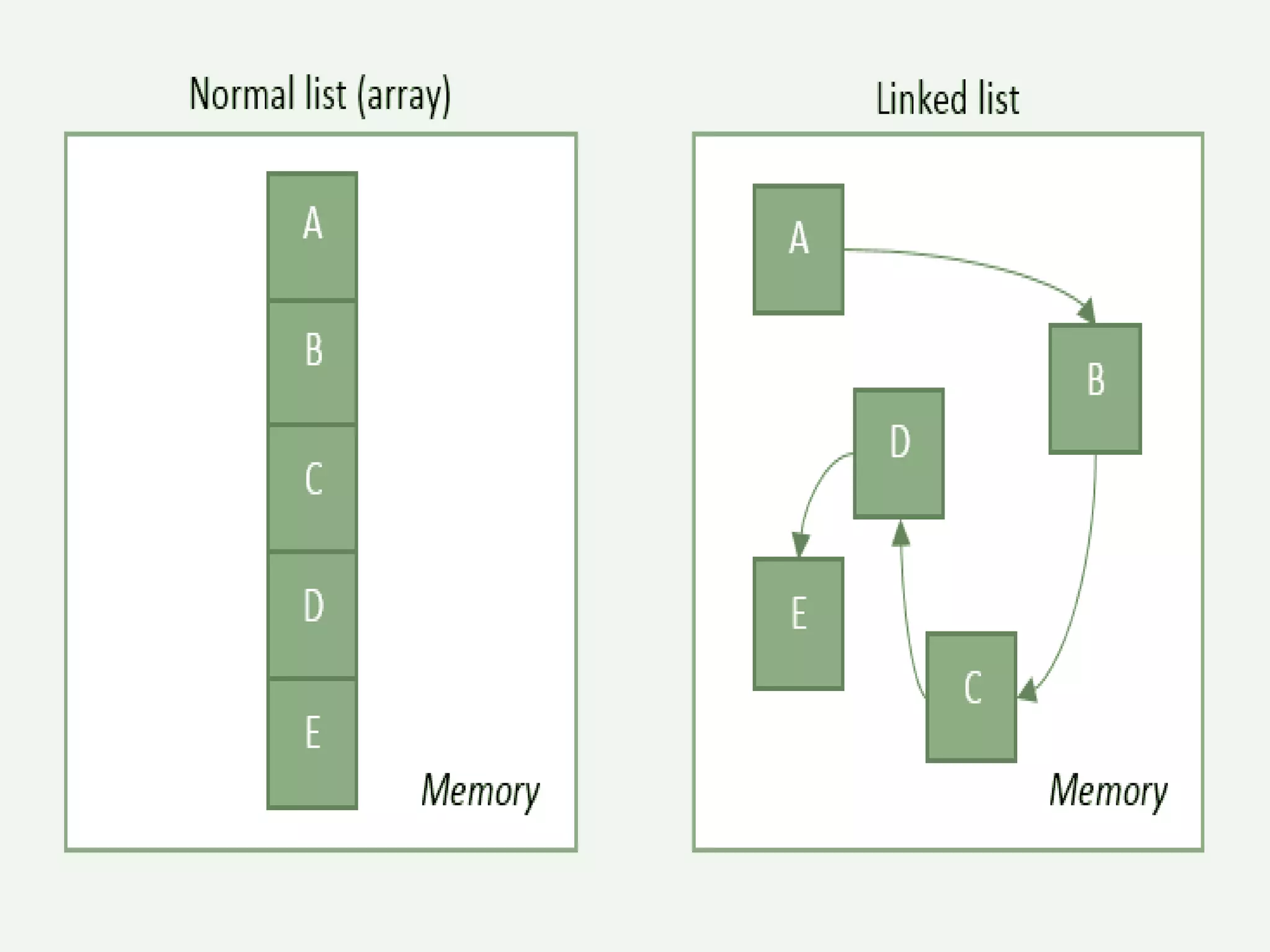
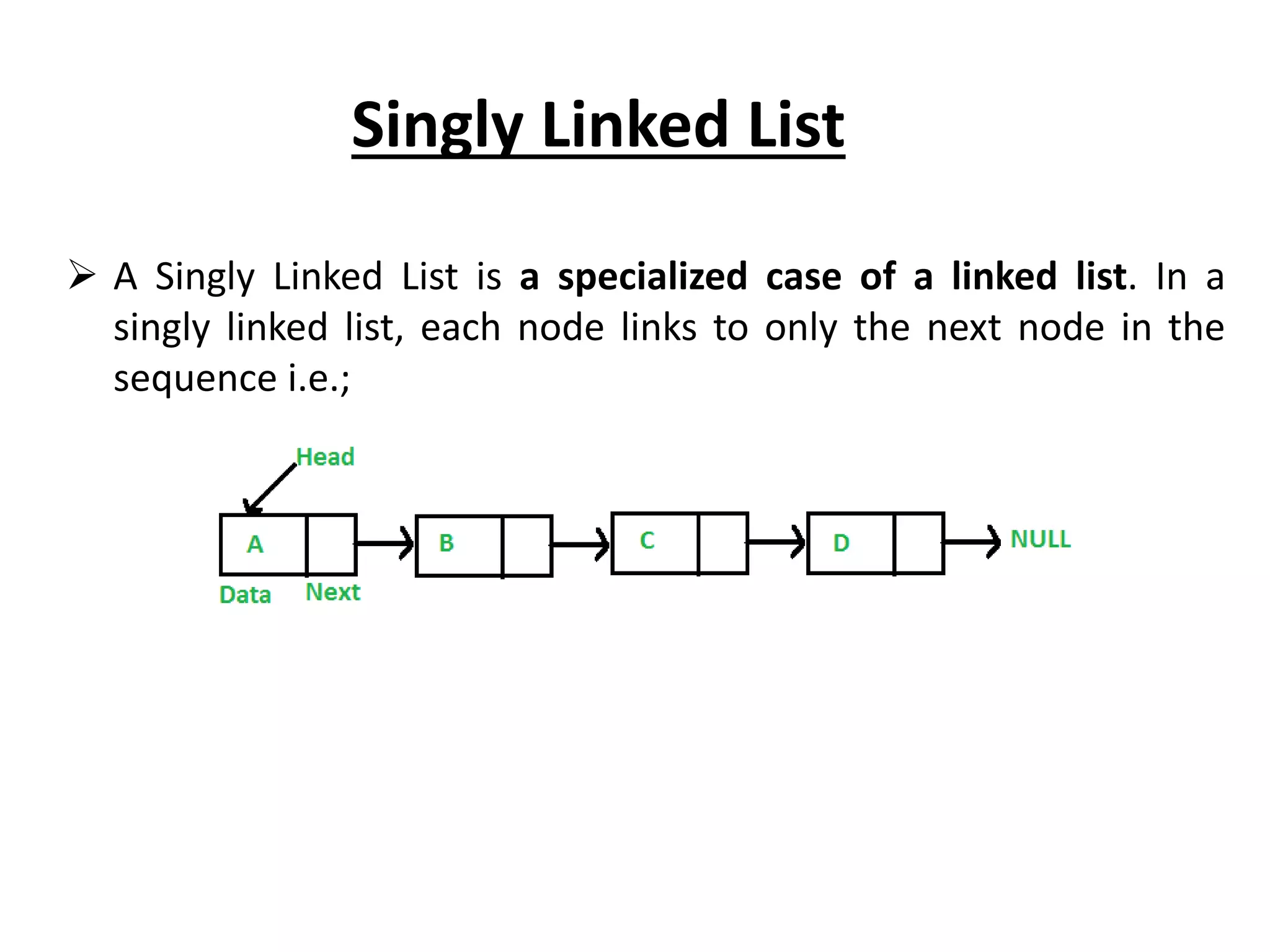
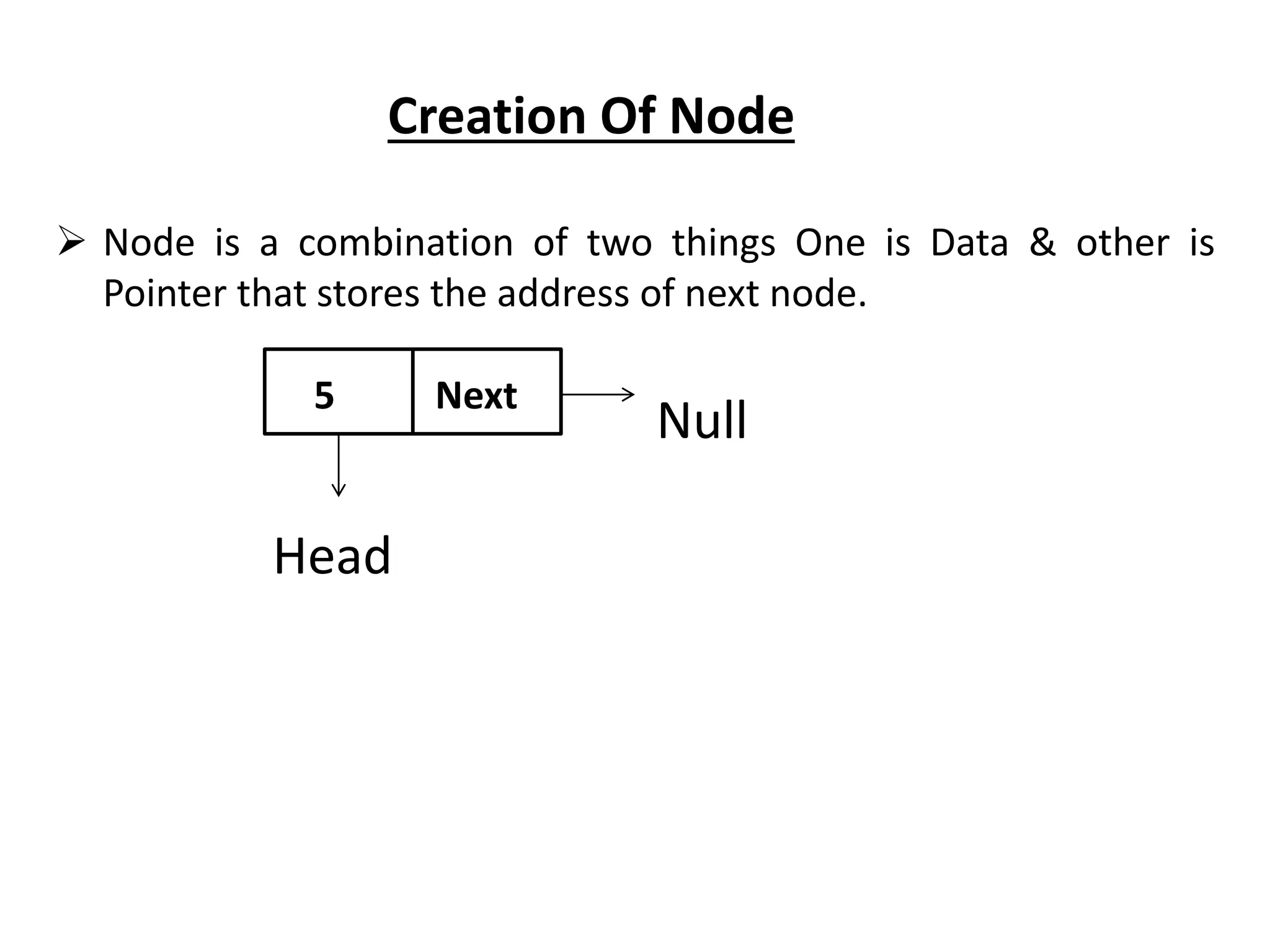
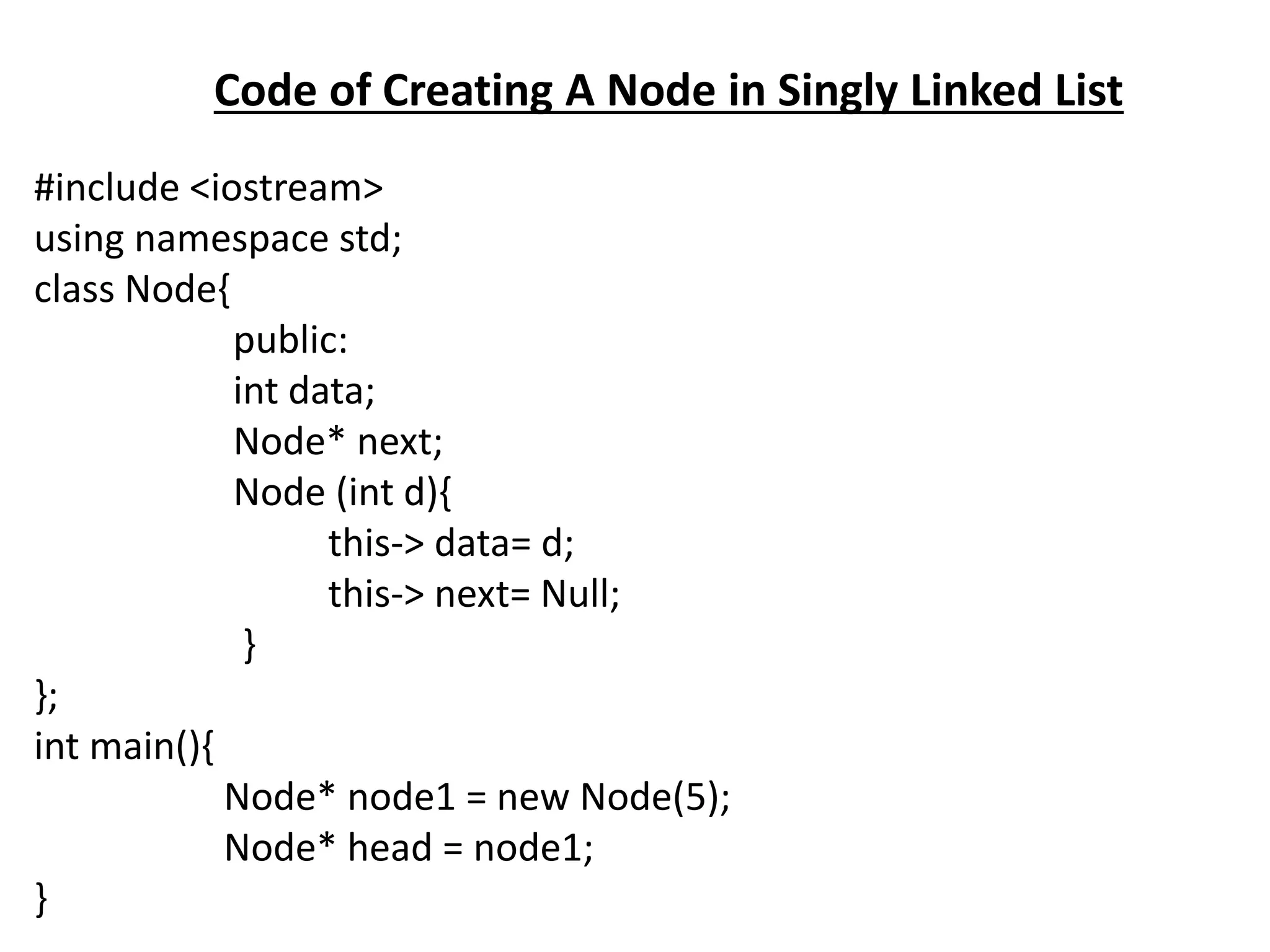
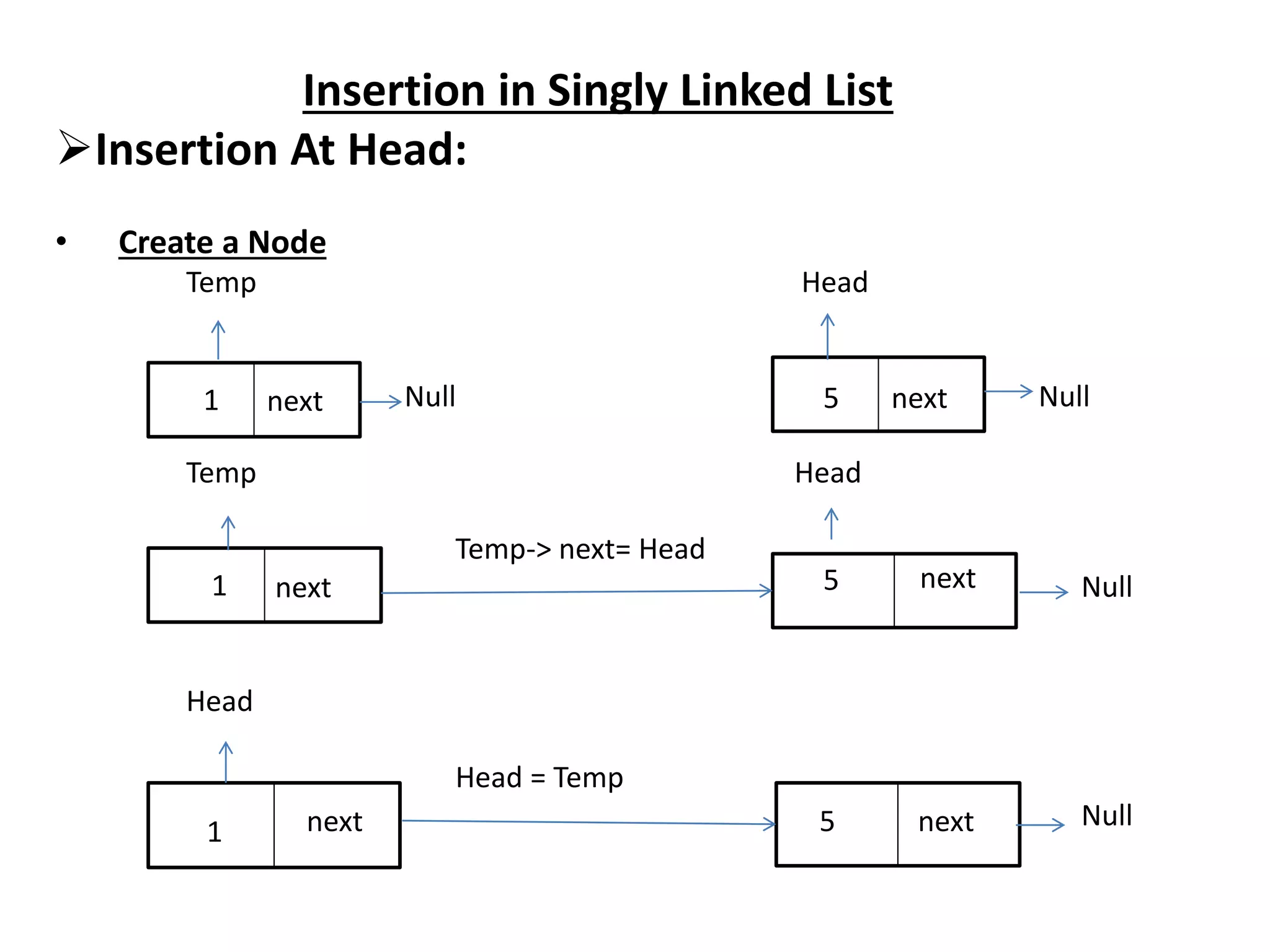
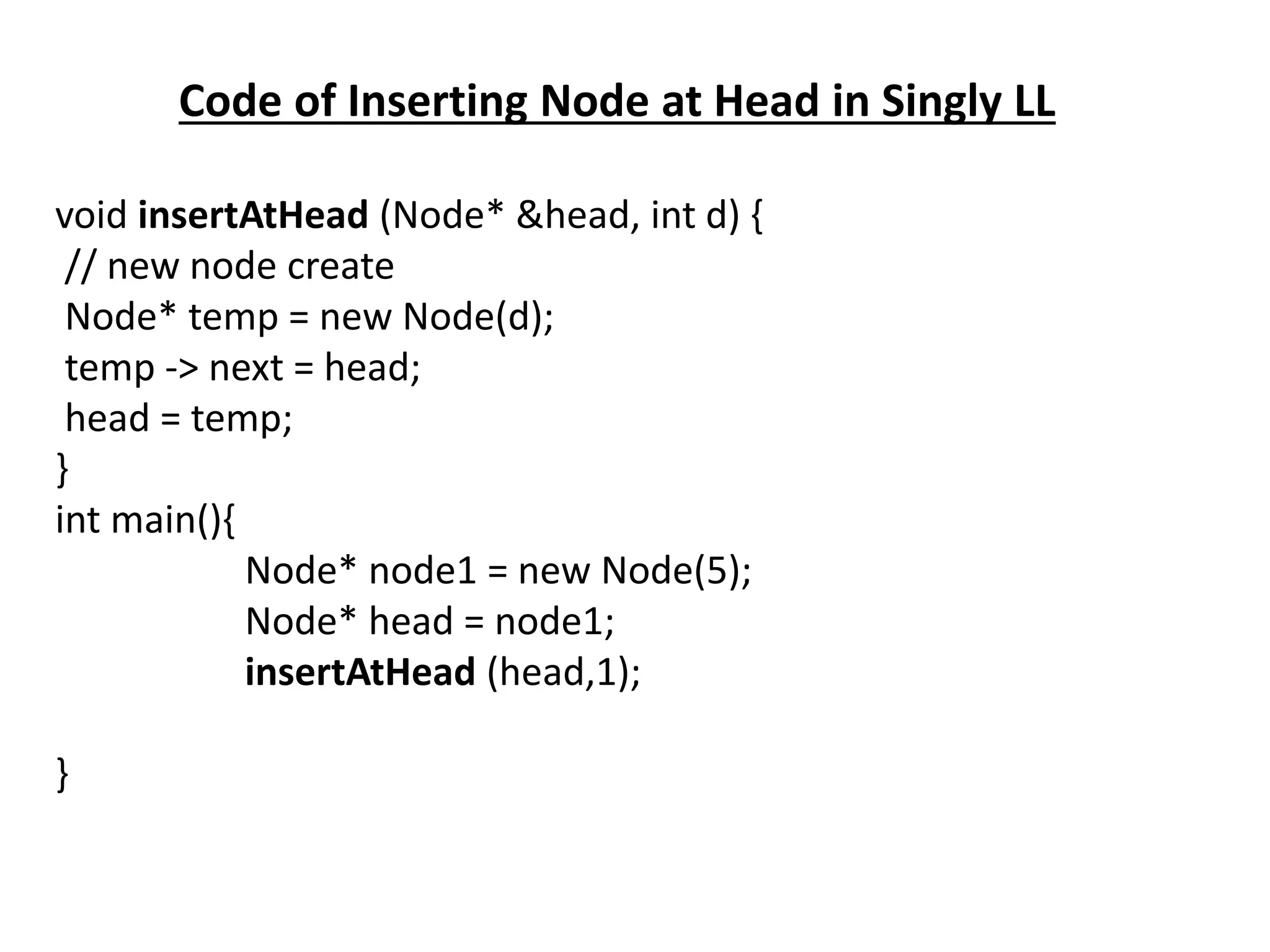
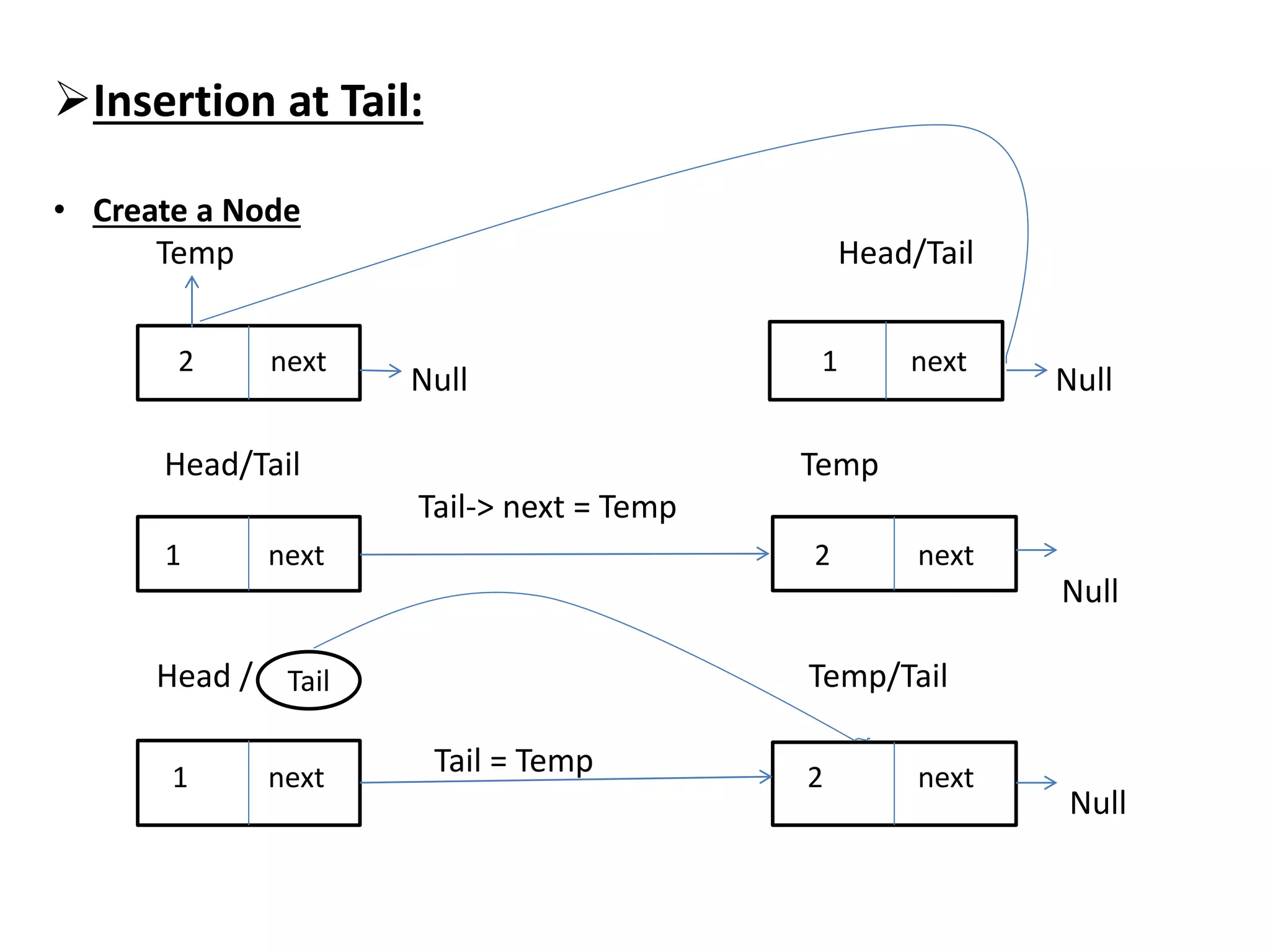
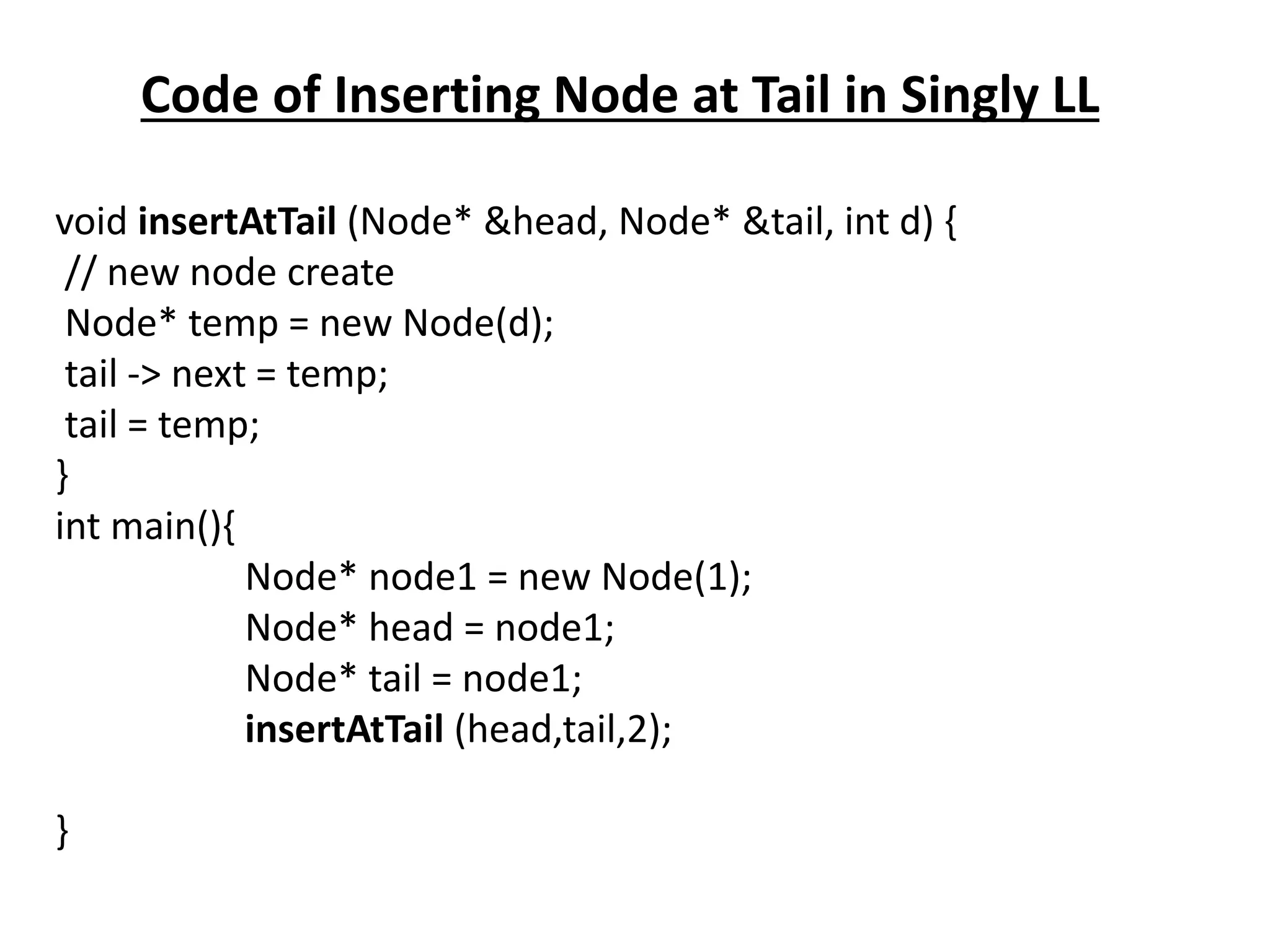
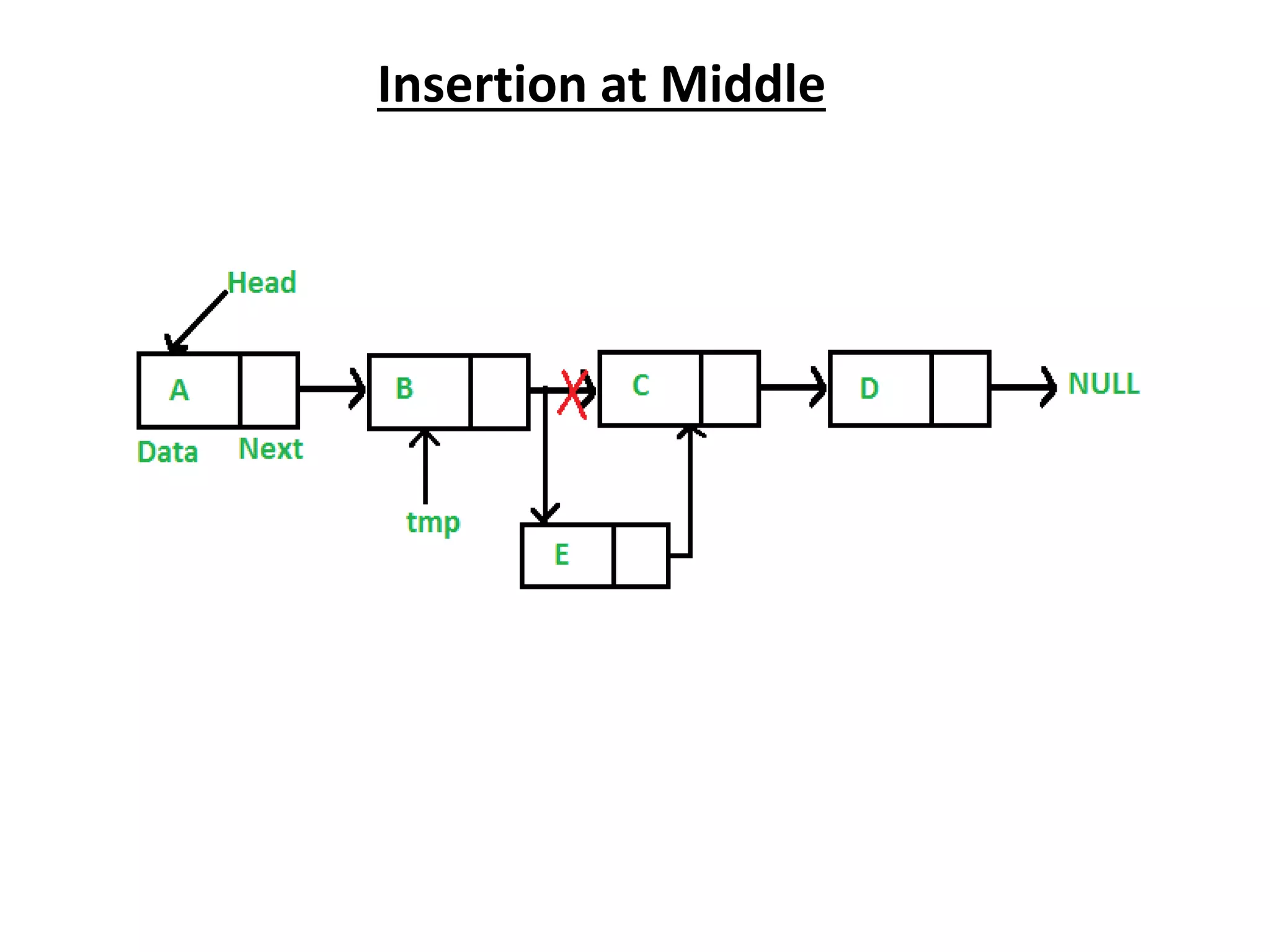
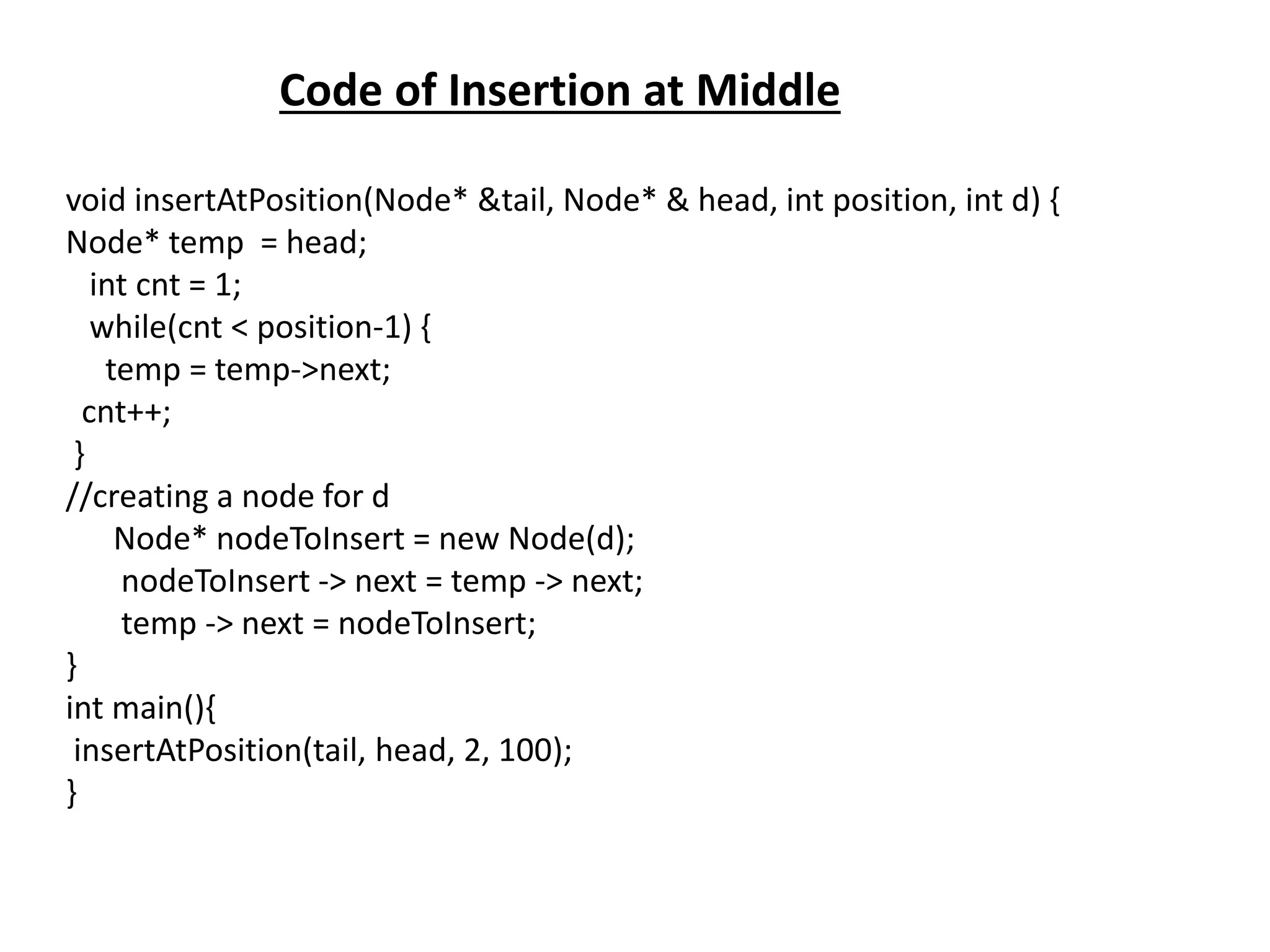
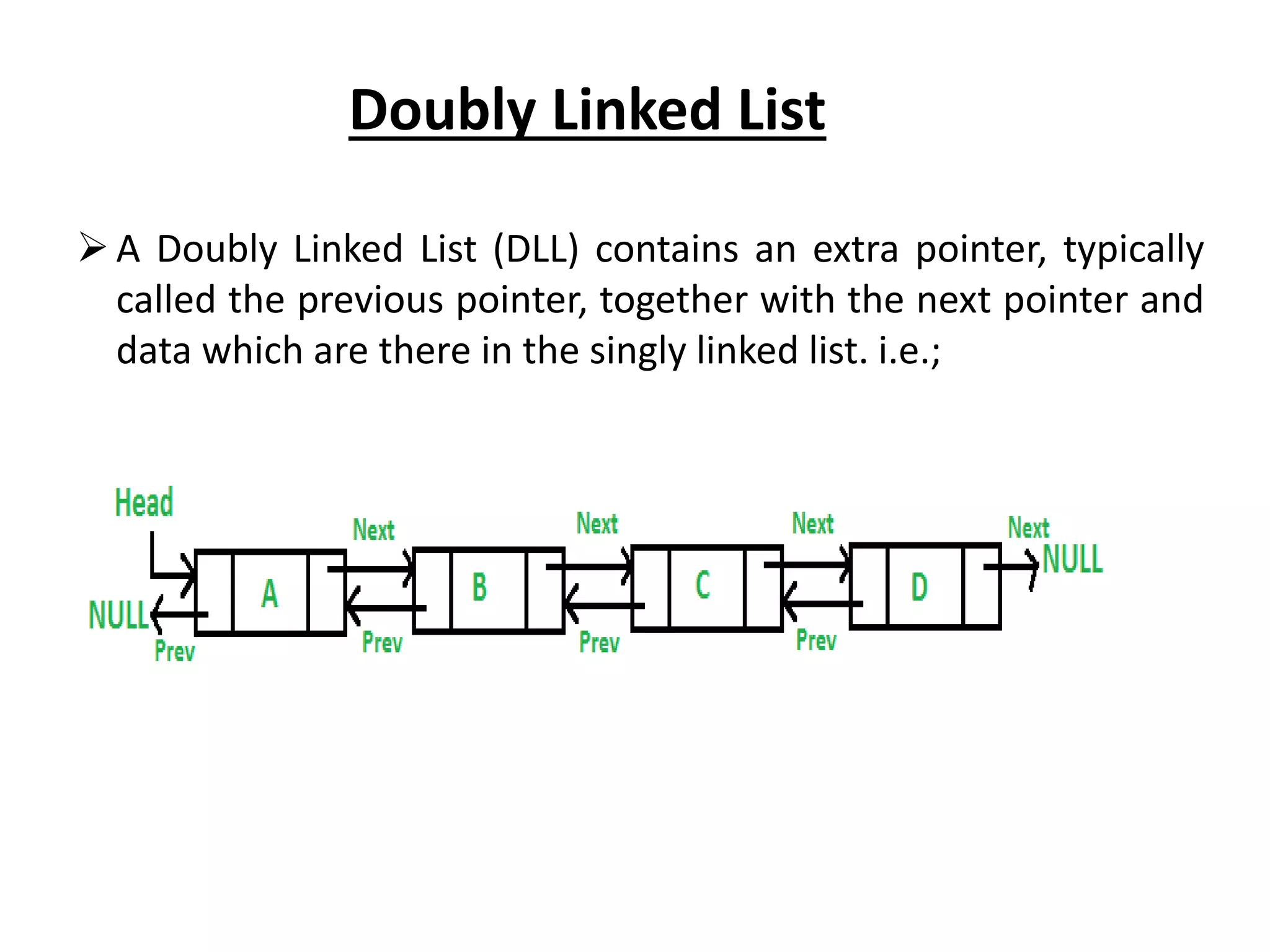
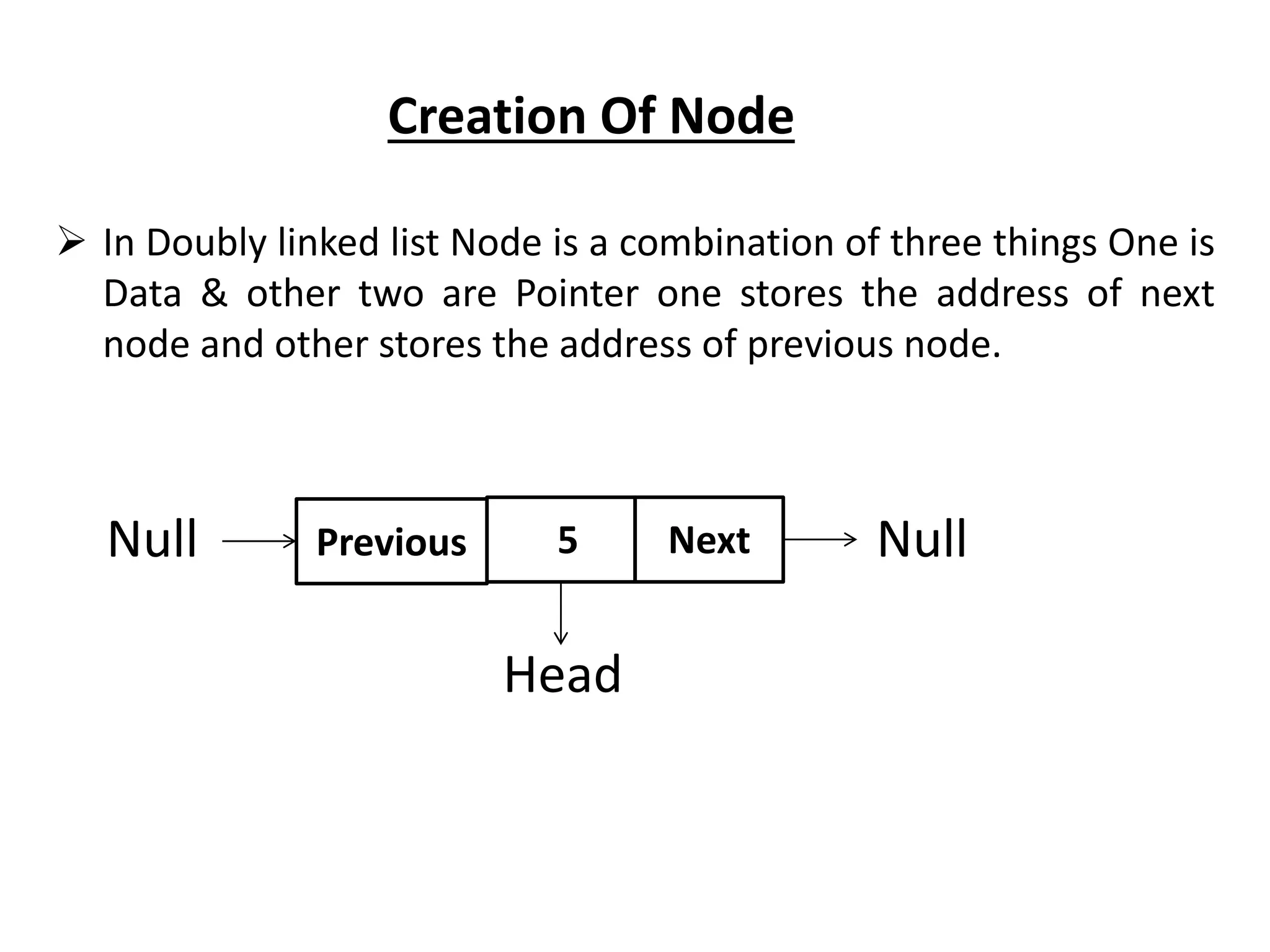
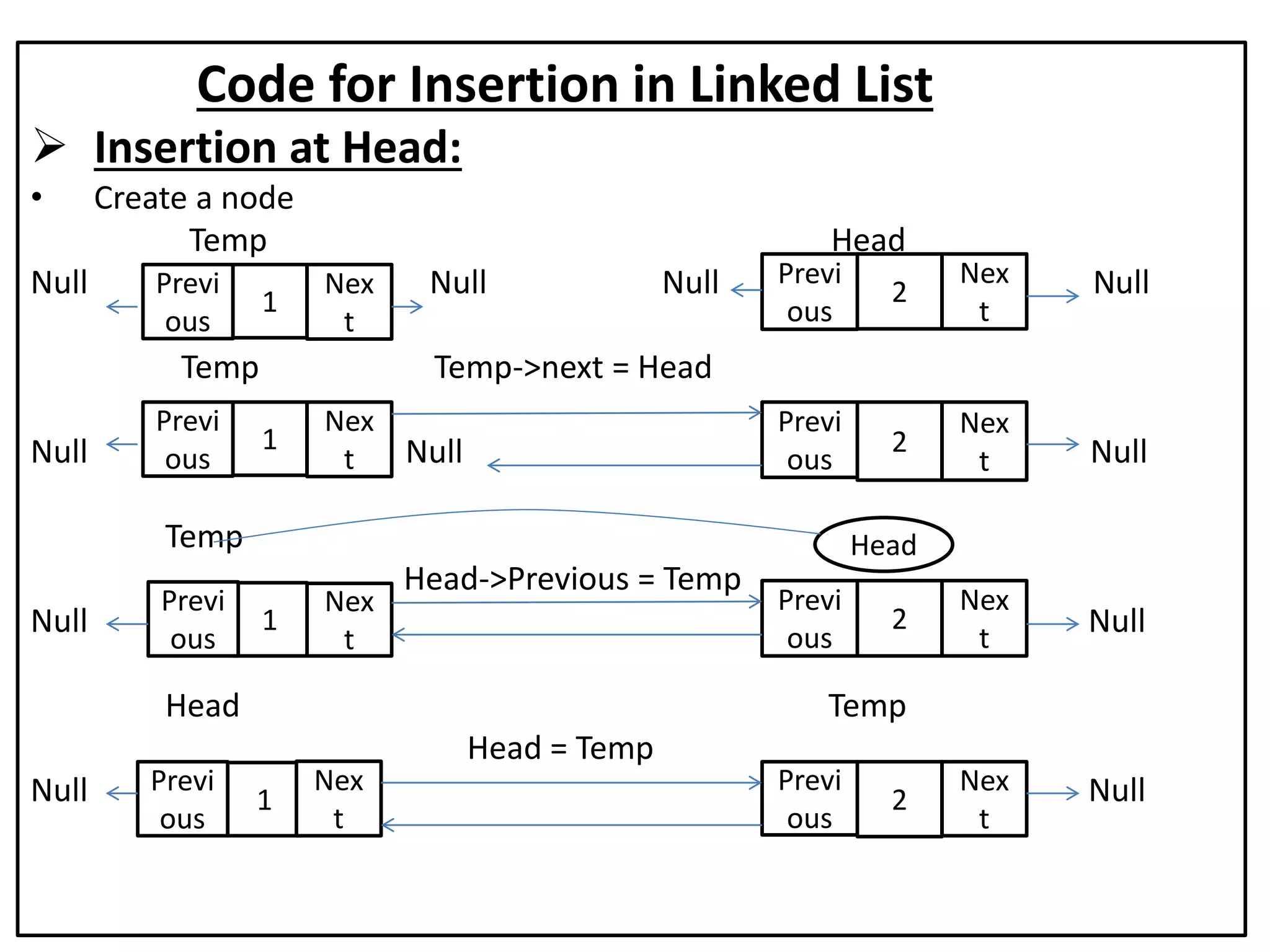
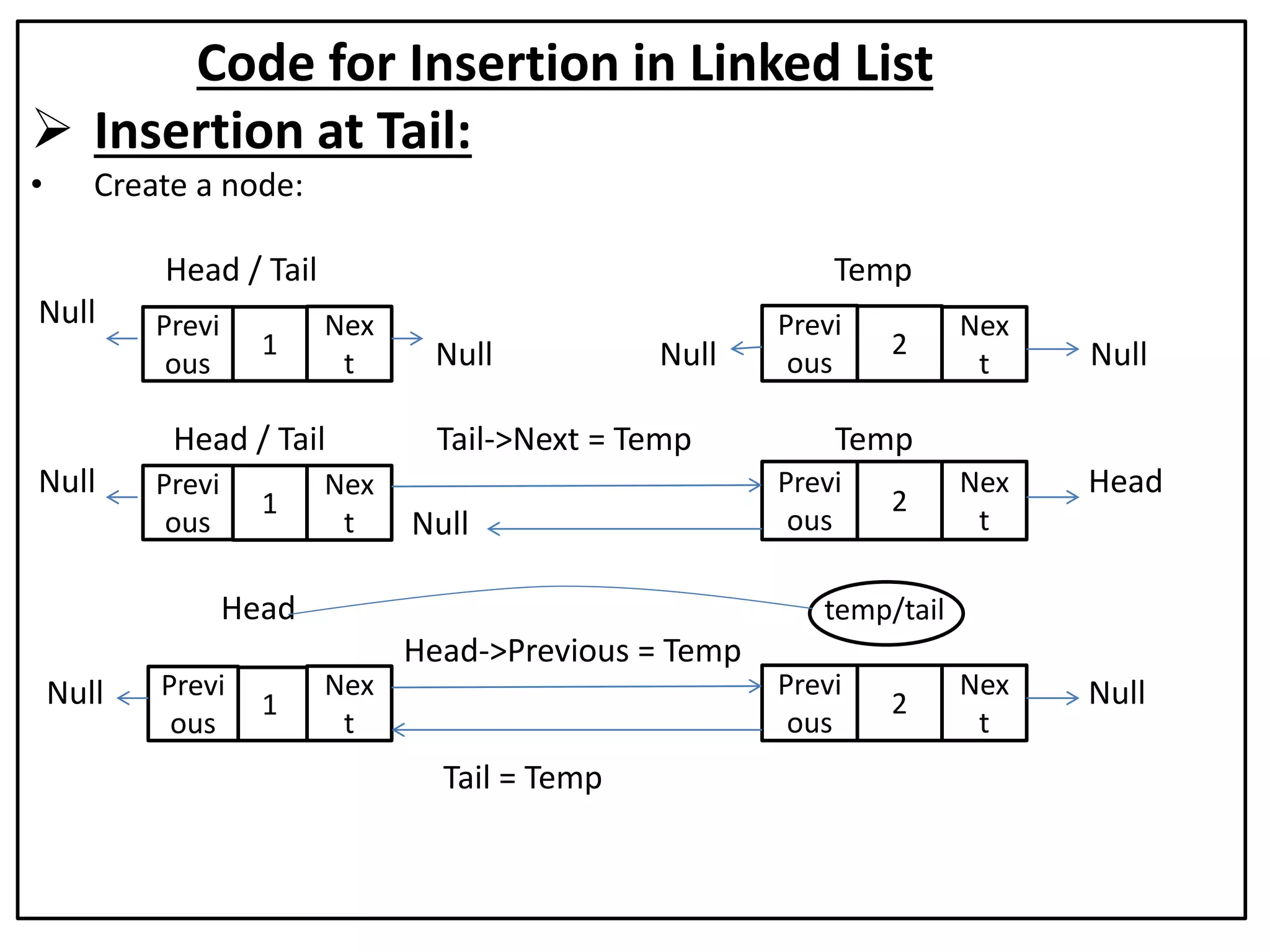
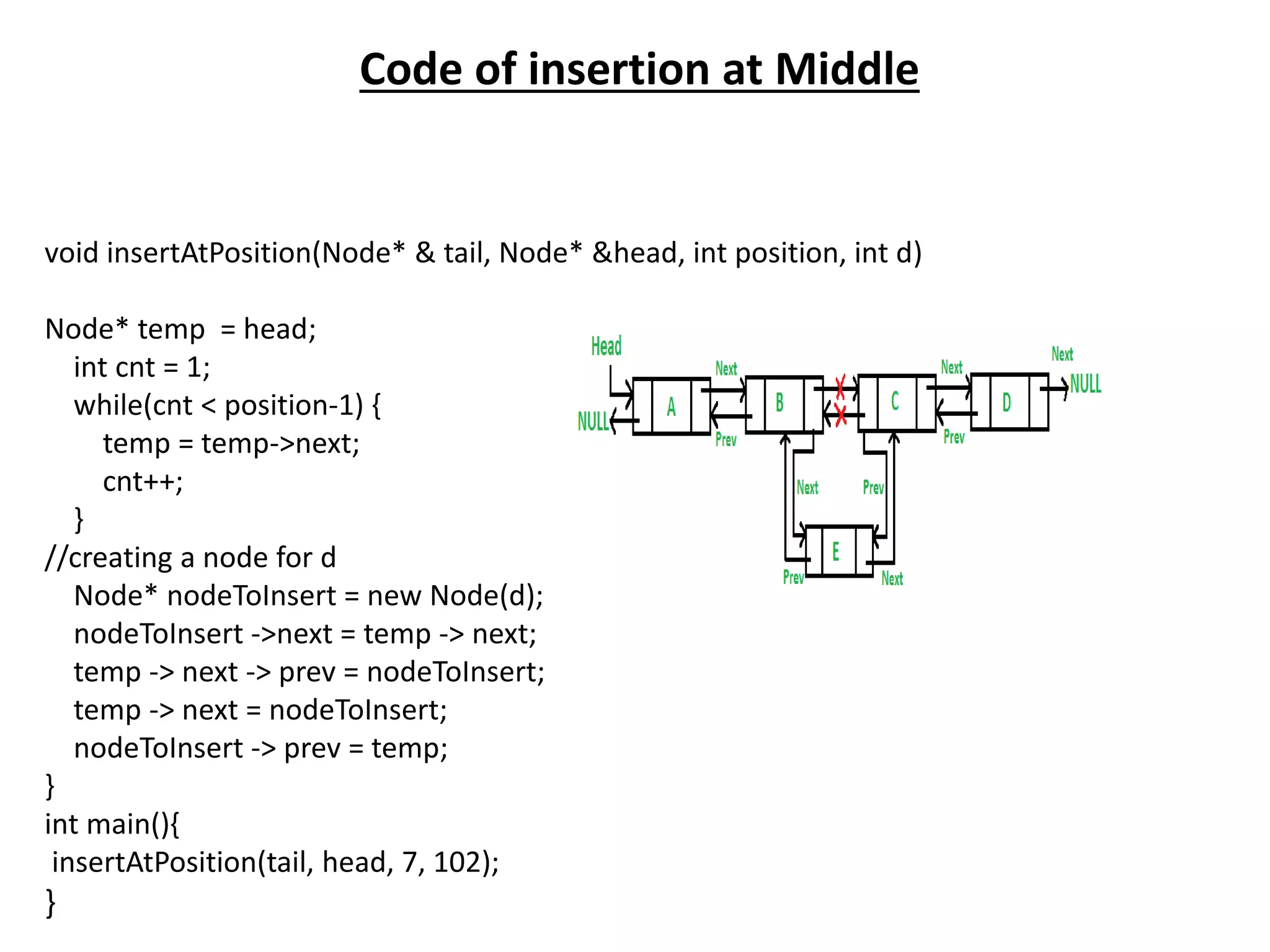
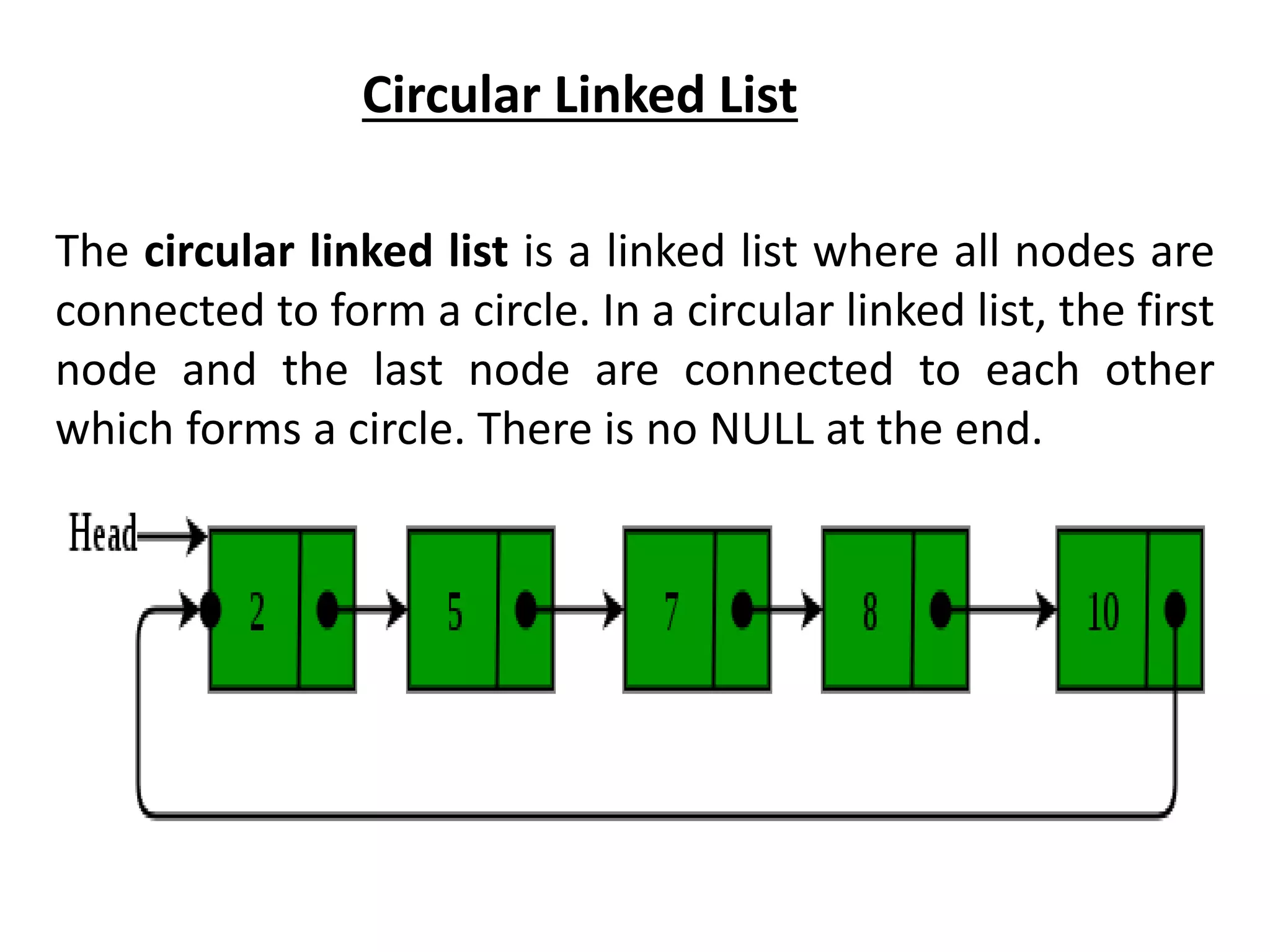
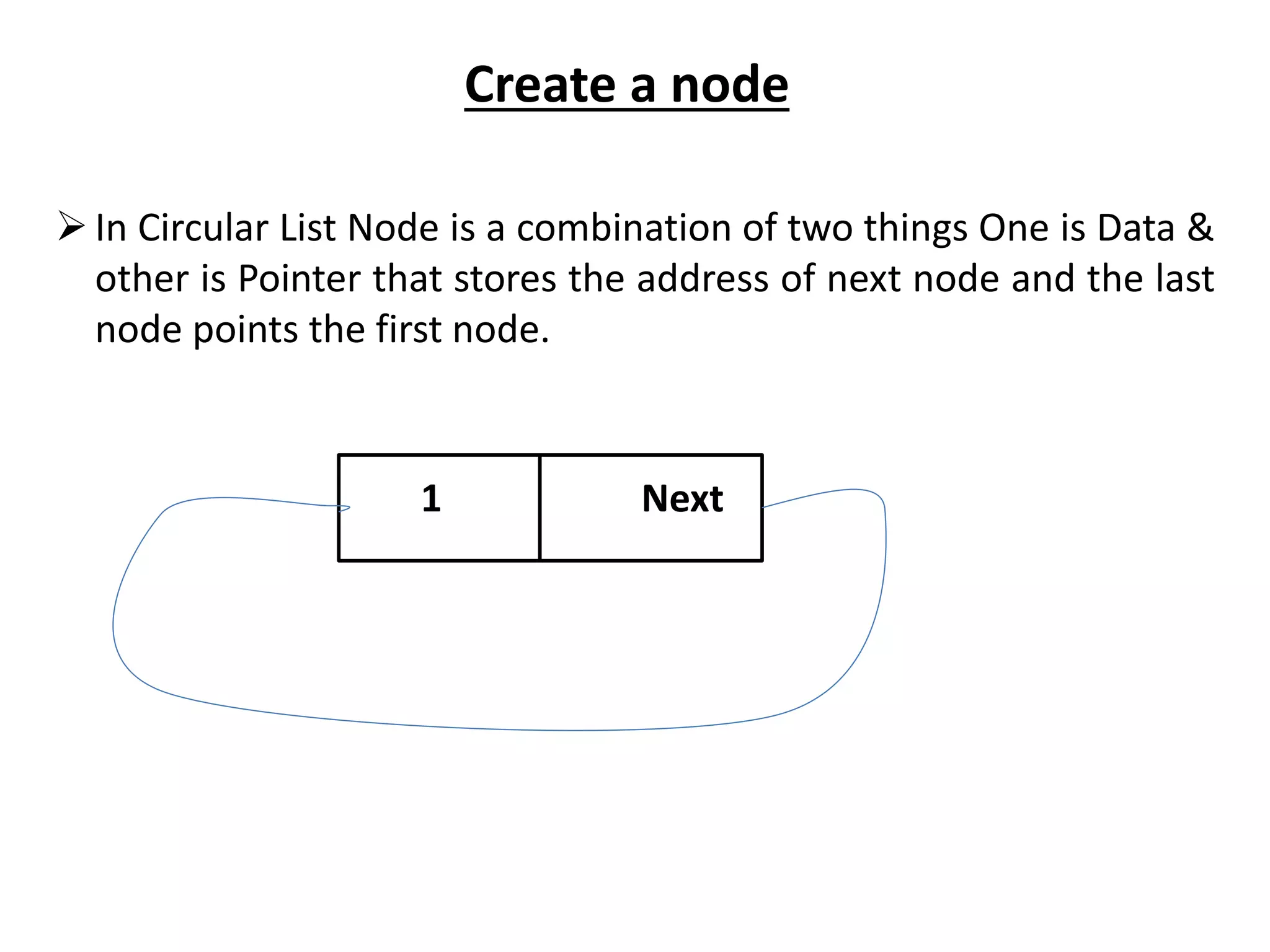
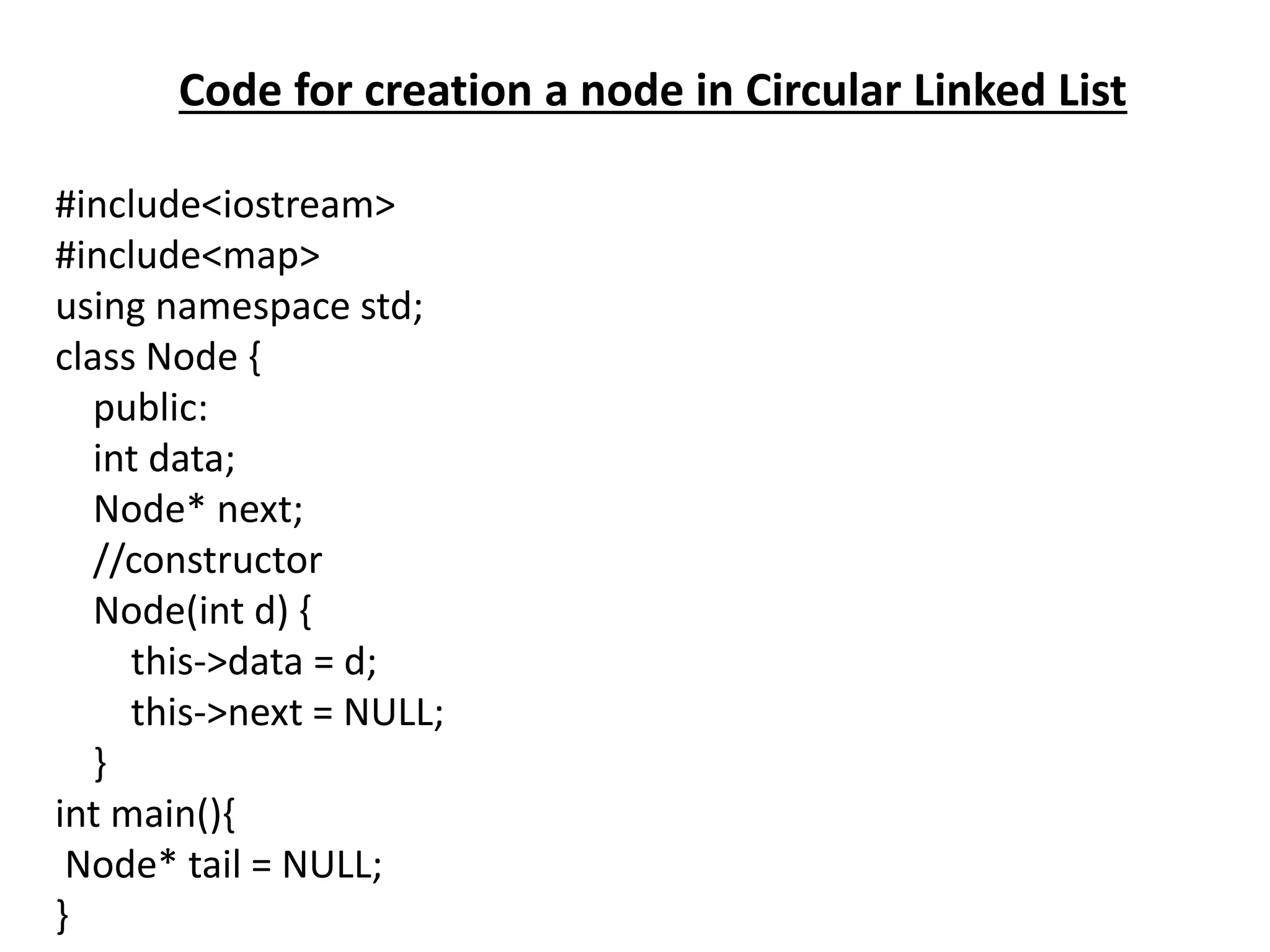
The document summarizes key concepts about linked lists including different types like singly linked lists, doubly linked lists, and circular linked lists. It provides code examples for creating nodes and performing operations like insertion, deletion, and traversal for each type of linked list. Specifically, it shows code for inserting nodes at the head, tail, and middle of singly, doubly, and circular linked lists. It also includes code for deleting nodes from singly, doubly, and circular linked lists.