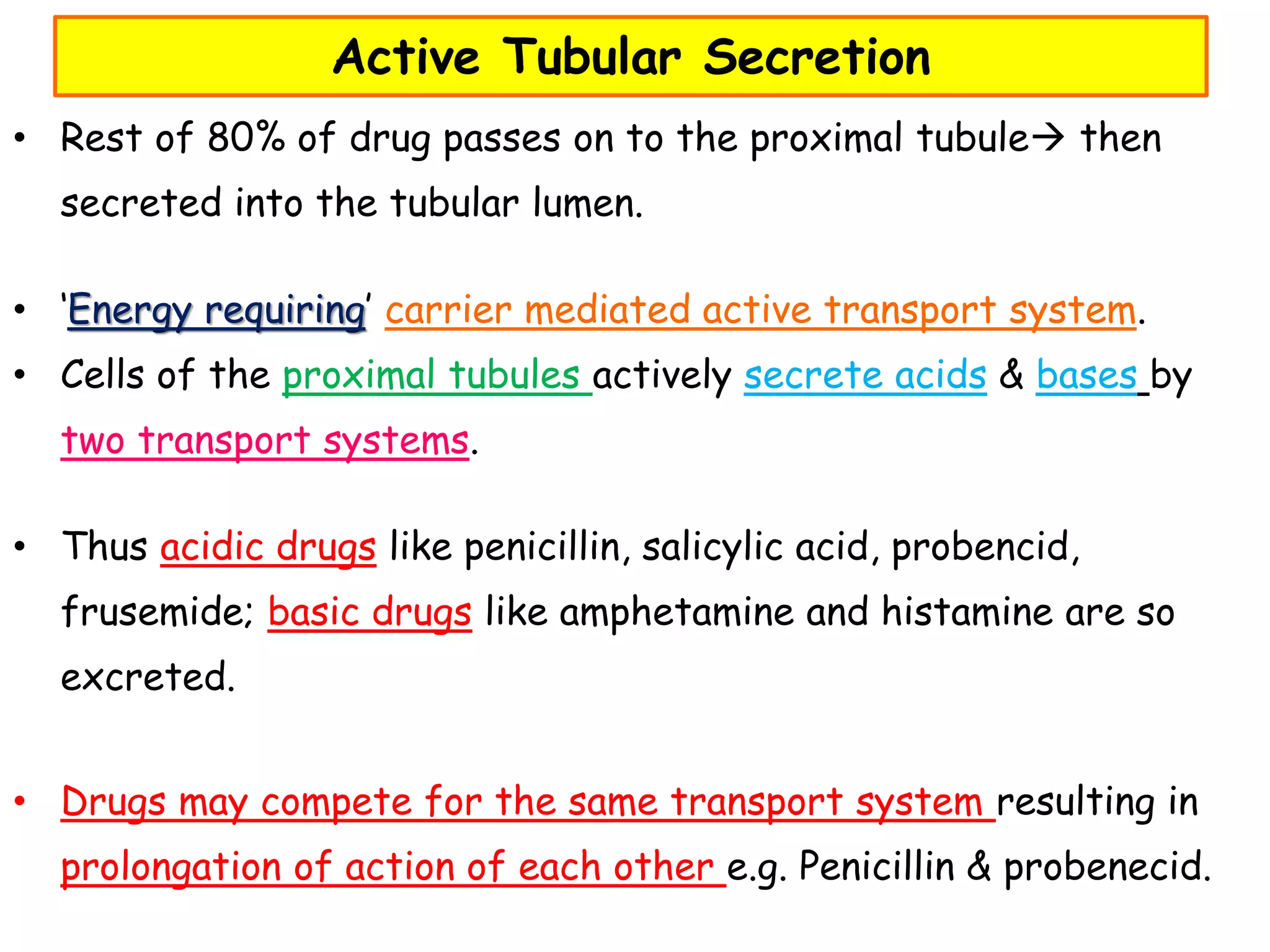
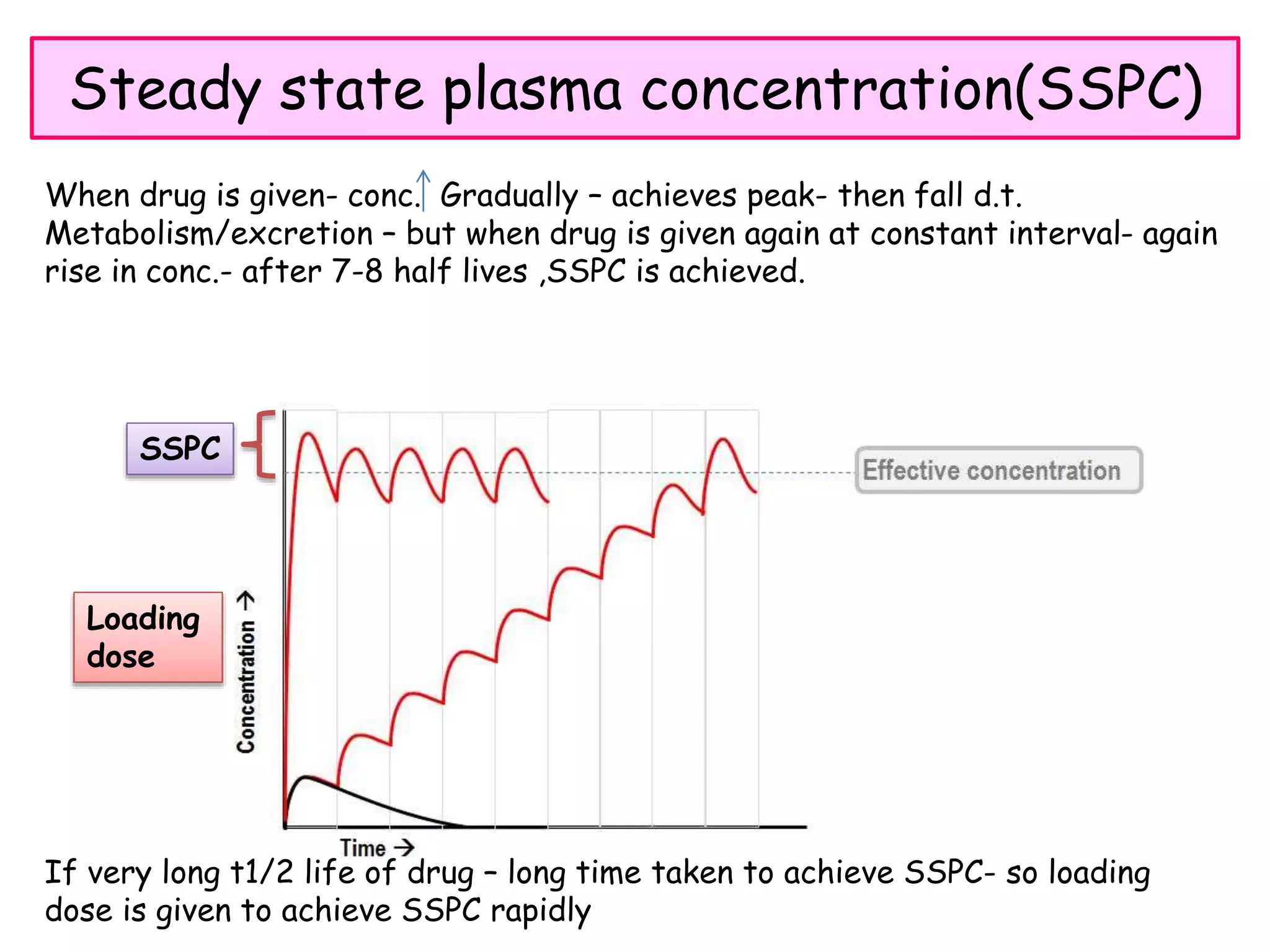
This document discusses various processes involved in the removal of drugs and their metabolites from the body. The major routes of excretion include renal, biliary, fecal, alveolar, and others like milk, skin, hair, sweat and saliva. Renal excretion depends on glomerular filtration, active tubular secretion, and passive tubular reabsorption. The molecular size, plasma protein binding, and renal blood flow influence the amount of drug excreted through glomerular filtration. Active tubular secretion is an energy-requiring process where drugs are secreted into the tubular lumen. Biliary excretion involves drugs being excreted in bile and sometimes undergoing enterohepatic circulation. Drug clearance