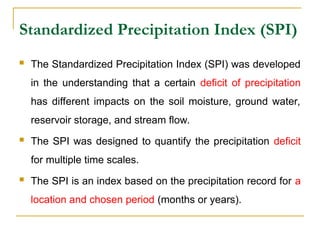
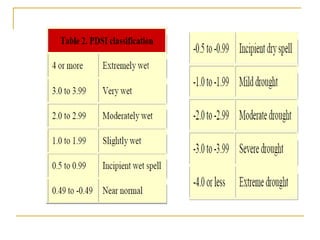
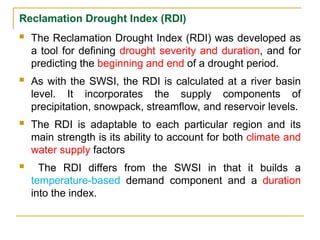
A drought index assimilates thousands of data on rainfall, snowpack, stream flow and other water-supply indicators into a comprehensible picture.
A drought index is typically a single number, far more useful than raw data for decision making.
The relations between drought intensity, duration and frequency can be studied with conceptual models, which deal with meteorological droughts lasting at least one year, with specific applicability to subtropical and mid latitudinal regions
The climate types are defined across the climatic spectrum in terms of the ratio of mean annual precipitation to annual global terrestrial precipitation Pma / Pagt , and additionally, on the ratio of annual potential evapotranspiration to mean annual precipitation Eap / Pma
To complete the description, the length of rainy season Lrs across the climatic spectrum is also indicated.
TRANSPIRATION PULL THEORY
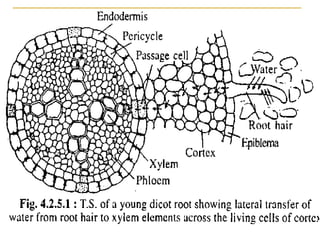
During transpiration, water evaporates from the inter cellular spaces of the leaves to the outer atmosphere through the stomata.
More water is released into the intercellular spaces from the mesophyll cells and in turn, mesophyll cells draw water from the xylem of the leaf.
Due to this, a tension is created in water in the xylem elements of the leaves and this tension is transmitted downward to water in the xylem of root through xylem of stem.
Water is pulled upward in the form of a continuous unbroken water column to reach the transpiring surface up to the top of the plants.
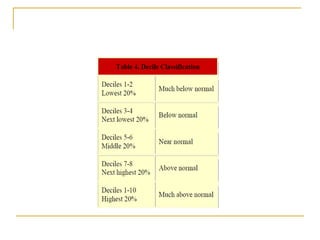
Arranging the monthly precipitation data into deciles.
The technique divides the distribution of occurrences over a long-term precipitation record into tenths of the distribution. Each of these categories is a "decile."
The first decile is the rainfall amount not exceeded by the lowest 10% of the precipitation occurrences.
The second decile is the precipitation amount not exceeded by the lowest 20% of occurrences.
These deciles continue until the rainfall amount identified by the tenth decile is the largest precipitation amount within the long-term record.
ACTIVE TRANSPORT of these ions must occur.
Specific carrier proteins in the plasma membrane attract and carry their specific mineral into the cell.
A Proton Pump: H+ is pumped out of the cell causing a change in pH and a voltage across the membrane.
This helps drive the anions and cations into the cell.
Water and minerals cross the cortex in one of 2 ways: Via SYMPLAST which is the living continuum of cytoplasm connected by plasmodesmata.
Via APOPLAST which is nonliving matrix of cell walls.