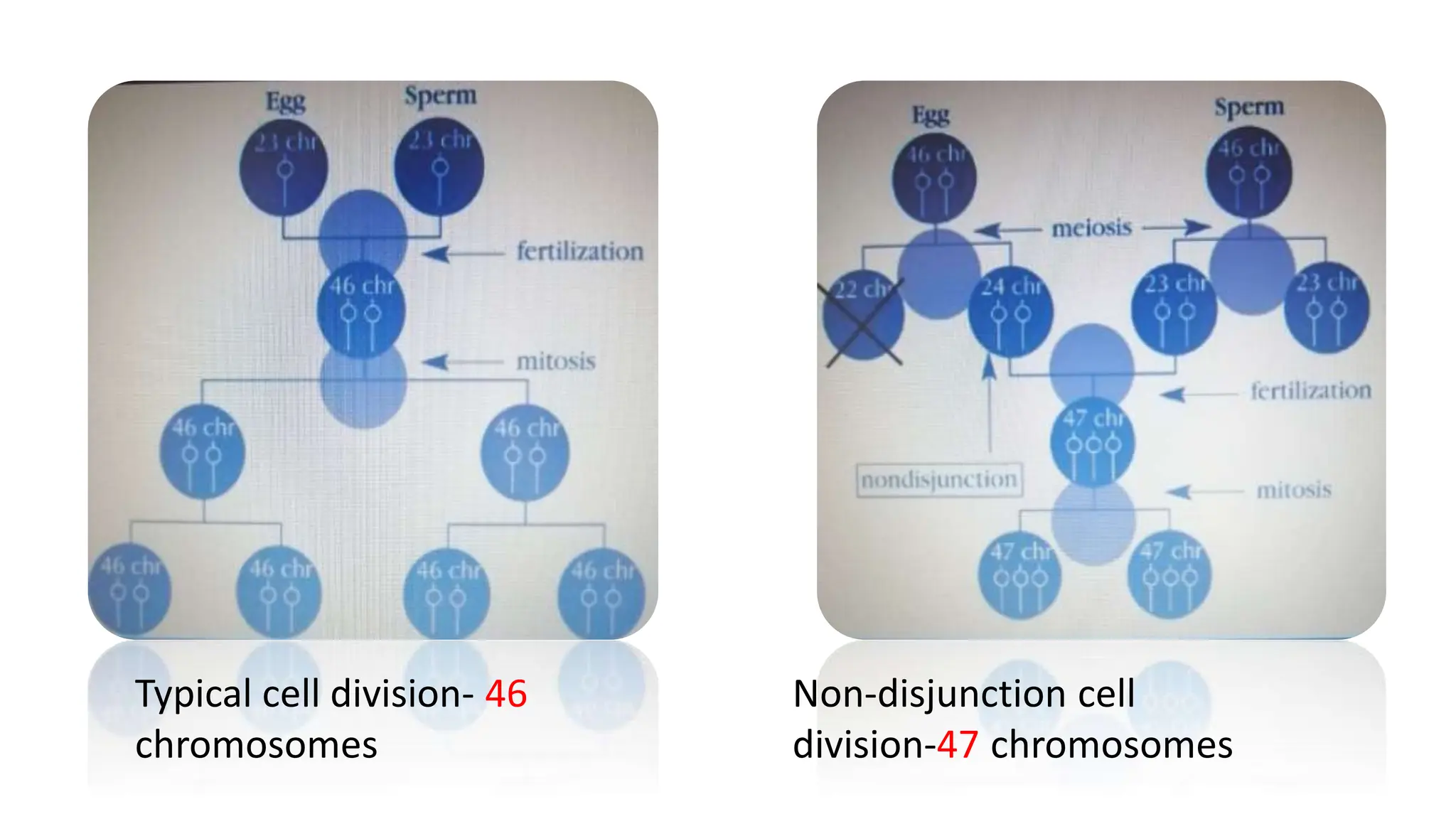
Down syndrome is a neurodevelopmental syndrome characterized by distinctive physical features and developmental delays. It is caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21, either full trisomy 21 or partial trisomy. Common physical features include a short neck, small ears, a tongue that sticks out, small hands and feet, and a single crease across the palm. Individuals with Down syndrome may experience health issues such as heart defects, hearing loss, thyroid problems, celiac disease, seizures, and sleep apnea.