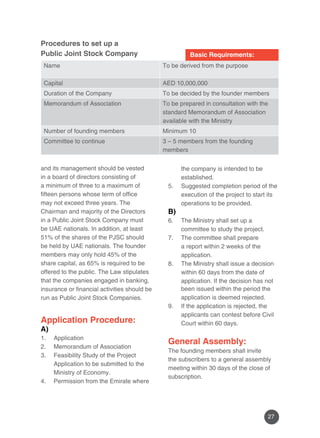
The document outlines the trading regulations and commercial agency laws for doing business in Abu Dhabi, emphasizing the need for foreign companies to establish local representation to engage effectively in the market. It details the various legal structures available for businesses, including sole proprietorships, limited liability companies, and public joint stock companies, along with the requirements for setting them up. Furthermore, it discusses the importance of compliance with UAE laws, including appointing local service agents and obtaining the necessary licenses from governmental bodies.