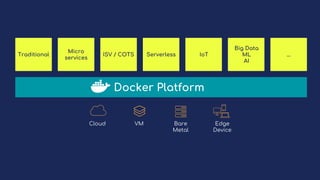
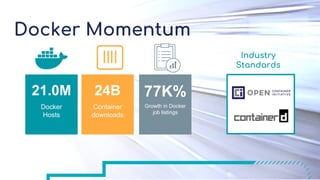
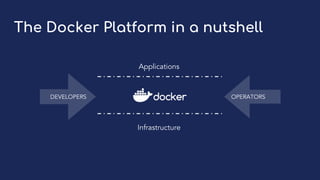
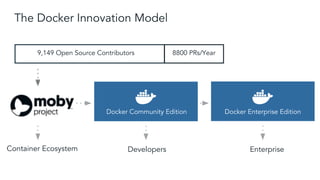
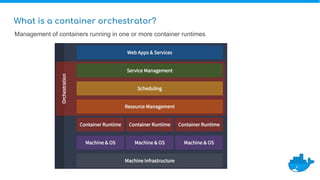
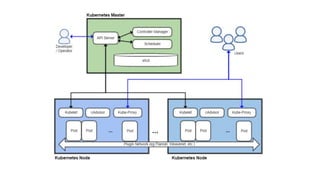
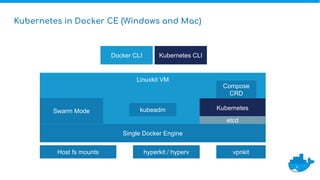
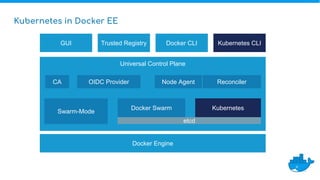
Tom Barlow discusses Docker's platform, focusing on Kubernetes integration for managing containerized applications. The presentation covers Kubernetes architecture, components, and the advantages of using Docker Enterprise Edition for enterprise container security and management. Key features include native Kubernetes support, authentication mechanisms, resource management, and a streamlined development workflow for both local and production environments.