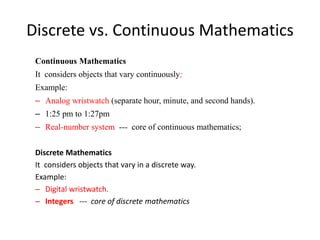
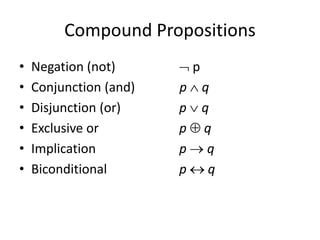
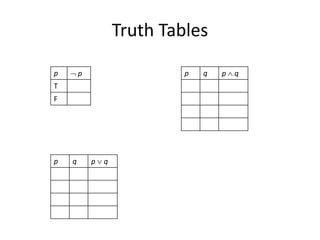
Discrete mathematics is the study of mathematical structures that are discrete rather than continuous. It considers objects that vary in a discrete way, such as digital watches showing integers of time, rather than analog watches with continuous hands. Problems in discrete mathematics cover non-continuous domains and consider questions about connecting cities with telephone lines or visiting islands with bridges without crossing any bridge twice. Logic and propositions are also key aspects of discrete mathematics, including defining statements, propositional variables, compound propositions using operators, truth tables, and negation, conjunction, disjunction and other operations.