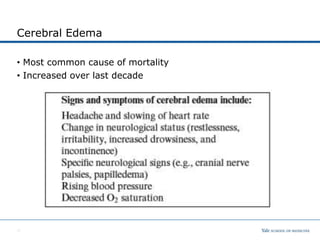
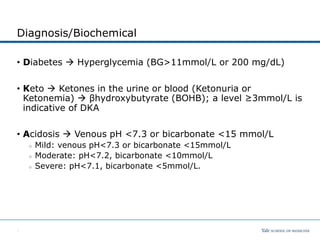
The document discusses diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in children, covering its epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, clinical signs, and complications. Key components include the importance of recognizing DKA to initiate timely therapy, with treatment goals centered on correcting dehydration, electrolytes, hyperglycemia, and acidosis. Cerebral edema is highlighted as the most common cause of mortality in DKA, necessitating careful monitoring and slow fluid administration during treatment.





![Laboratory Investigation
• Glucose, urine dip
• Blood gas (venous or arterial)
• Electrolytes and other labs
Na is typically low. For every 100 mg/dL glucose above 200 mg/dL,
the measure Na should be reduced by 1.6 mEq/L
Nacorrected = Nameasured + 1.6 x [Glucose] - 200
100
K+ total body depletion
Ca and phosp typically low
BUN/Cr typically elevated in dehydration
WBC and left shift typically due to acute stress but also look
for infectious trigger process
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dka-for-pem-1-230509141900-c213e159/85/DKA-for-PEM-1-pptx-8-320.jpg)