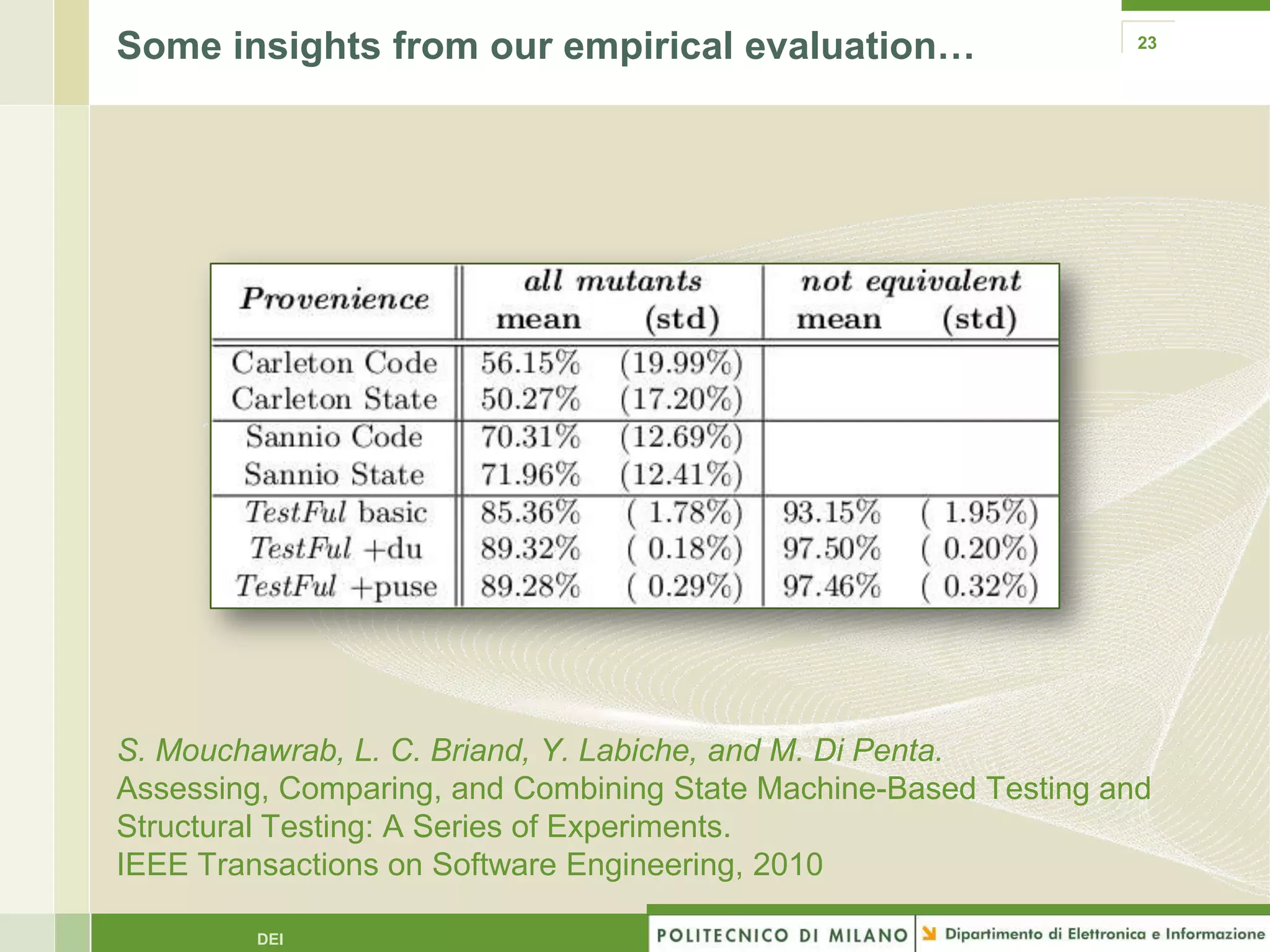
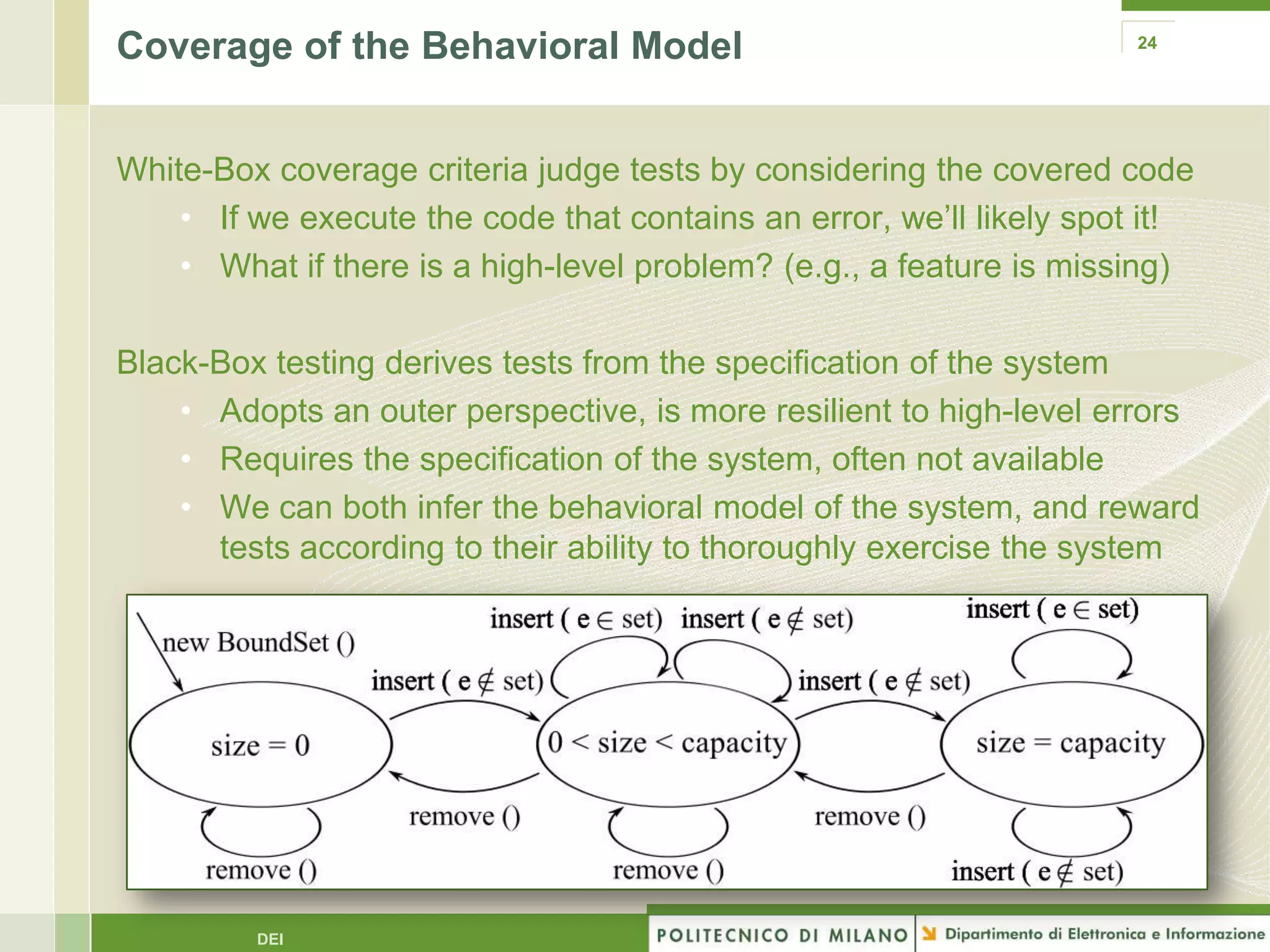
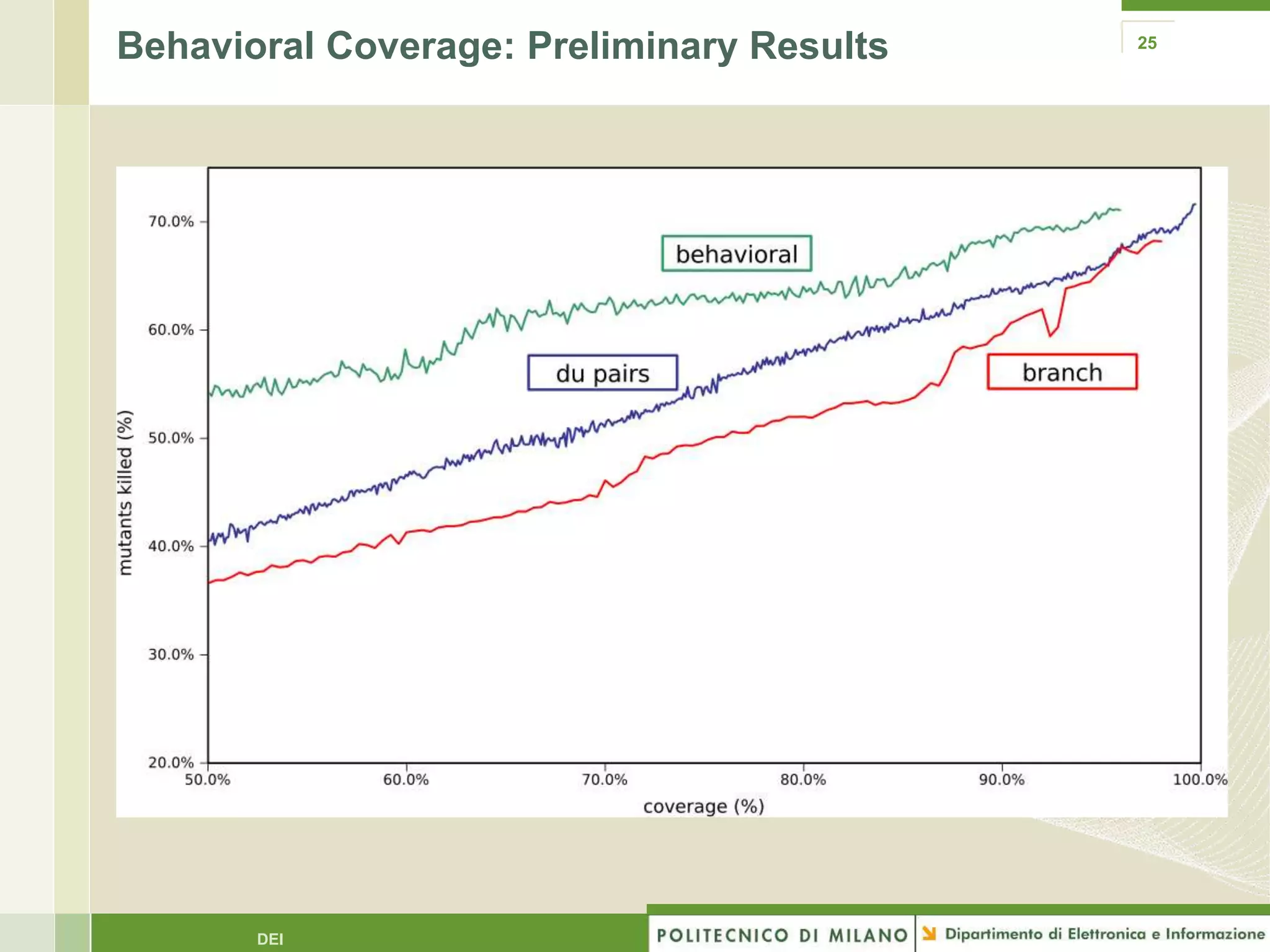
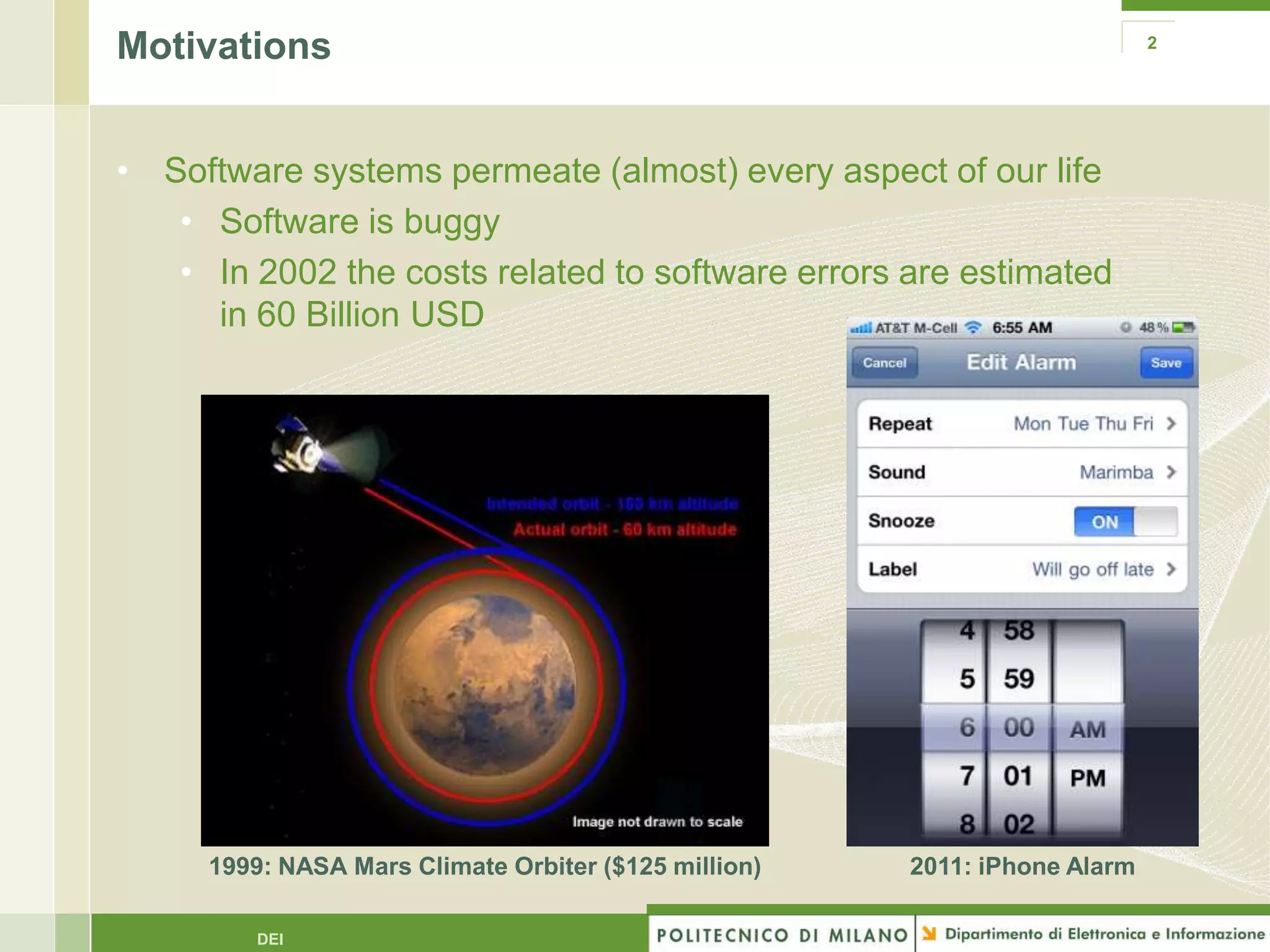
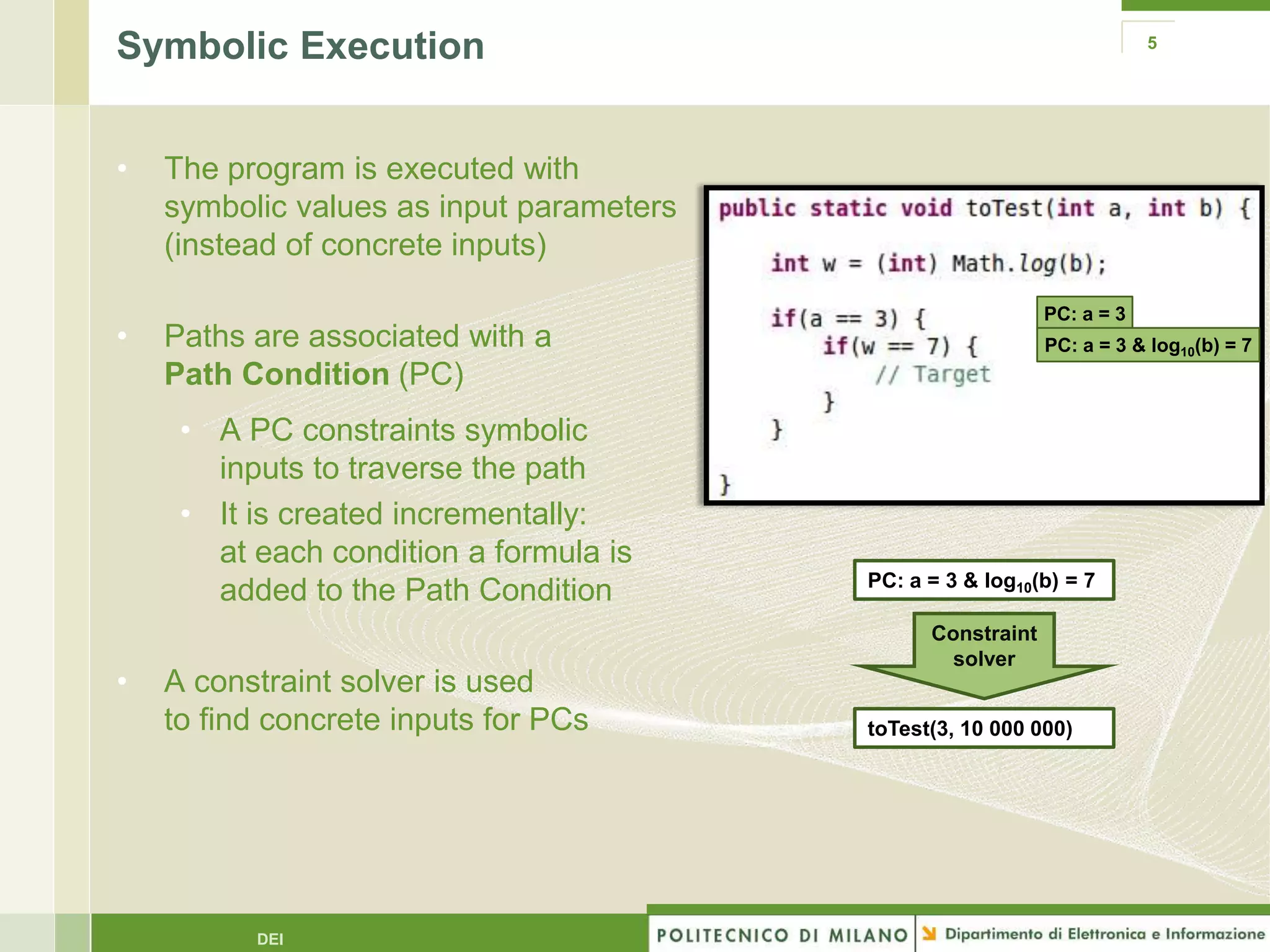
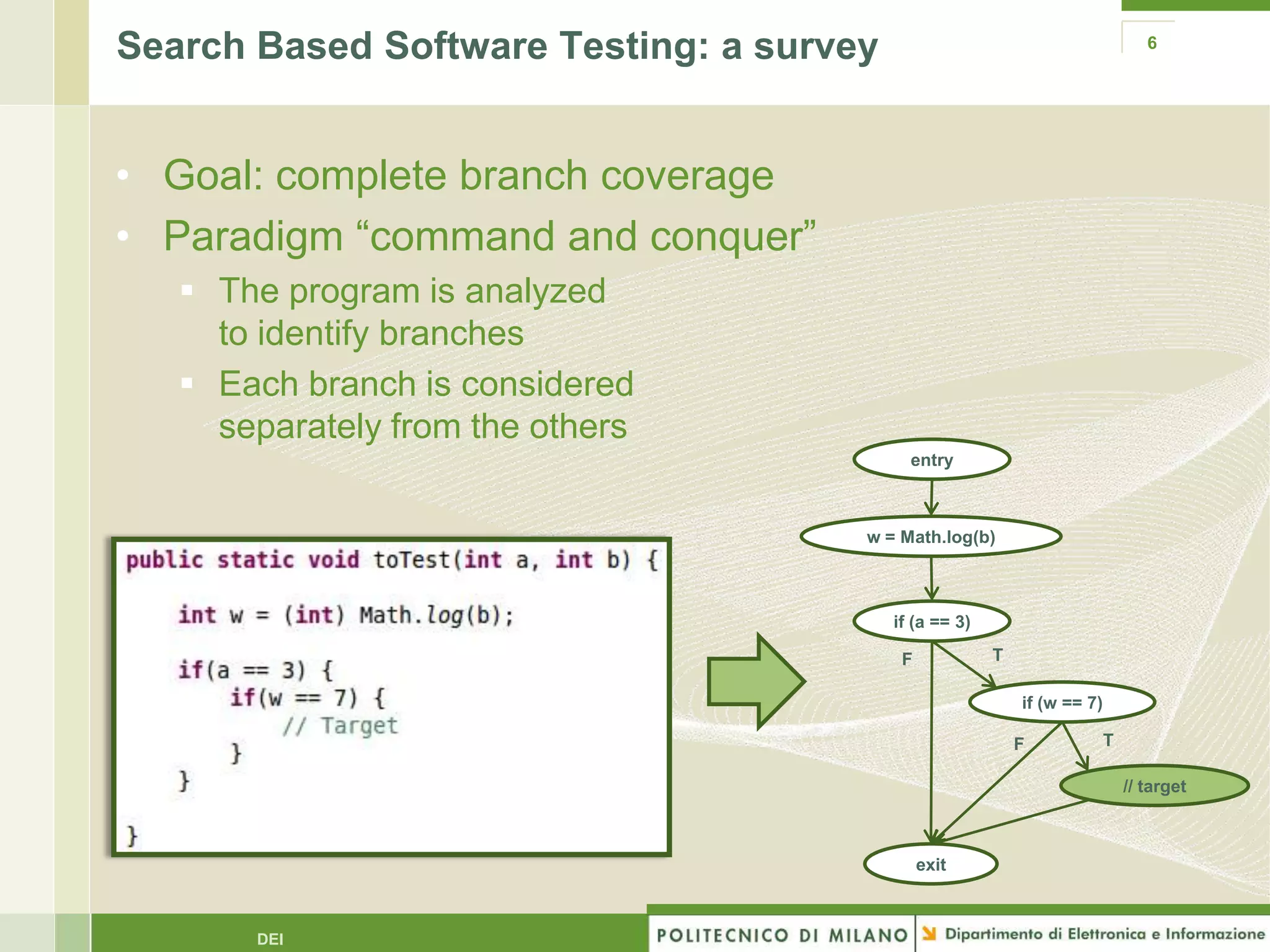
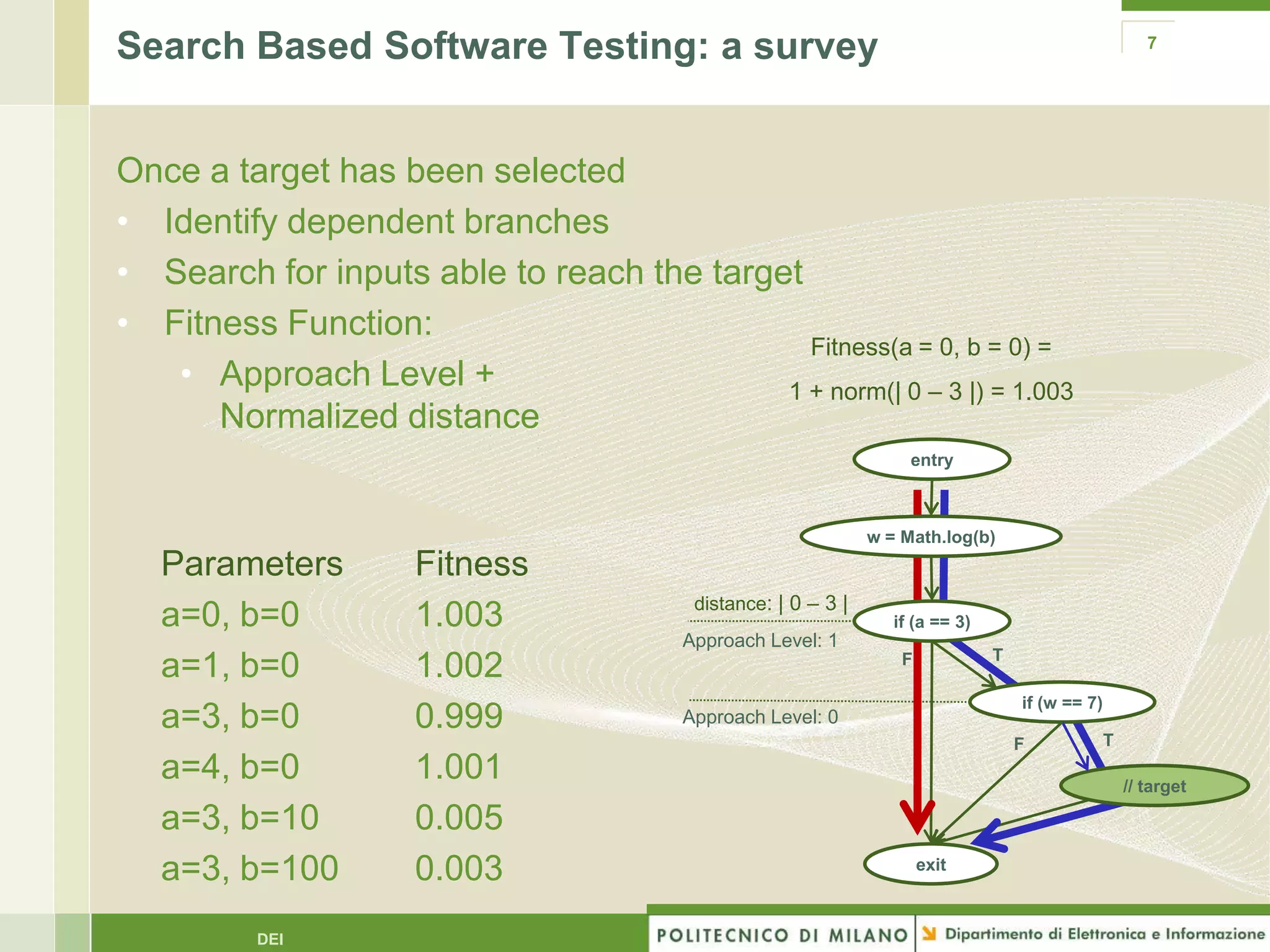
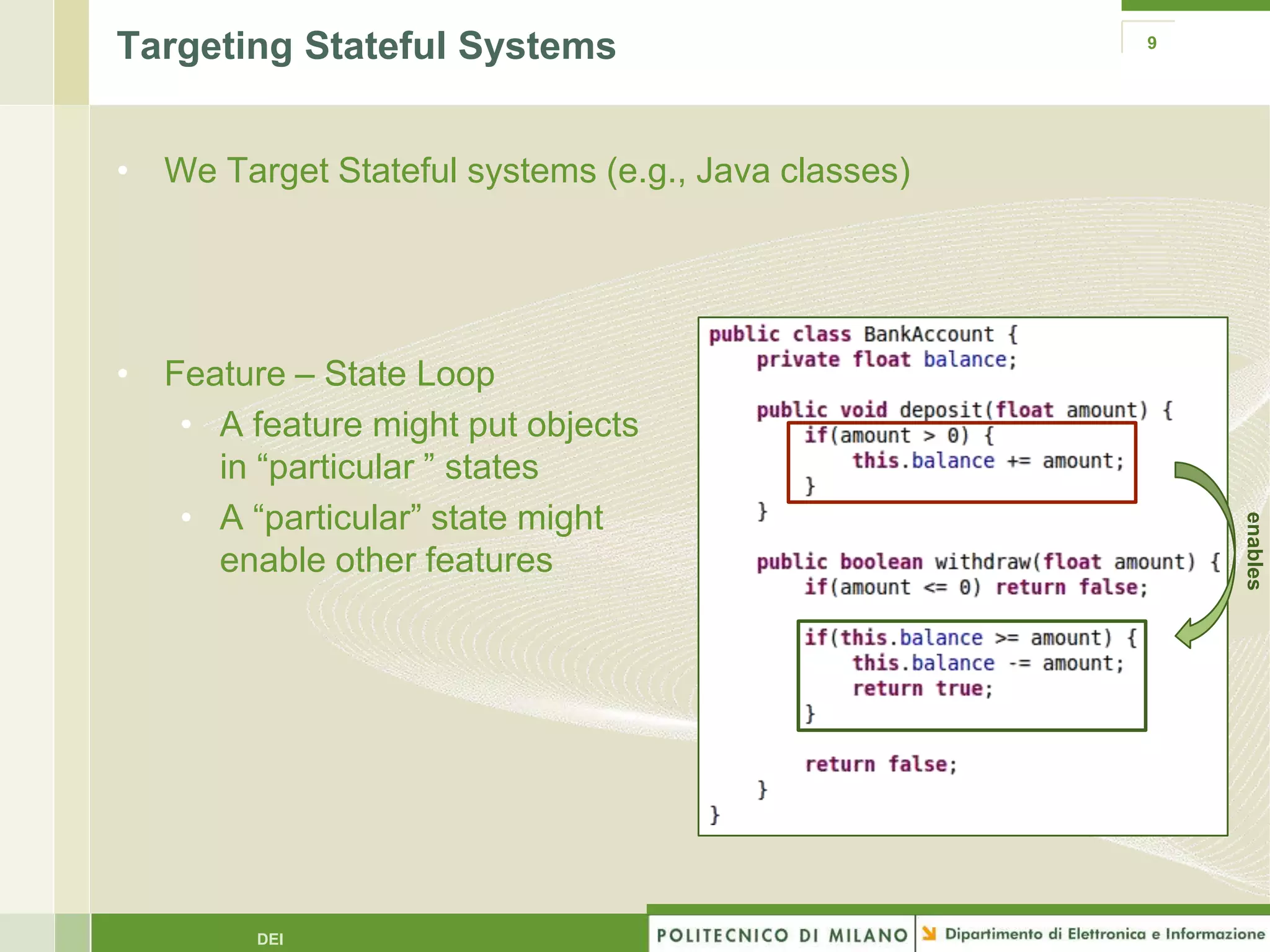
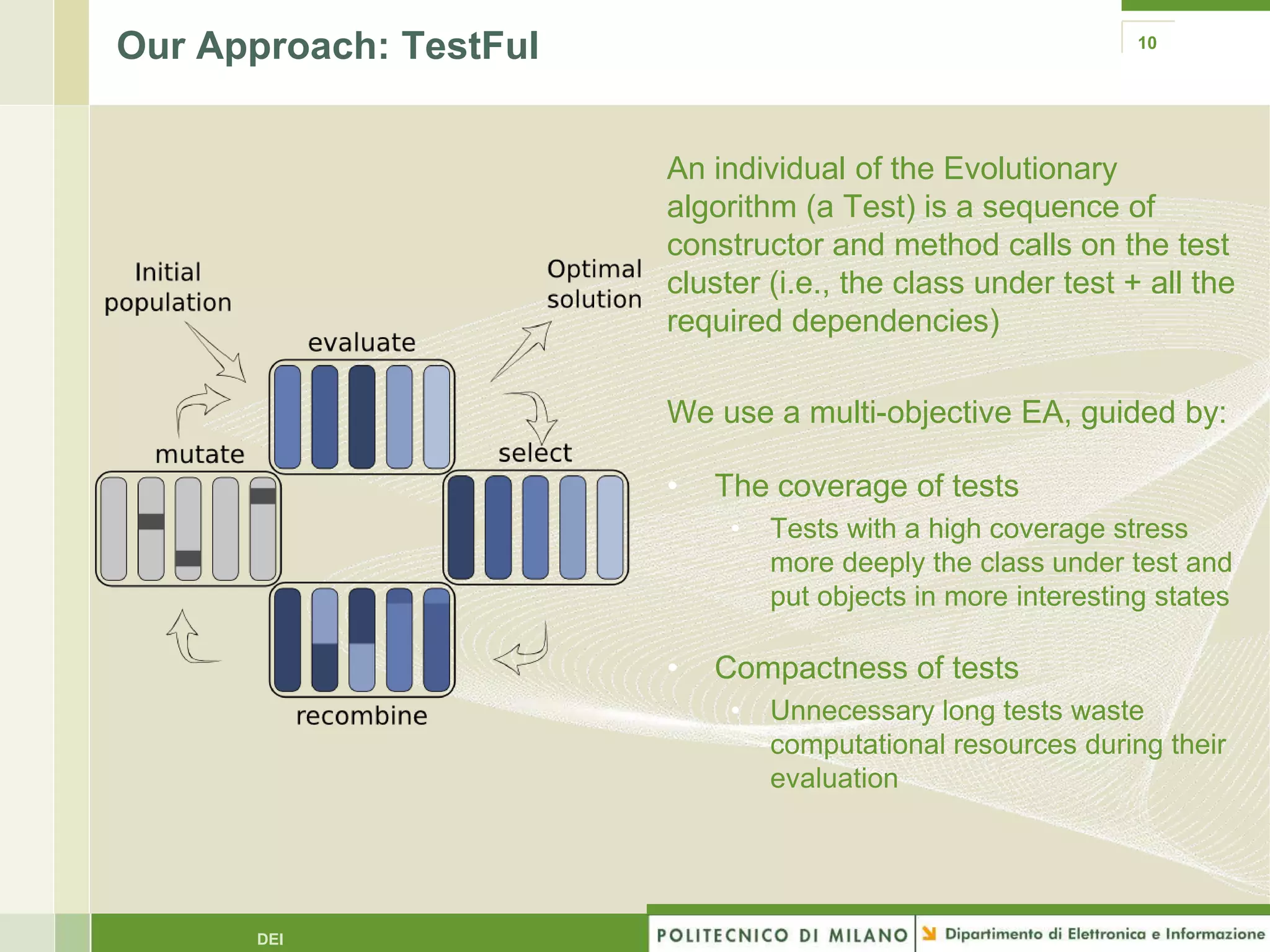
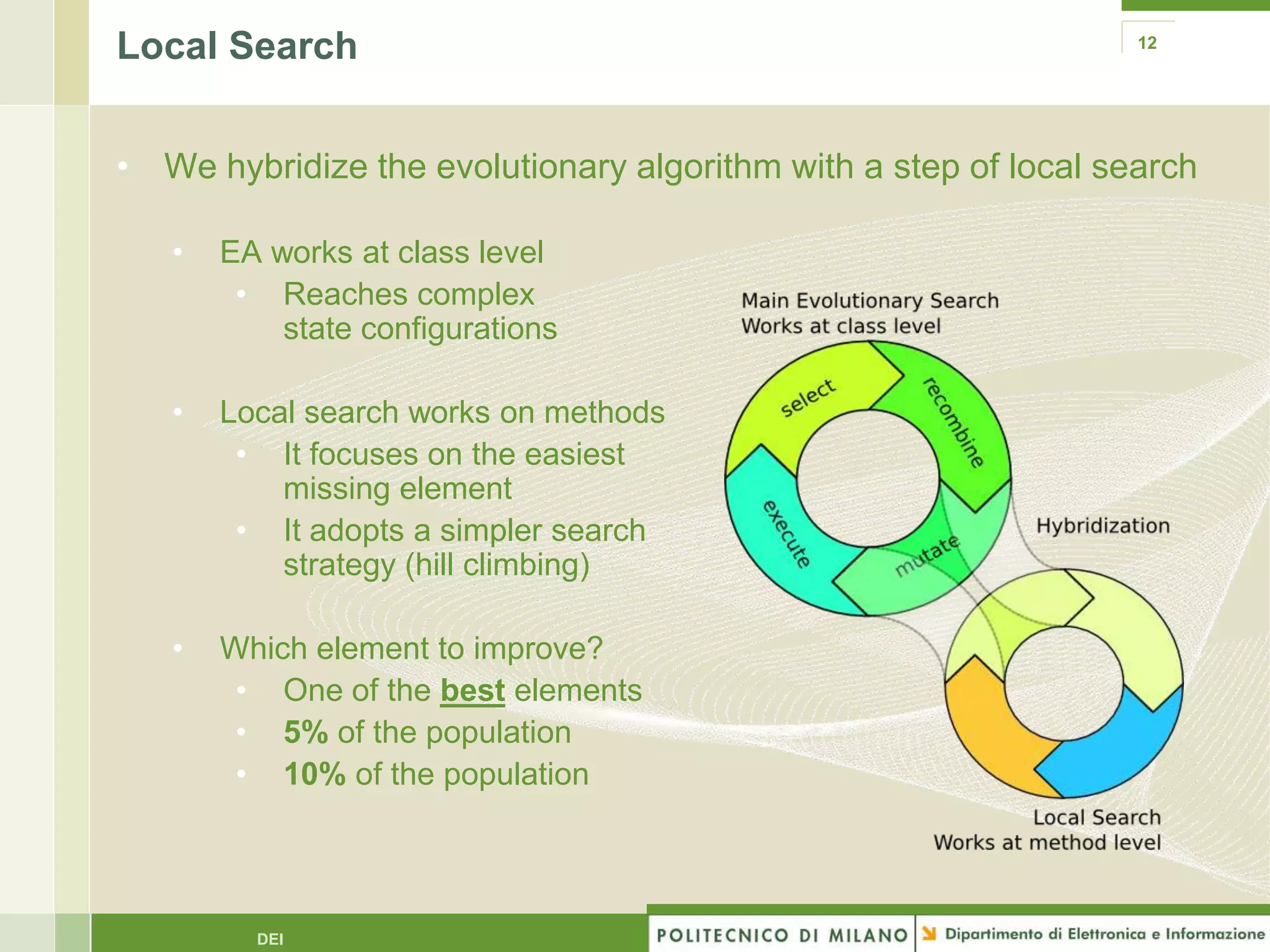
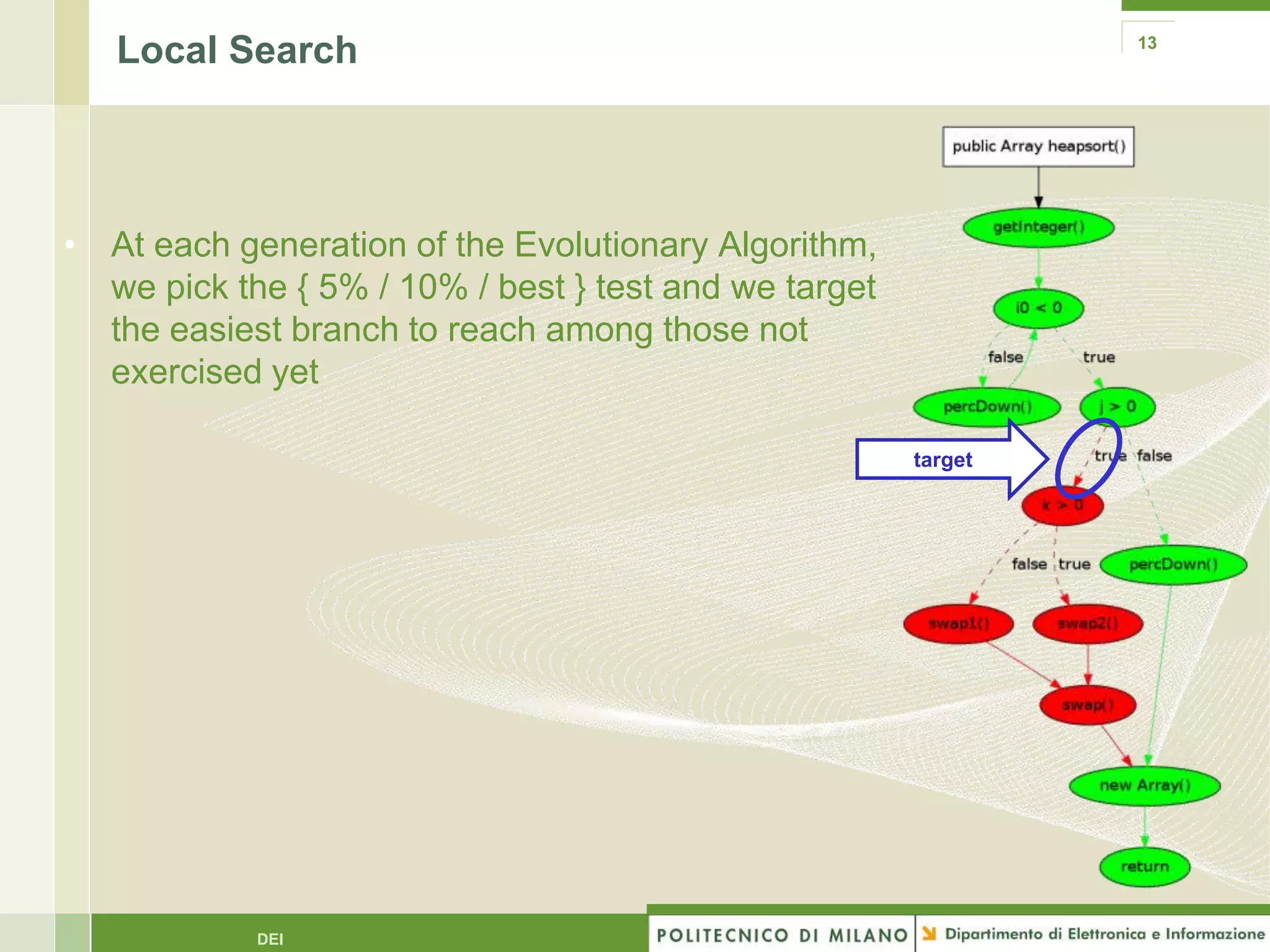
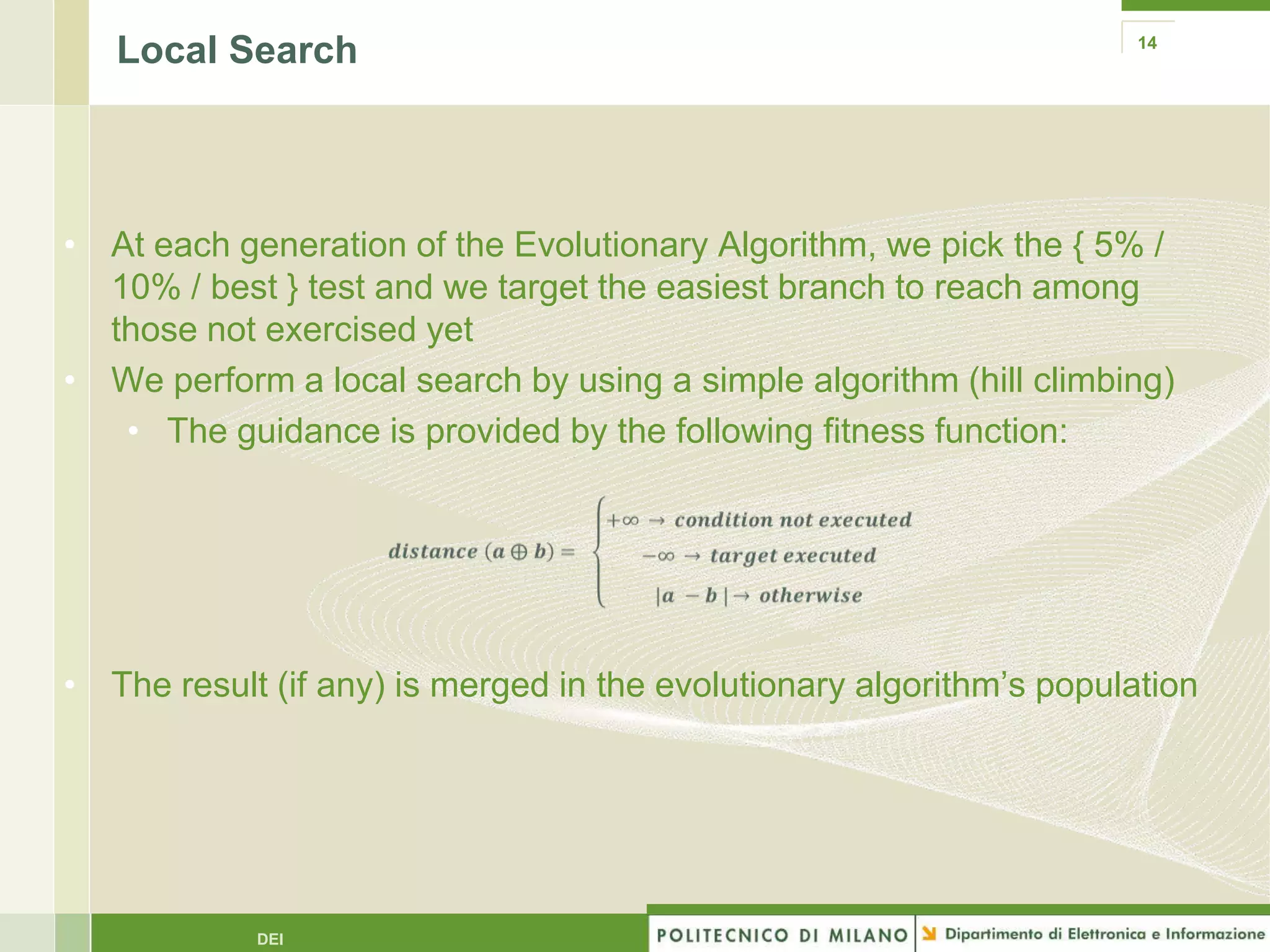
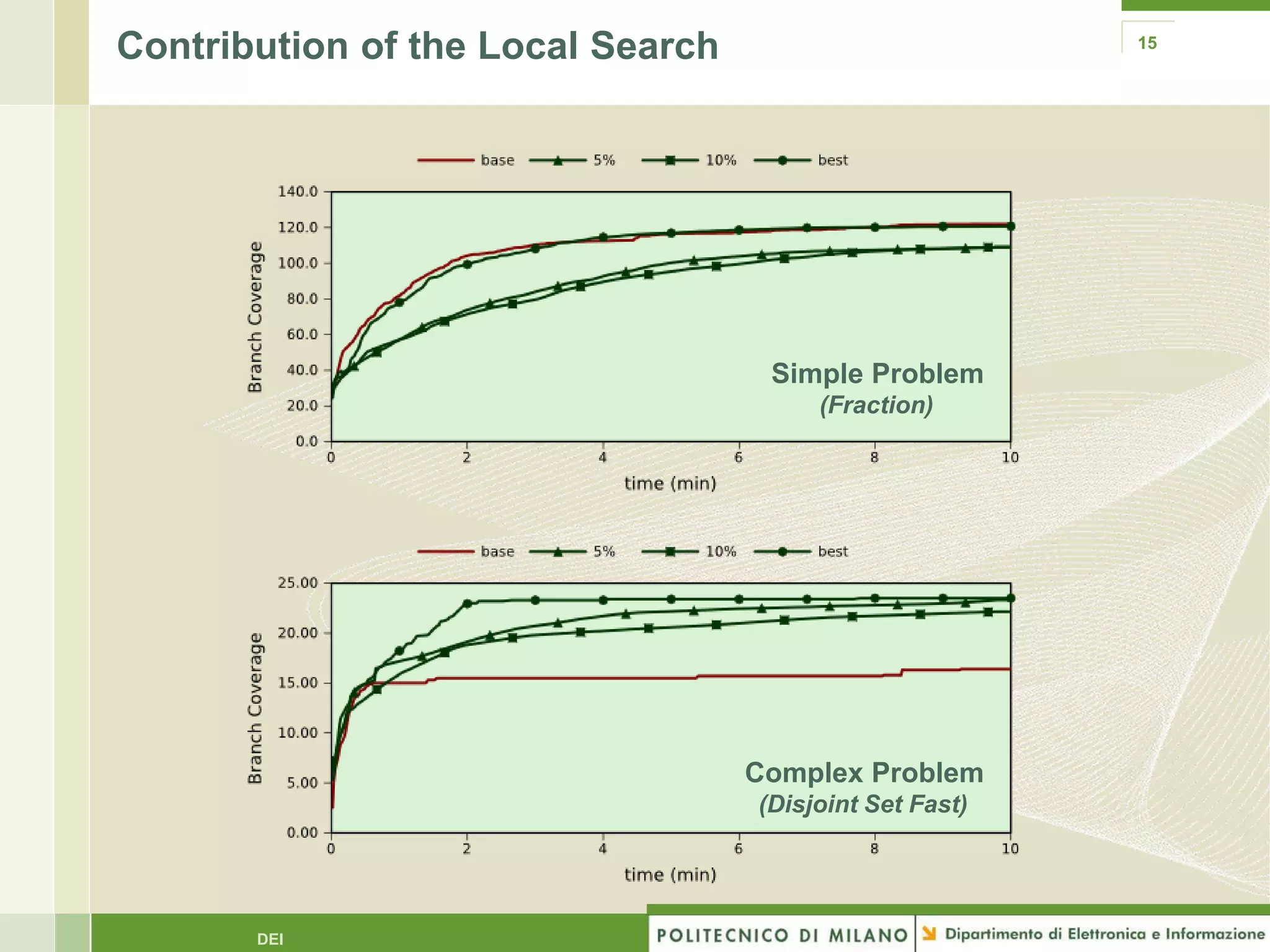
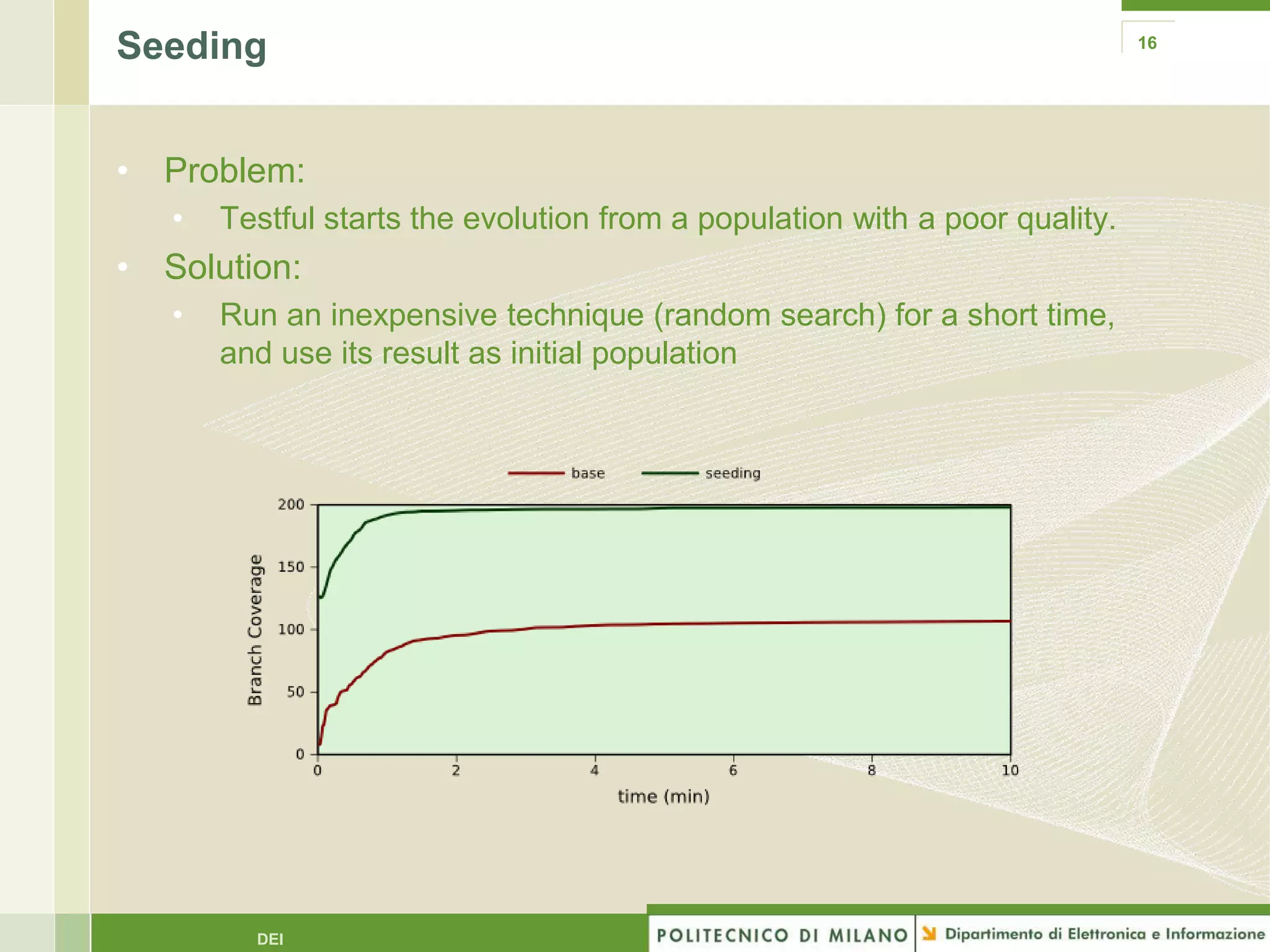
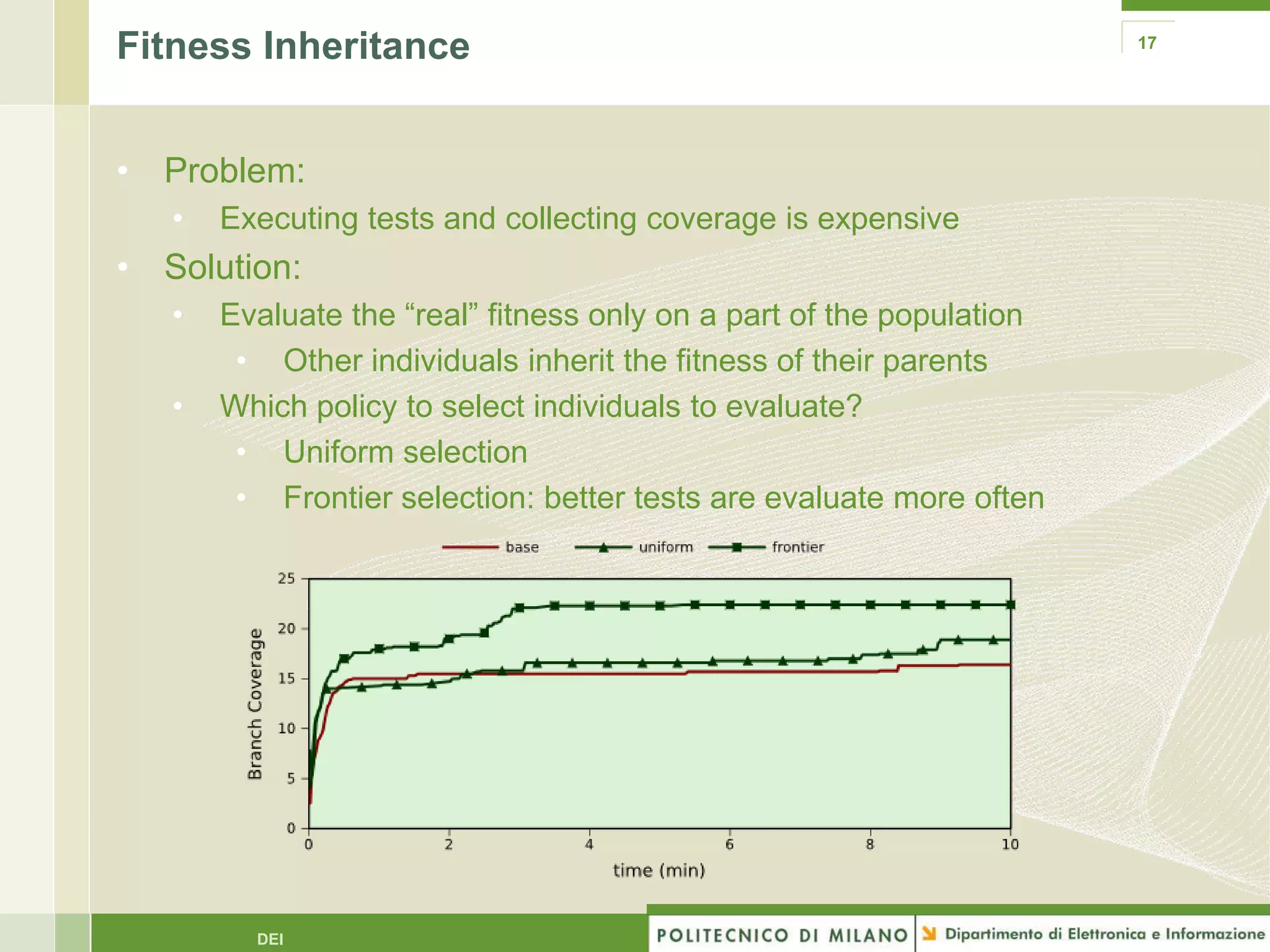
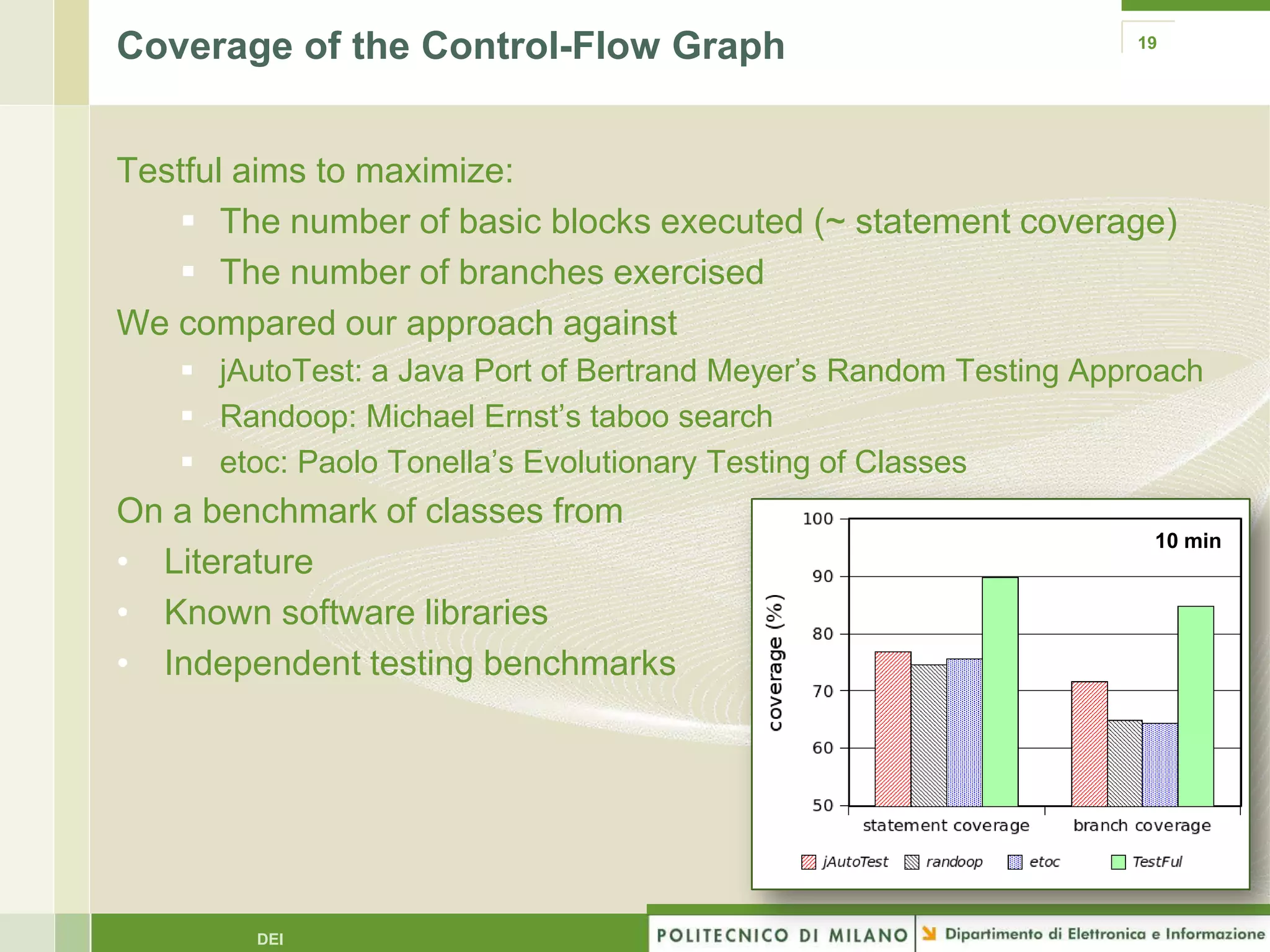
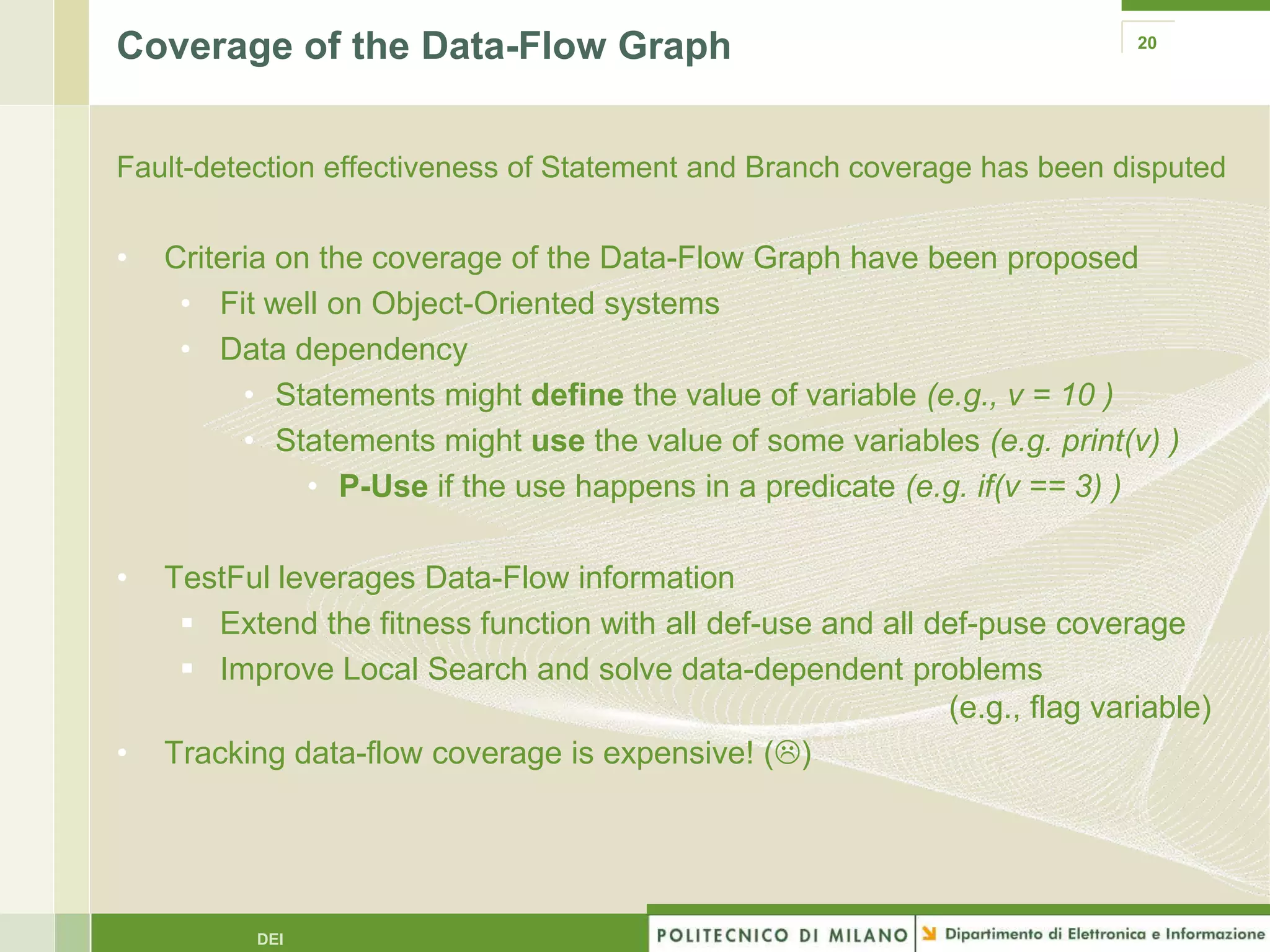
The document summarizes research on evolutionary testing of stateful systems. It discusses limitations of traditional search-based software testing approaches when applied to object-oriented systems, and proposes a new approach called Testful. Testful uses an evolutionary algorithm to generate test cases for a class under test and its dependencies. It aims to maximize both test coverage and compactness of tests. The paper describes improvements to Testful including local search, seeding, and fitness inheritance techniques to enhance efficiency. It then evaluates Testful's ability to achieve control flow and data flow coverage compared to other automated testing tools.



![Problems of Search Based Software Testing 8
Usage of a single guidance Works on isolated functions
Coarse / Misleading Modern systems are object-oriented
void foo(int []a) {
int flag = 0;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
if(a[i] == 23)
flag = 1;
if(flag == 1) {
// target
}
}
DEI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissertation-110223080040-phpapp02/75/Evolutionary-Testing-of-Stateful-Systems-a-Holistic-Approach-8-2048.jpg)


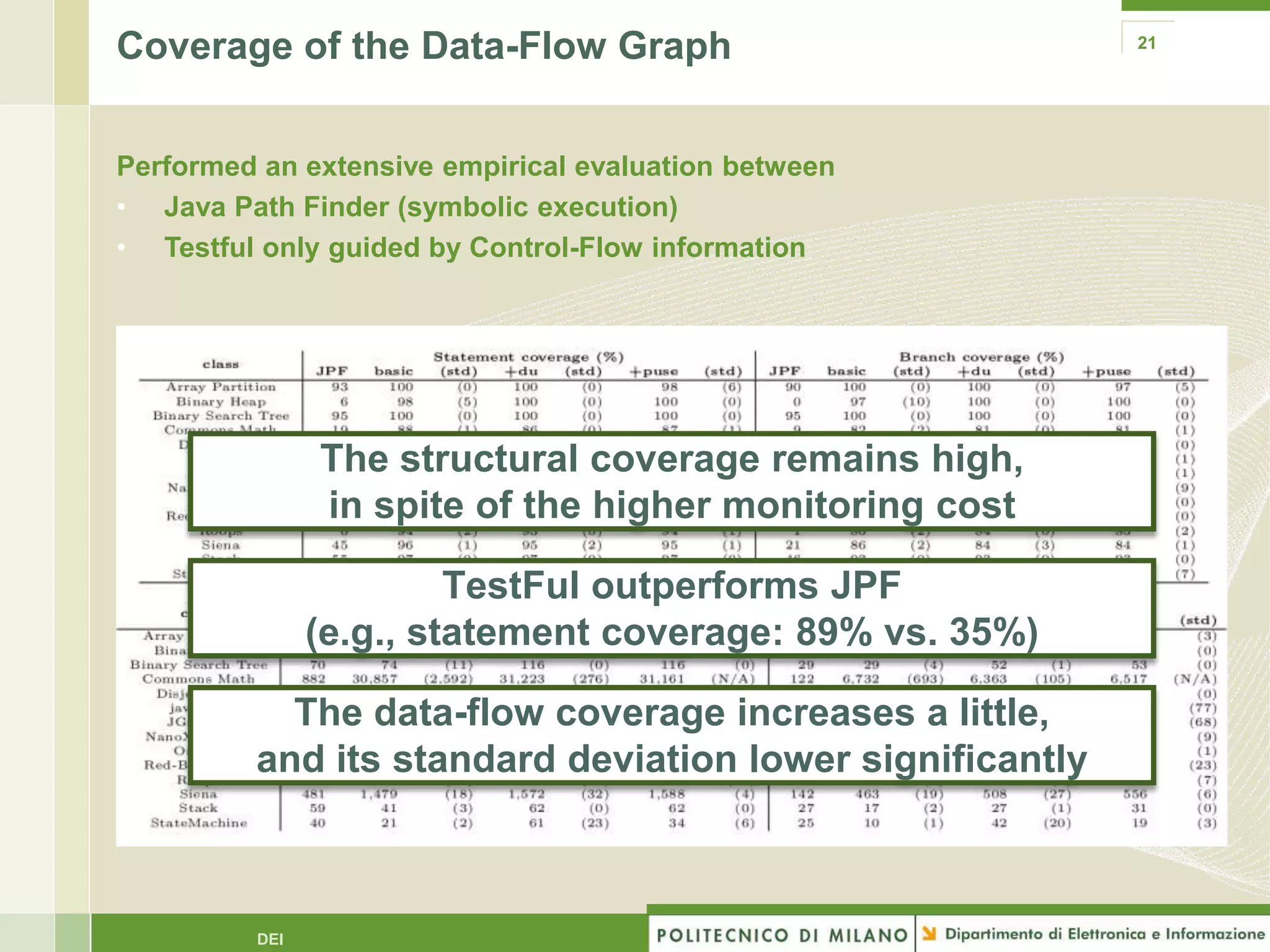
![Some insights from our empirical evaluation… 22
«container classes are the de facto benchmark
for testing software with internal state»
[ Arcuri 2010 ]
DEI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dissertation-110223080040-phpapp02/75/Evolutionary-Testing-of-Stateful-Systems-a-Holistic-Approach-22-2048.jpg)