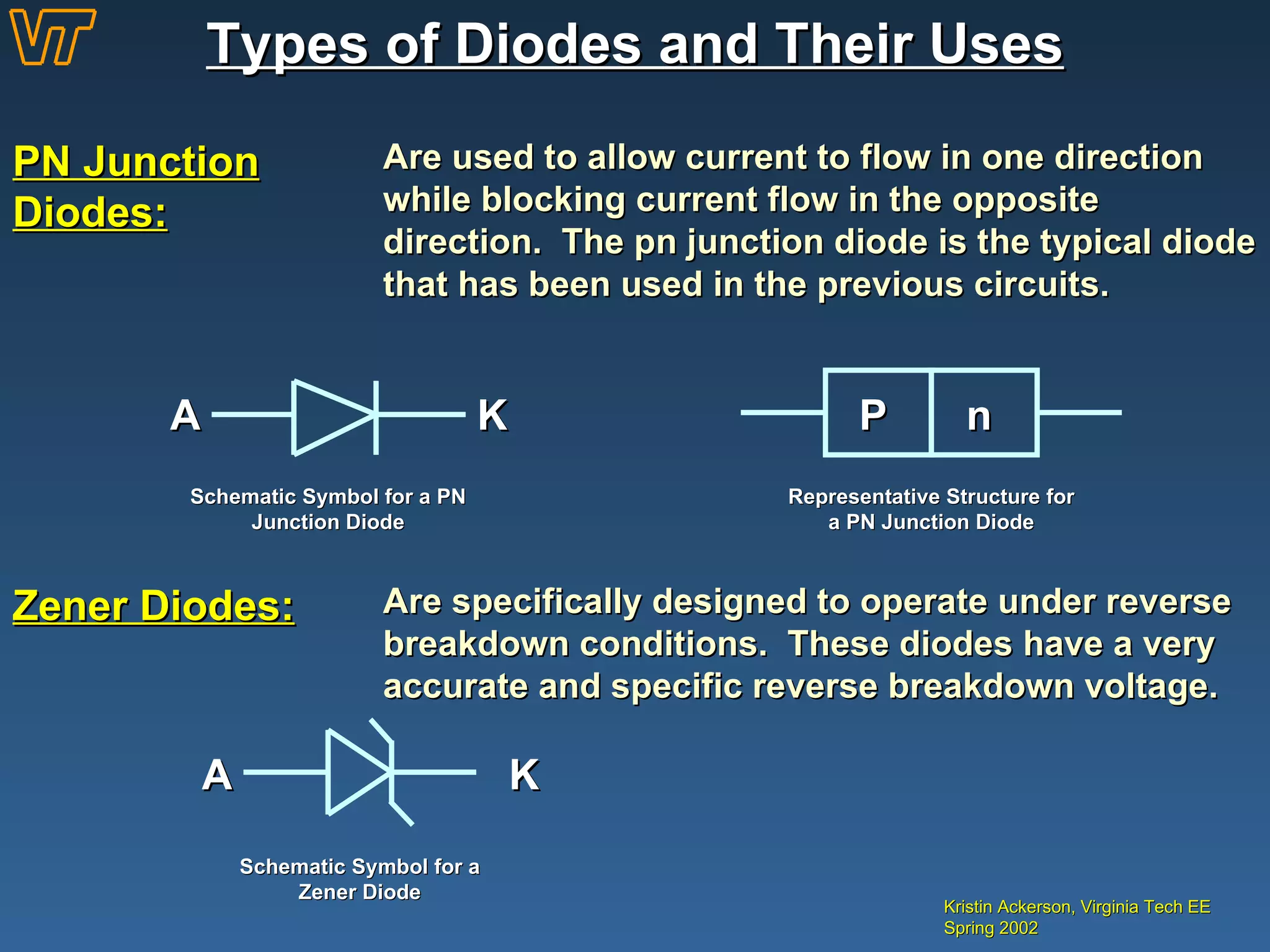
This document provides an overview of diodes, including:
- What materials diodes are made from, such as silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide.
- How n-type and p-type materials are created by doping semiconductors with different elements.
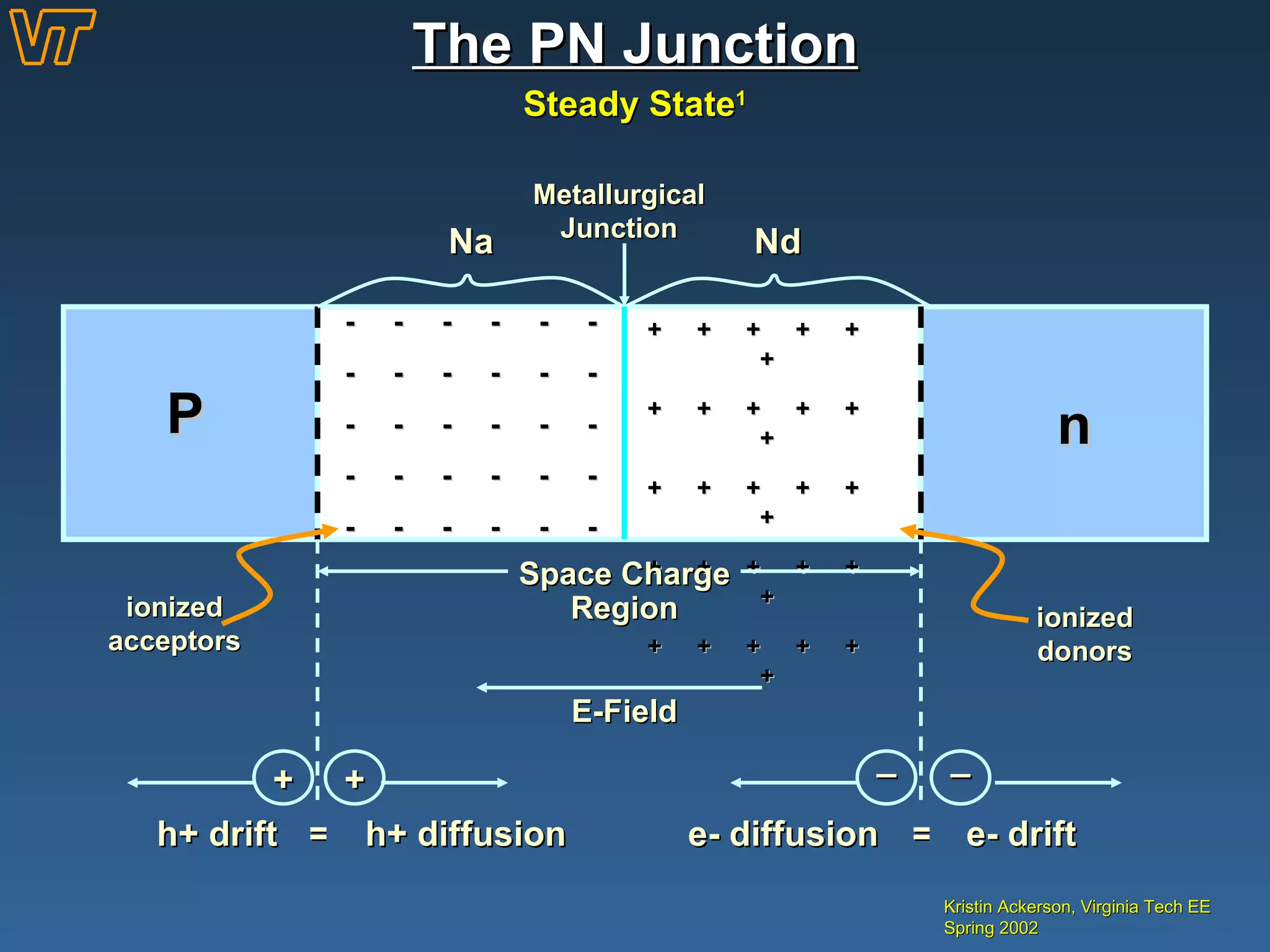
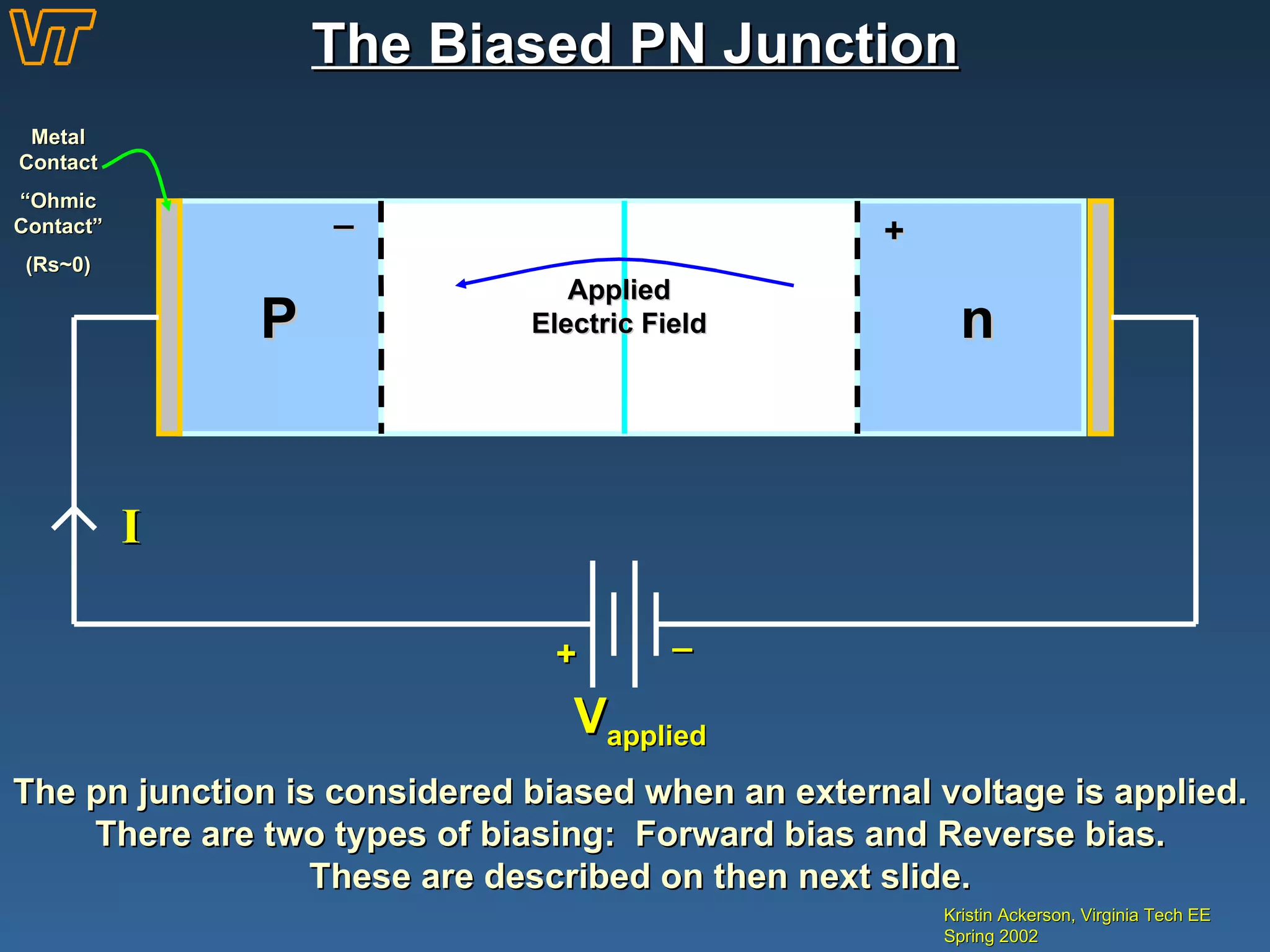
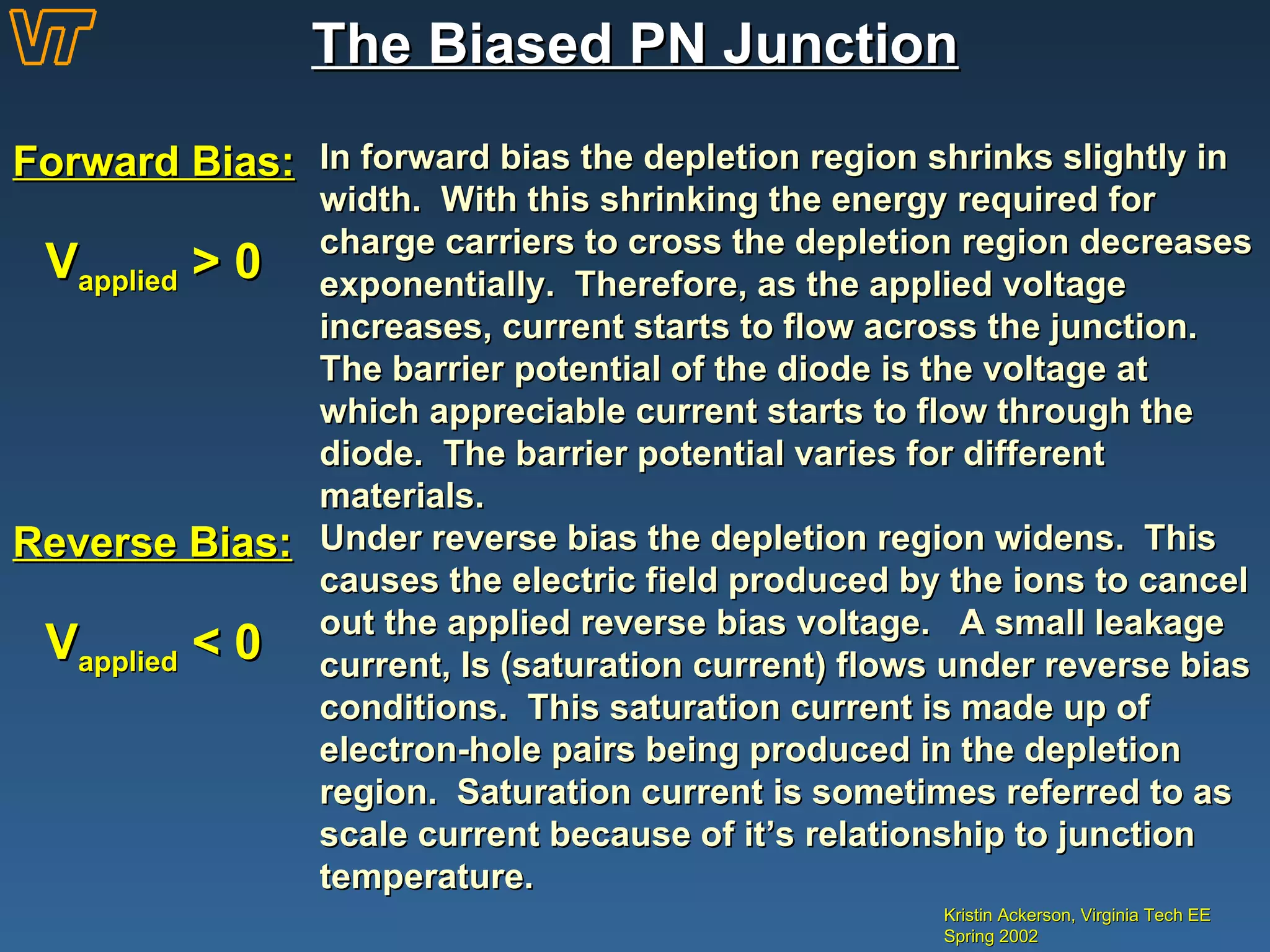
- How a pn junction is formed and its properties when biased, including the depletion region.
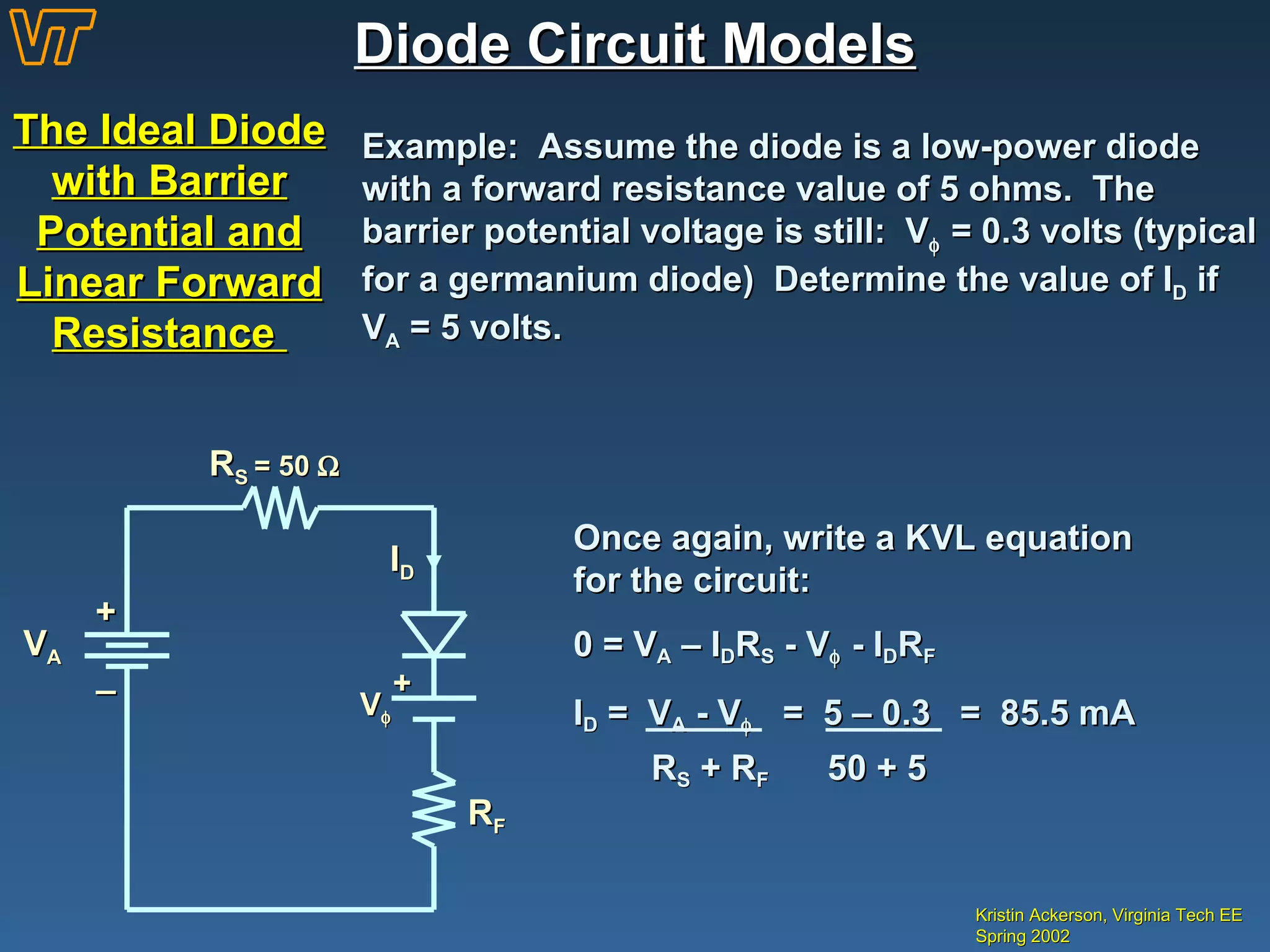
- Diode circuit models of increasing complexity, from ideal diode to models including barrier potential and resistance.
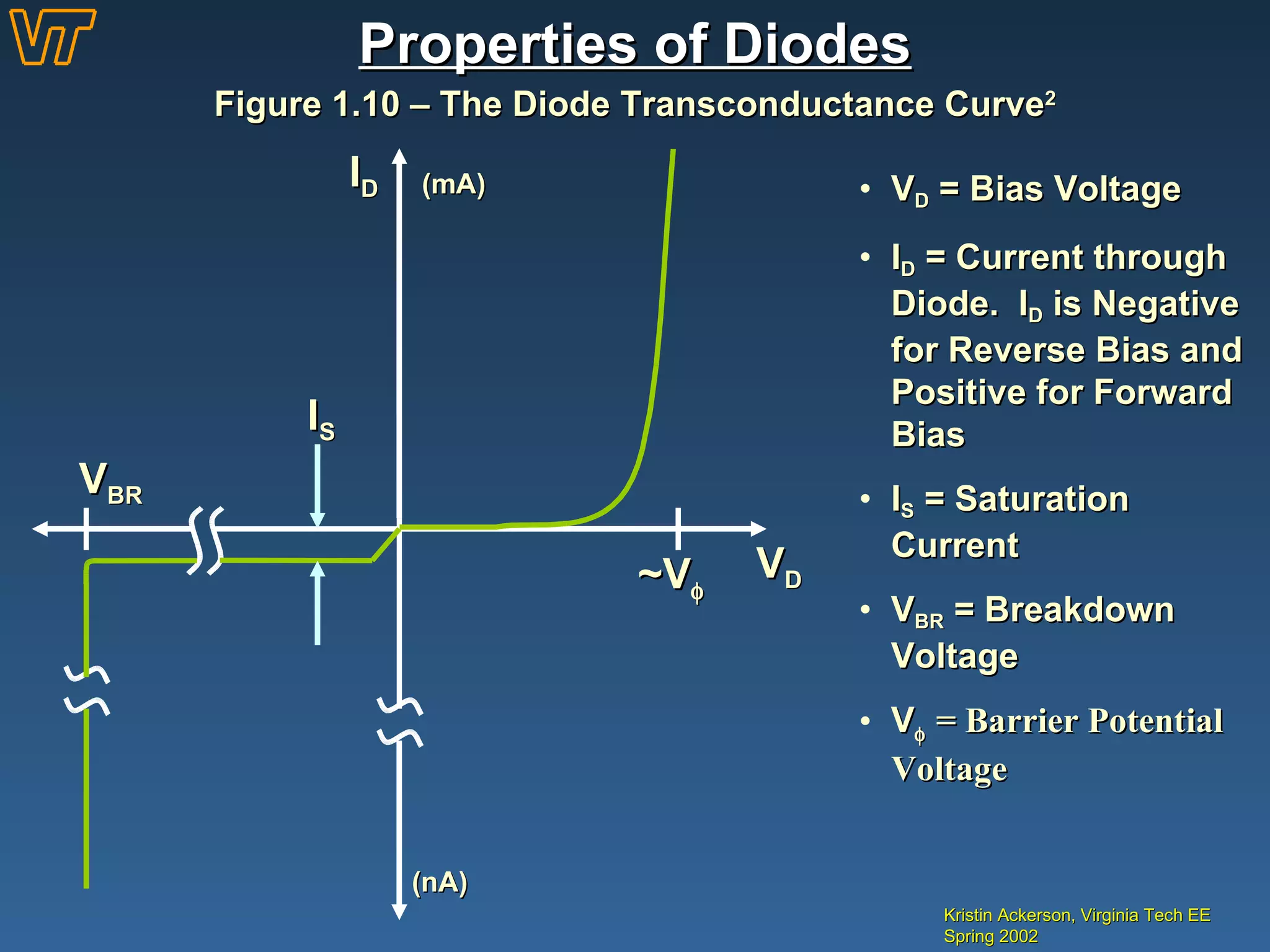
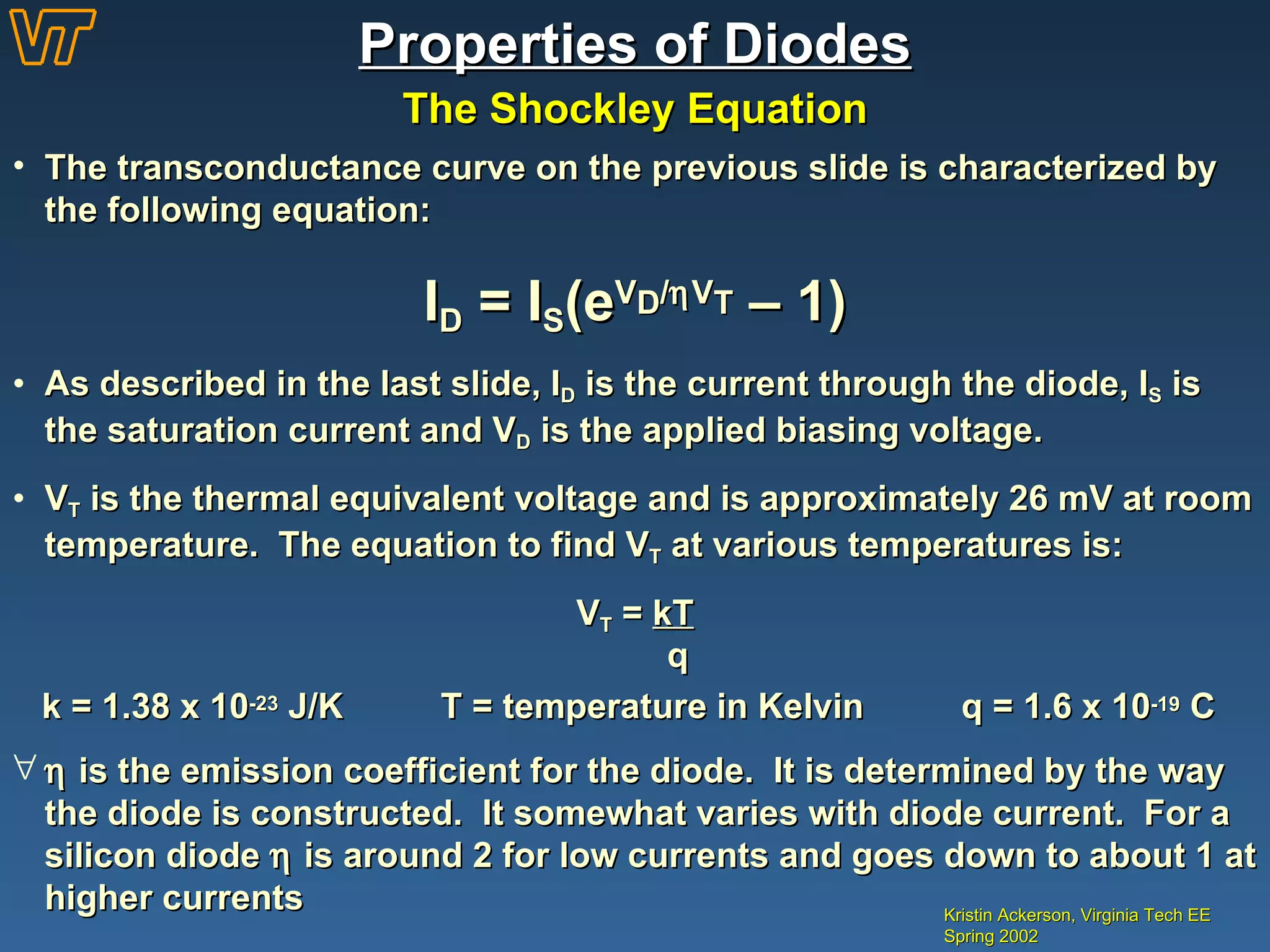
- Key diode characteristics like the shockley equation, transconductance curve, and dynamic resistance.
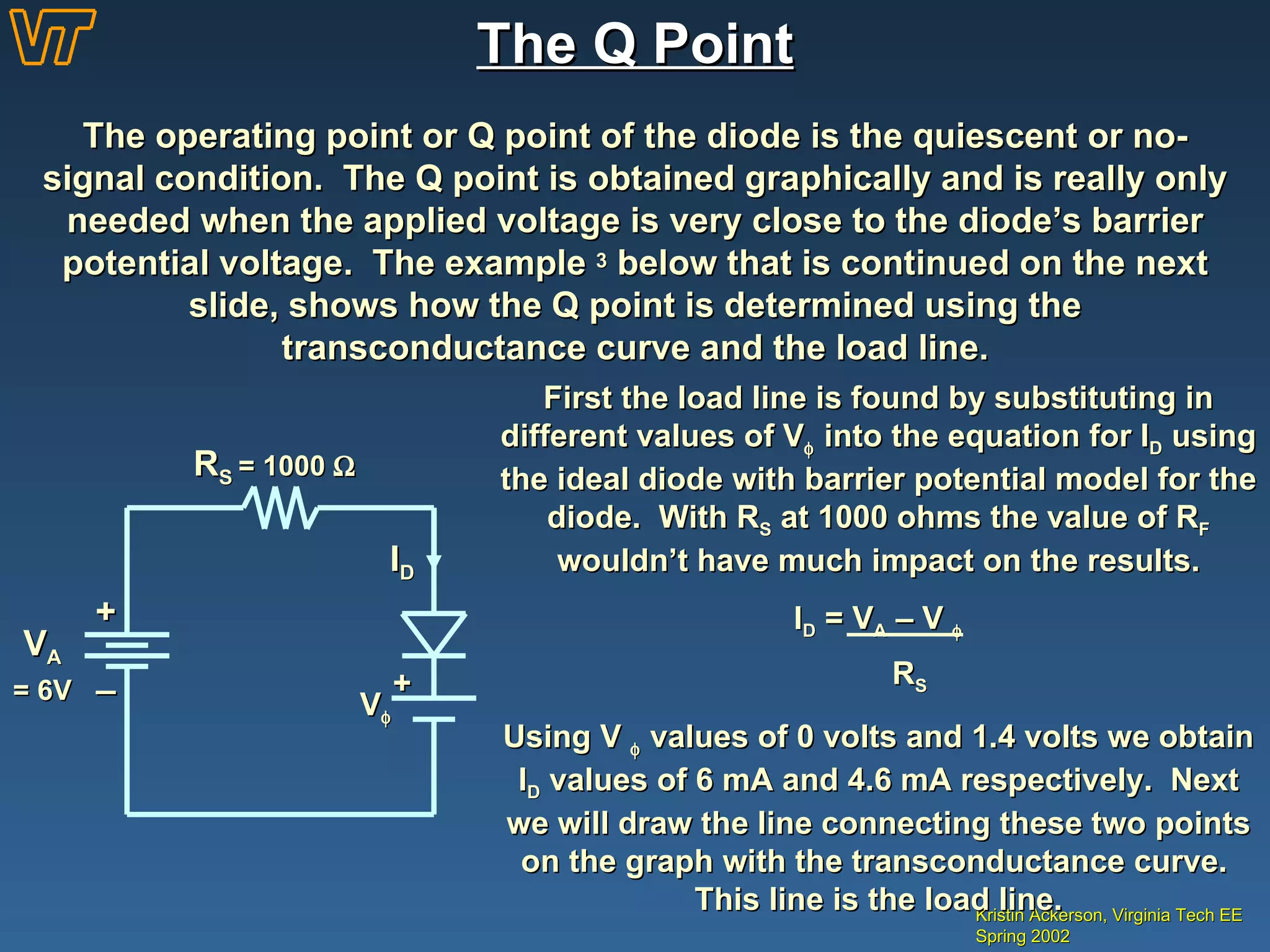
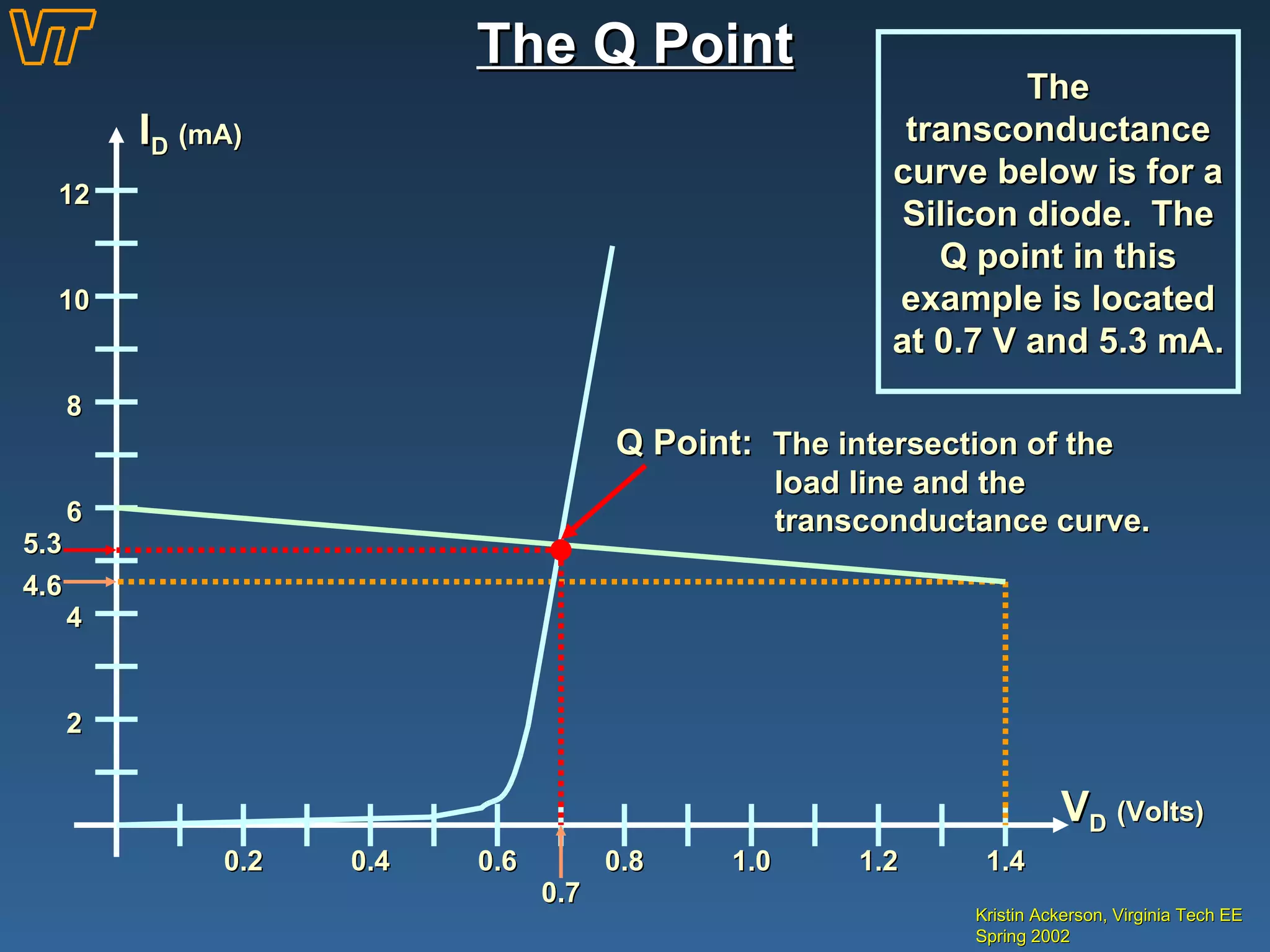
- Examples of calculating diode operating points and voltage drops in circuits.
- Different types of