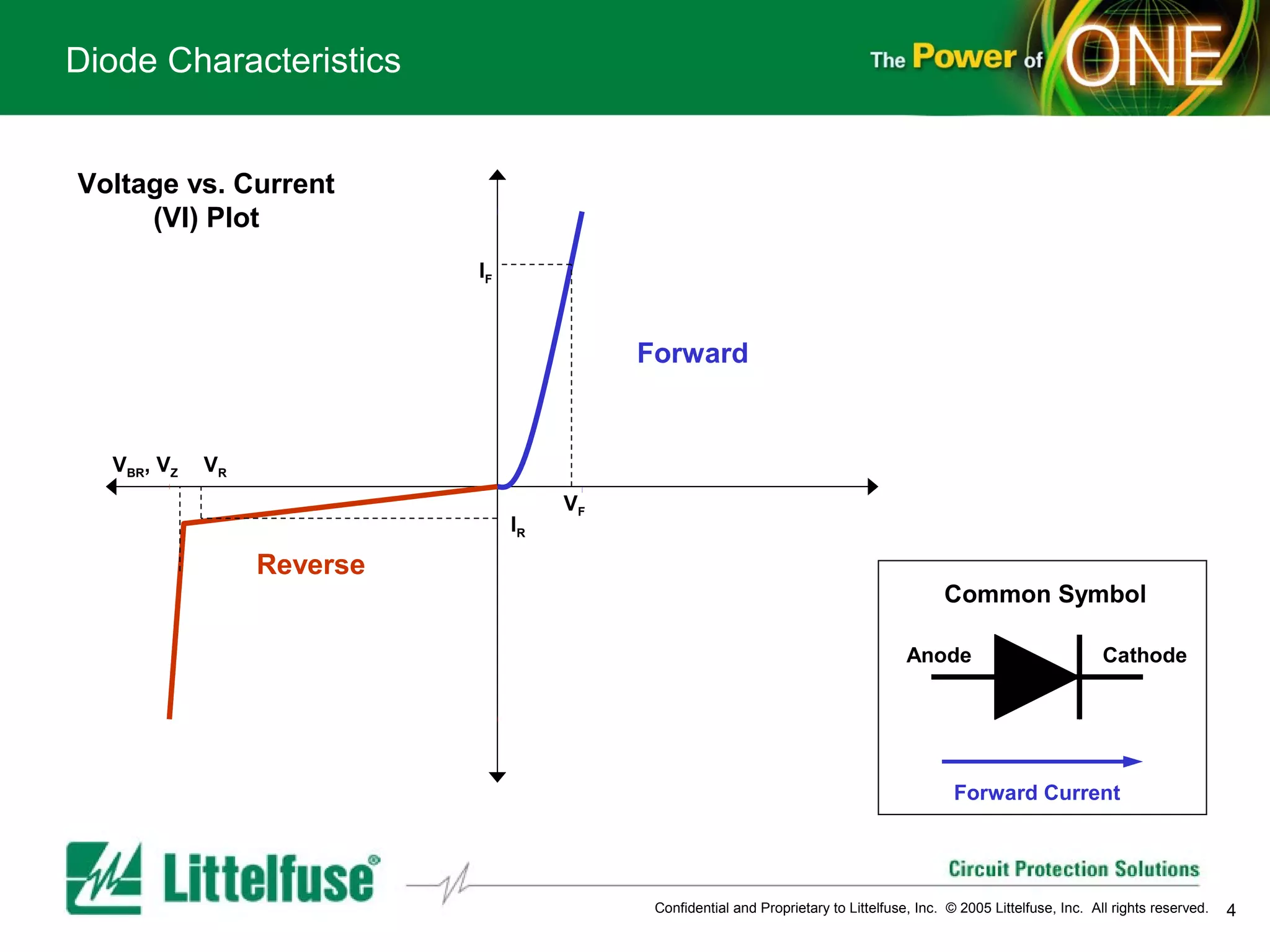
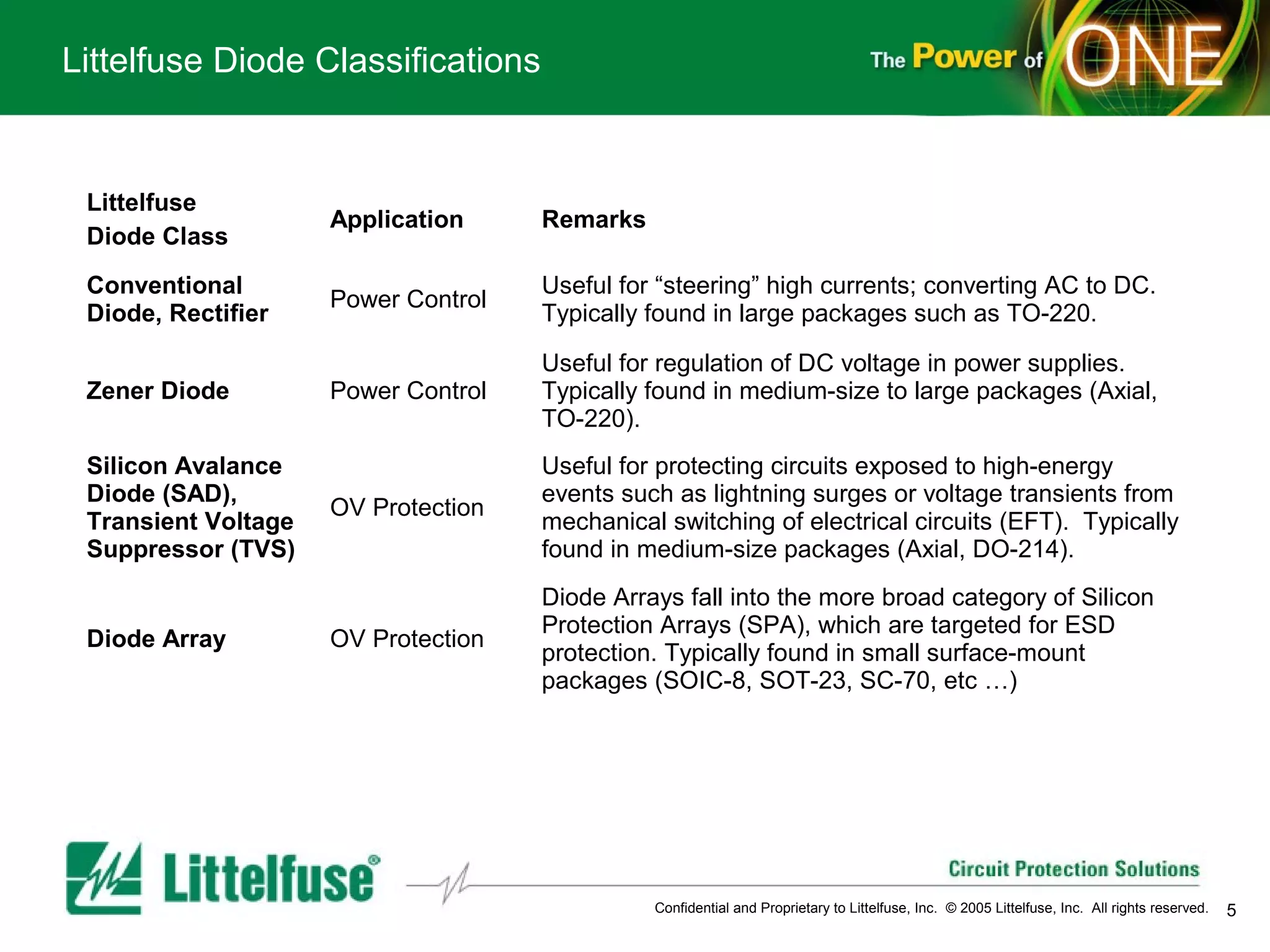
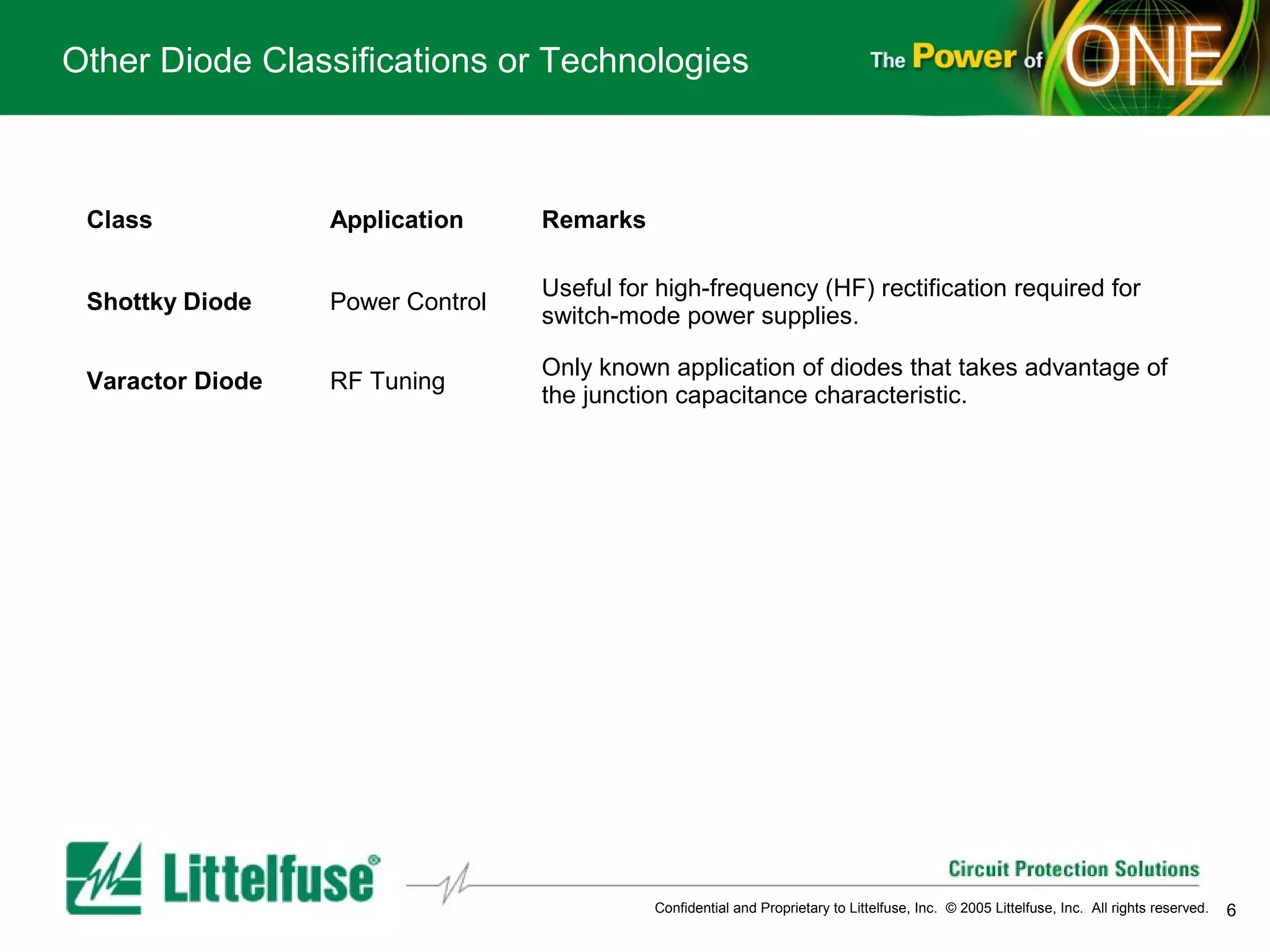
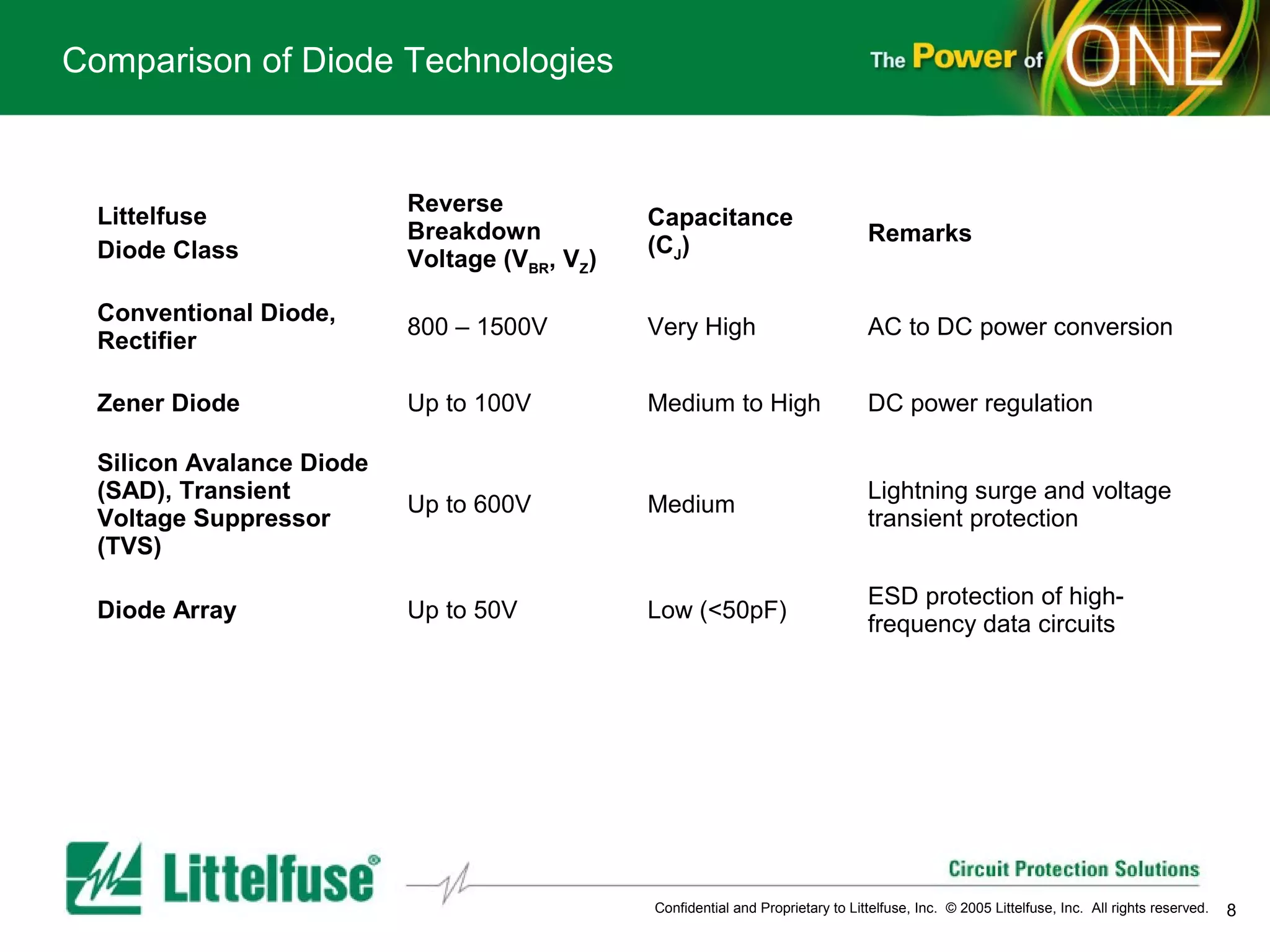
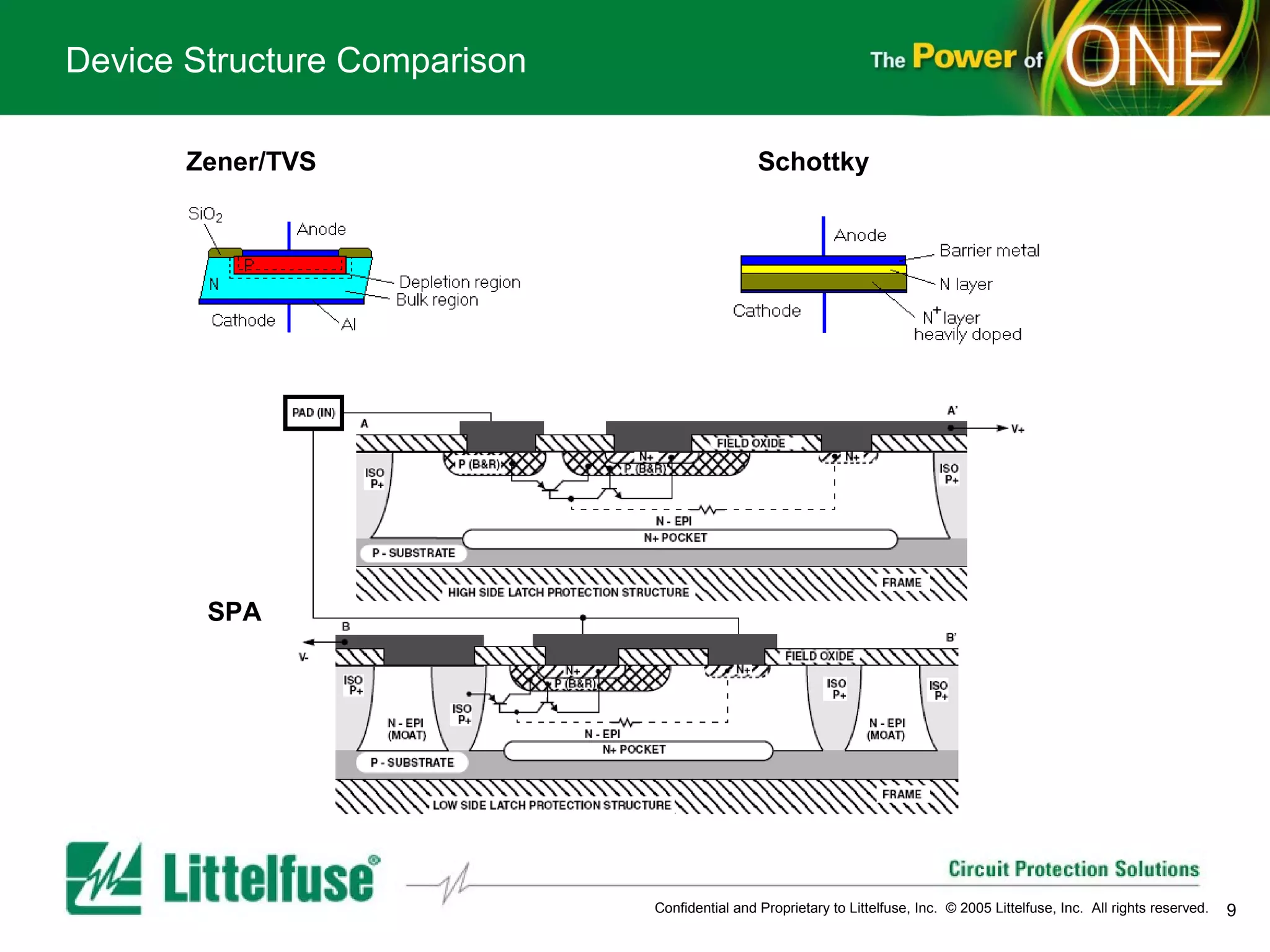
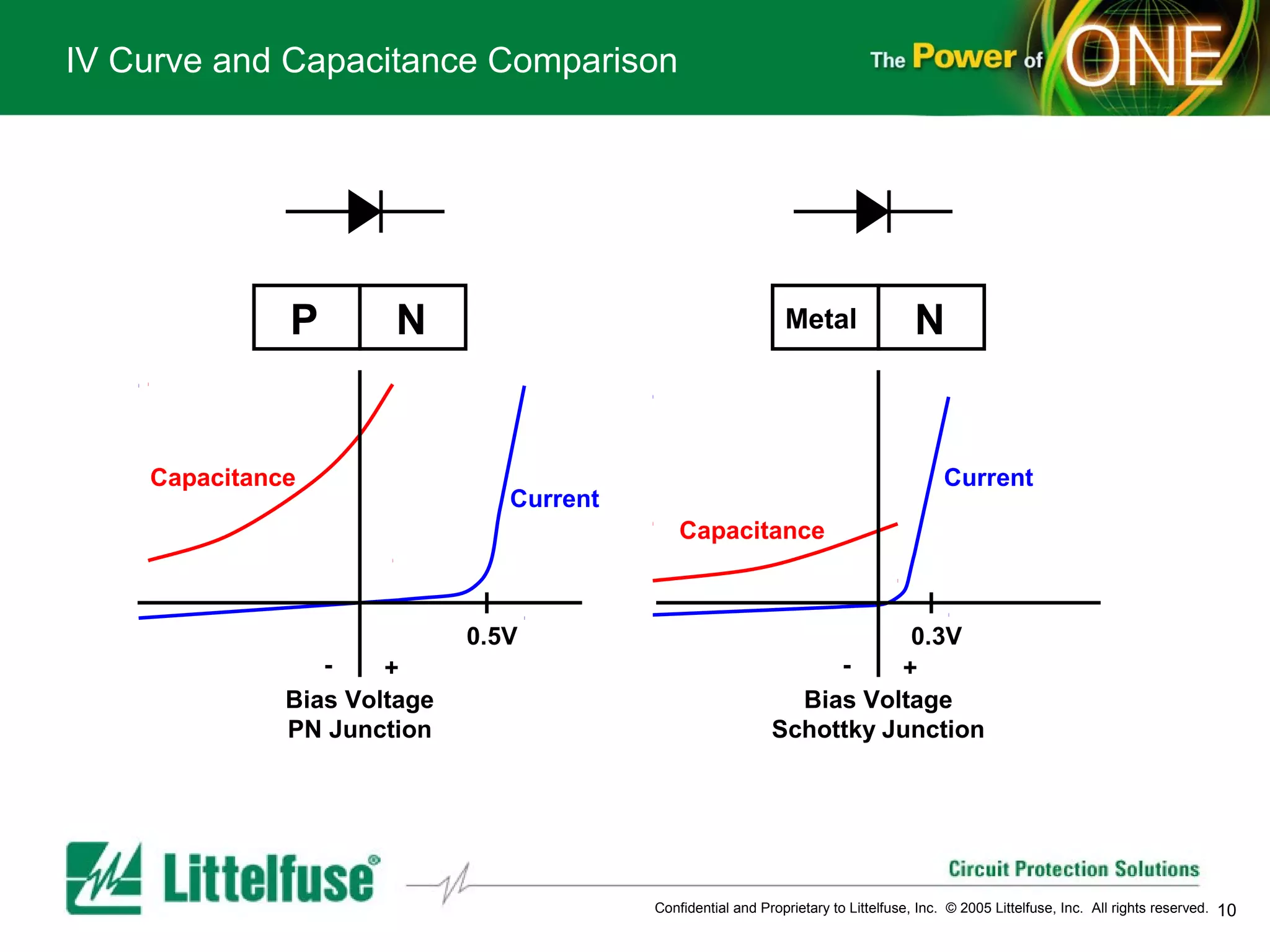
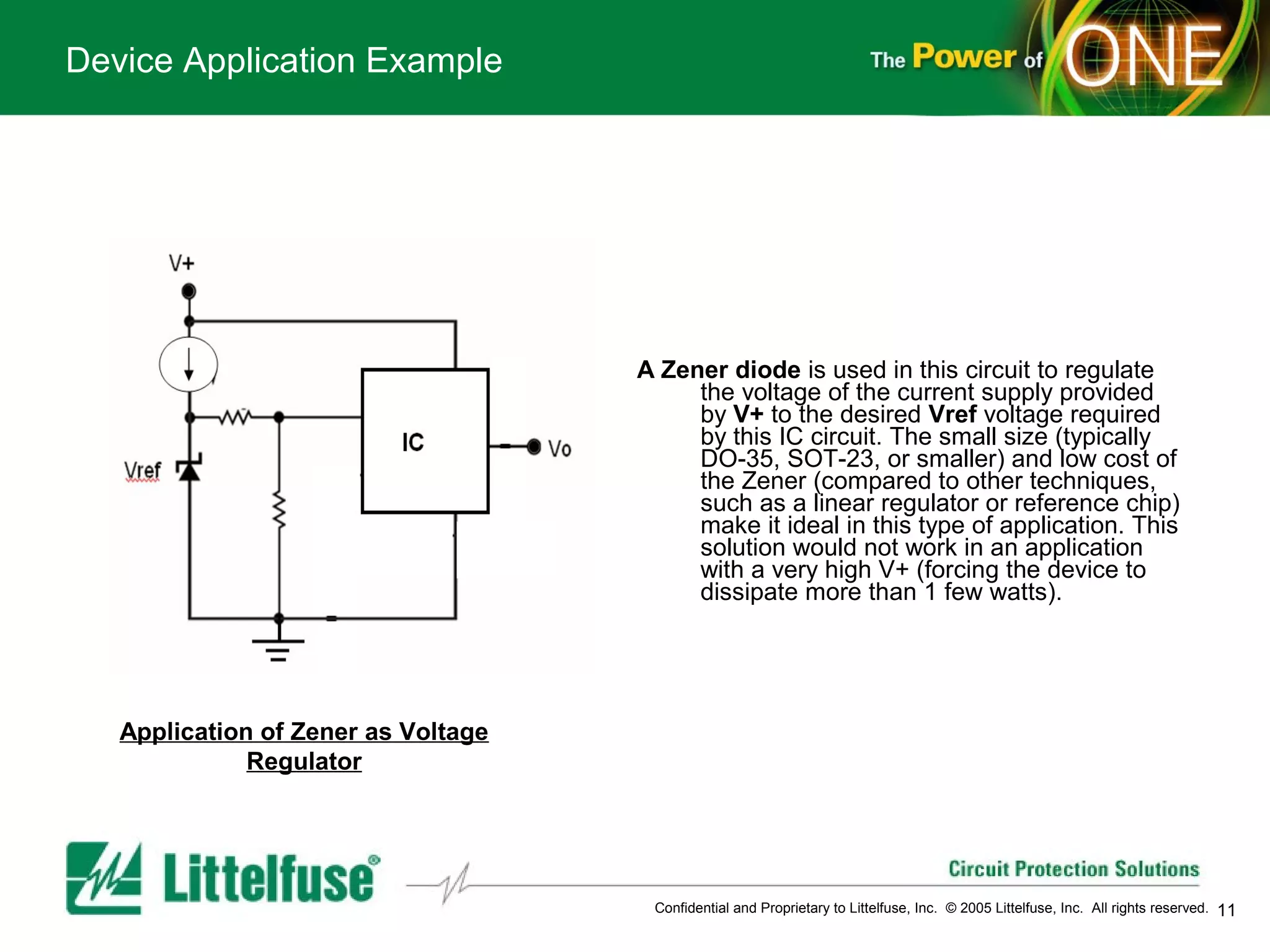
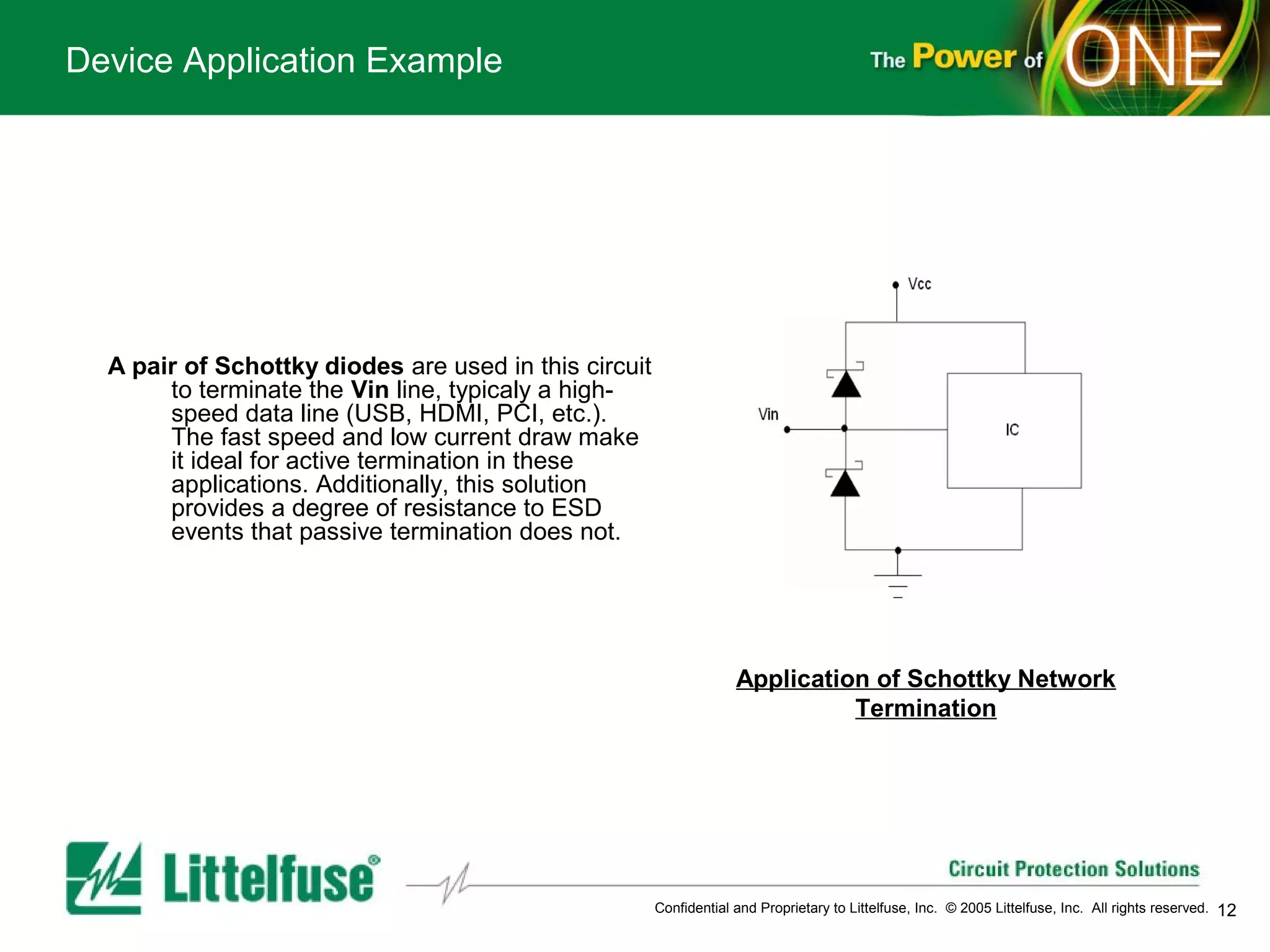
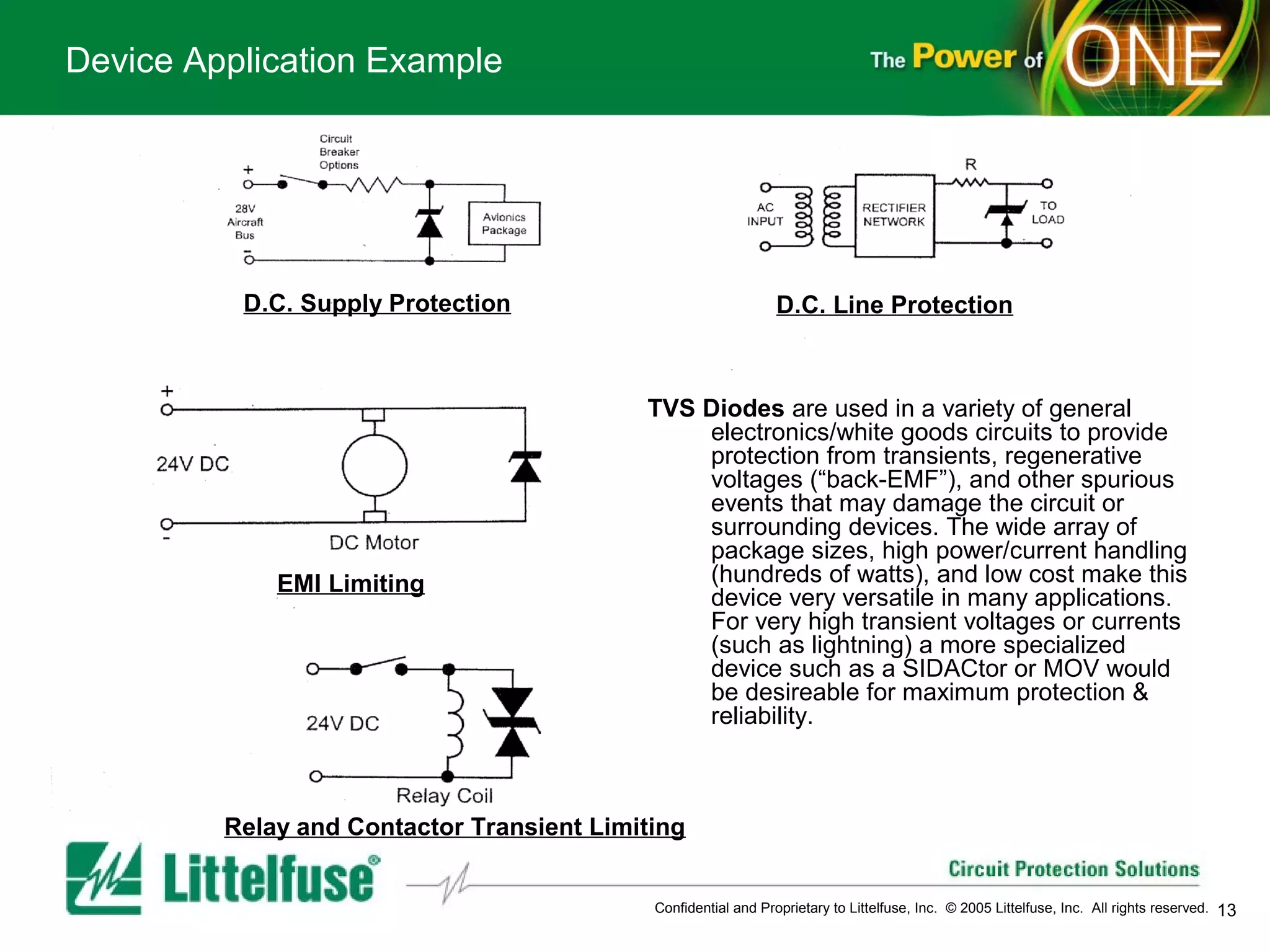
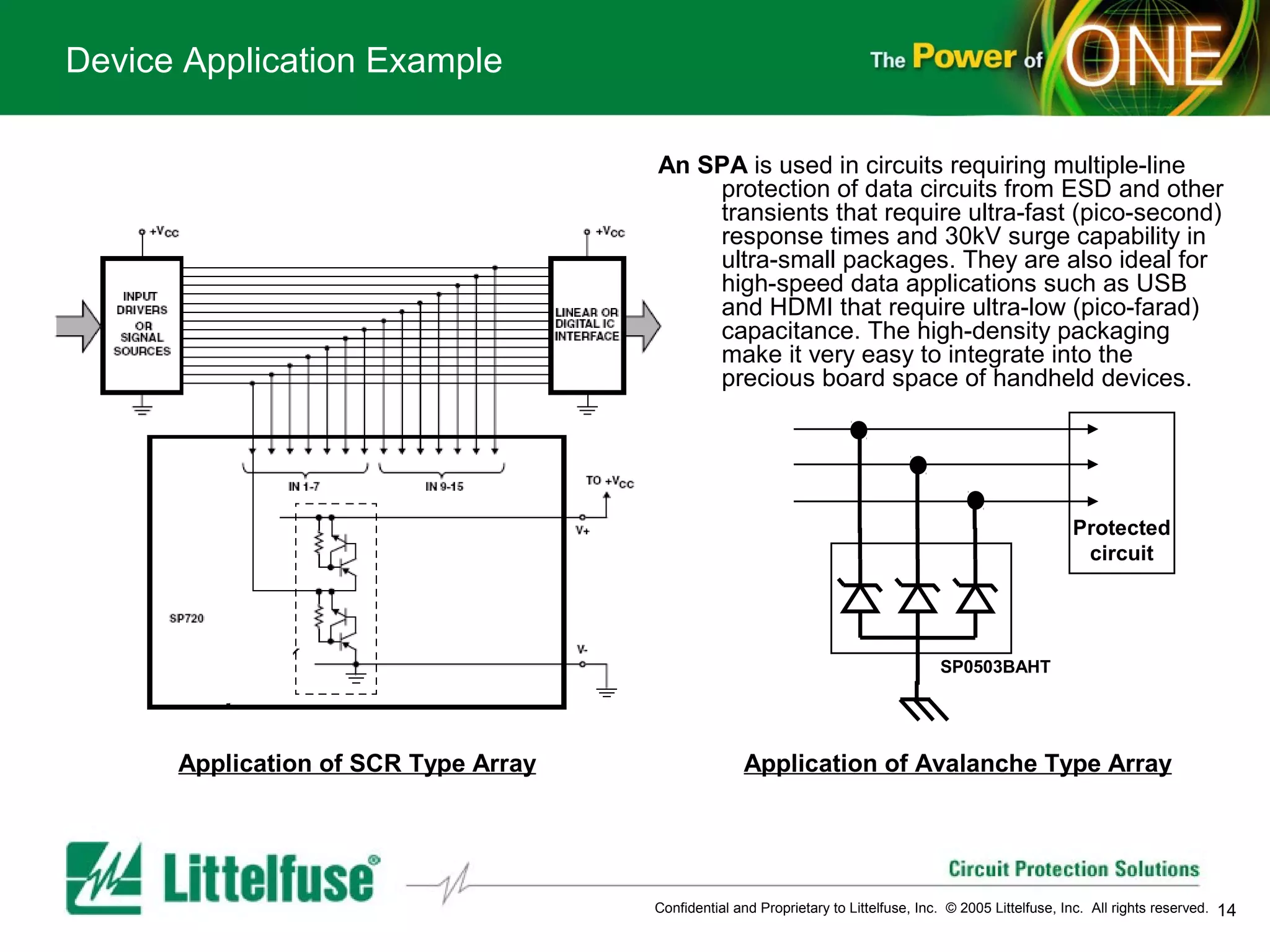
This document provides an overview and comparison of different types of diodes, including their descriptions, characteristics, classifications, structures, and applications. It discusses Schottky diodes, Zener diodes, transient voltage suppressor (TVS) diodes, silicon protection arrays (SPA), and conventional rectifier diodes. For each type, it covers key parameters like forward voltage, reverse breakdown voltage, leakage current, and capacitance. It also provides examples of how different diode types may be used in applications like power regulation circuits, ESD protection, and signal termination networks.