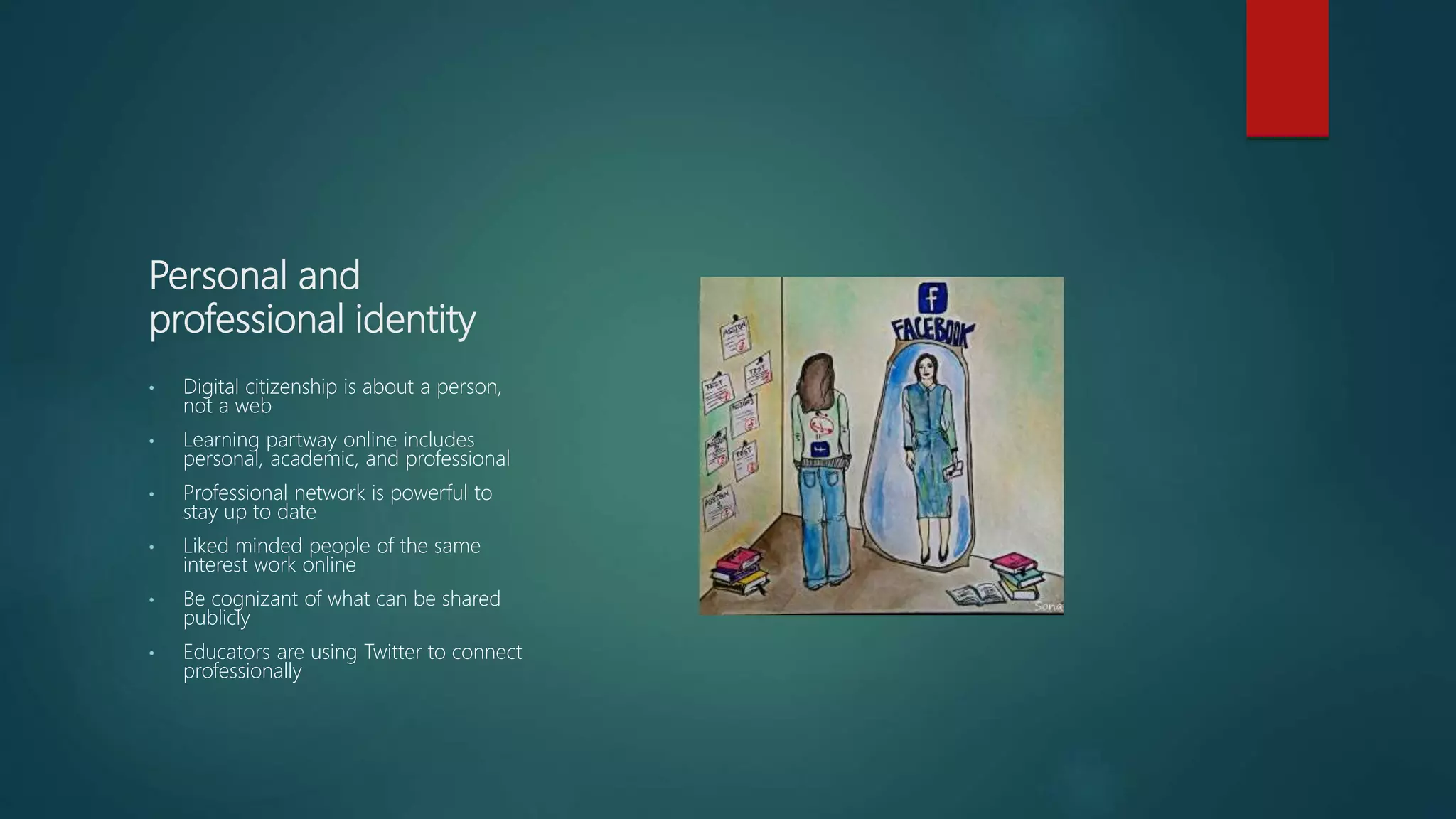
The document discusses several topics related to digital practices in the workplace. It first discusses how the future job market will be unpredictable with jobs being created and eliminated due to technology. It then discusses the importance of digital citizenship and maintaining an online professional identity. It also examines how technology continually changes society and business practices. The document explores how artificial intelligence will significantly impact jobs and tasks. Finally, it discusses how both white and blue collar jobs will be transformed by automation and the rise of creative bots and digital assistants.