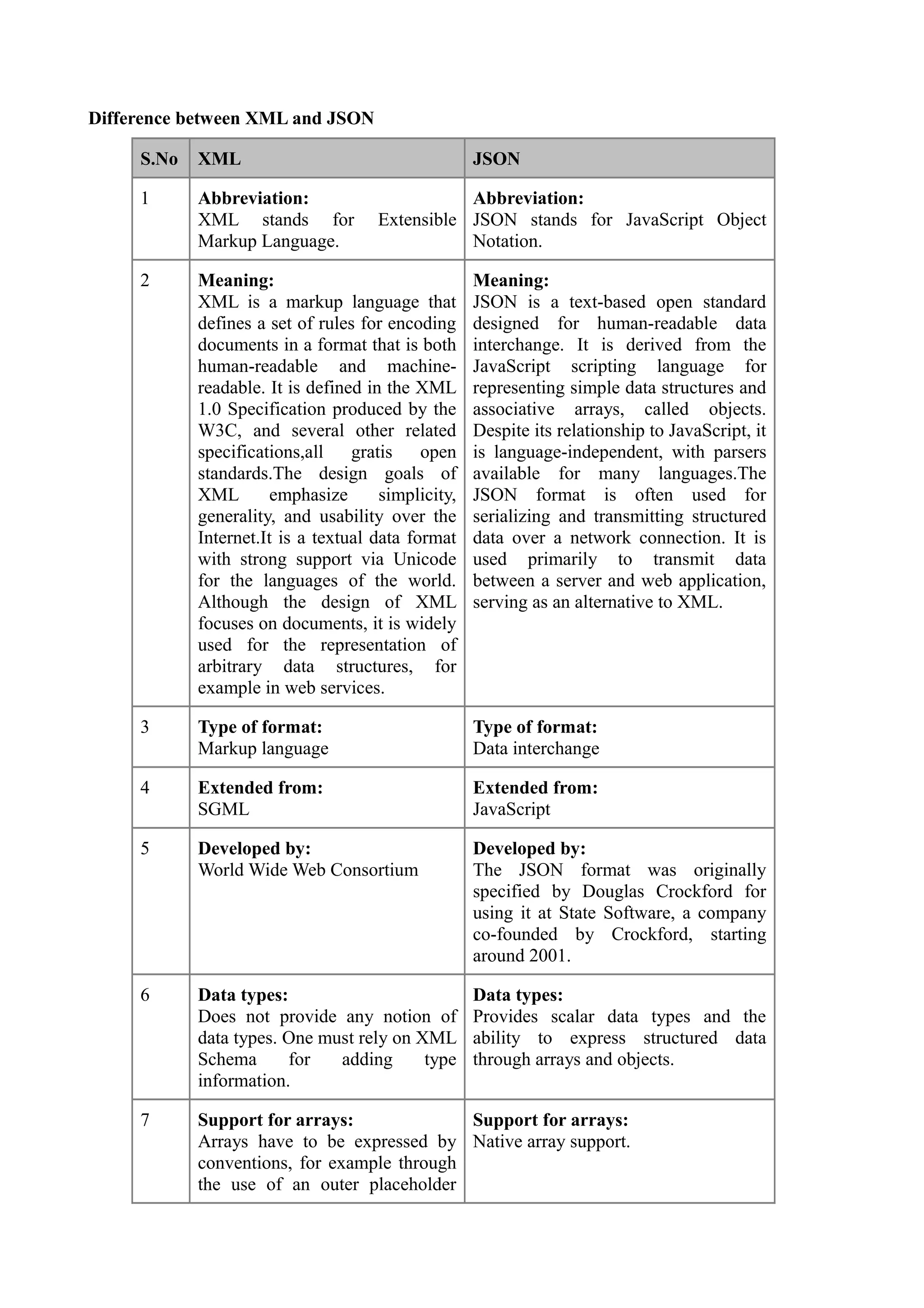
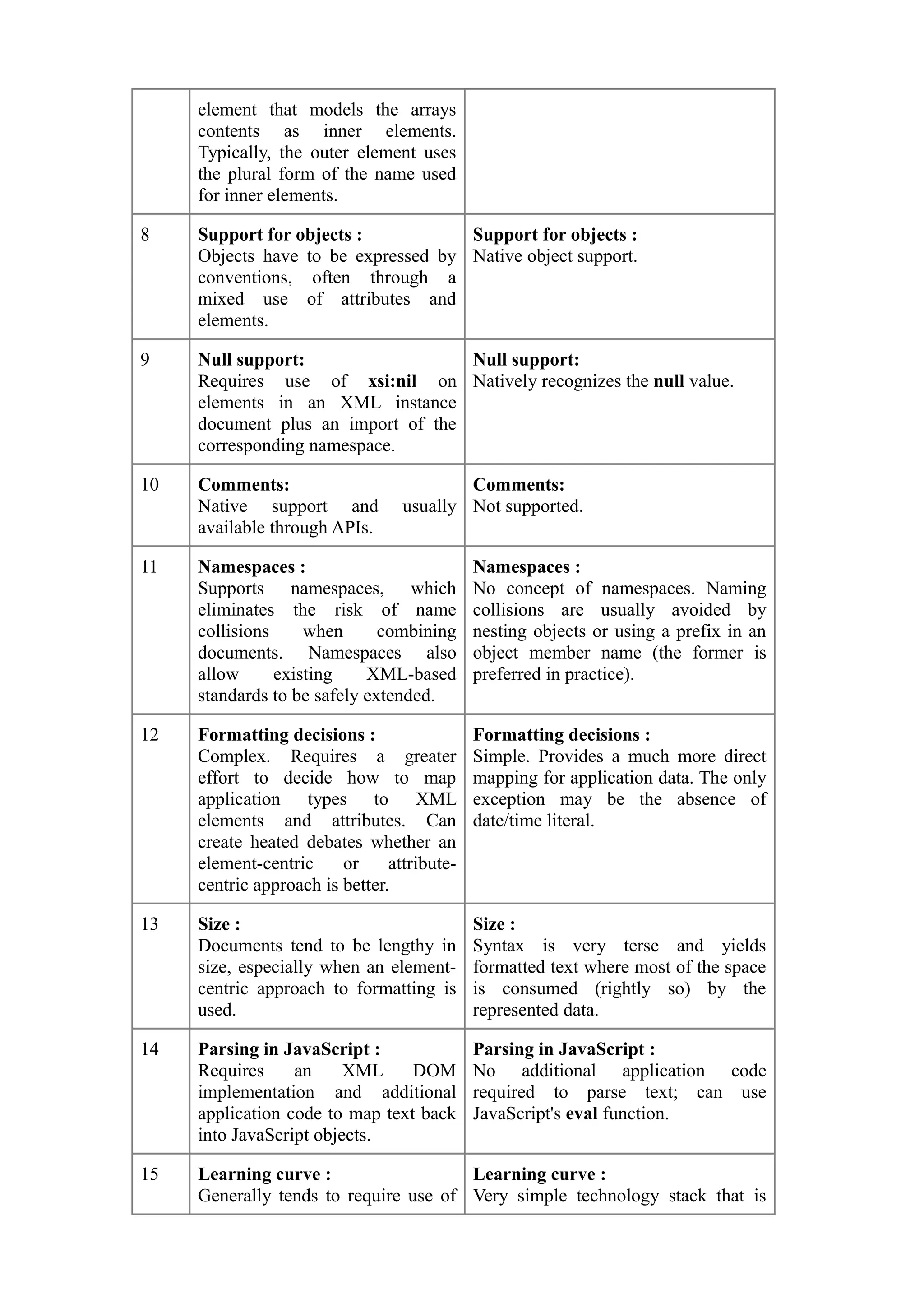
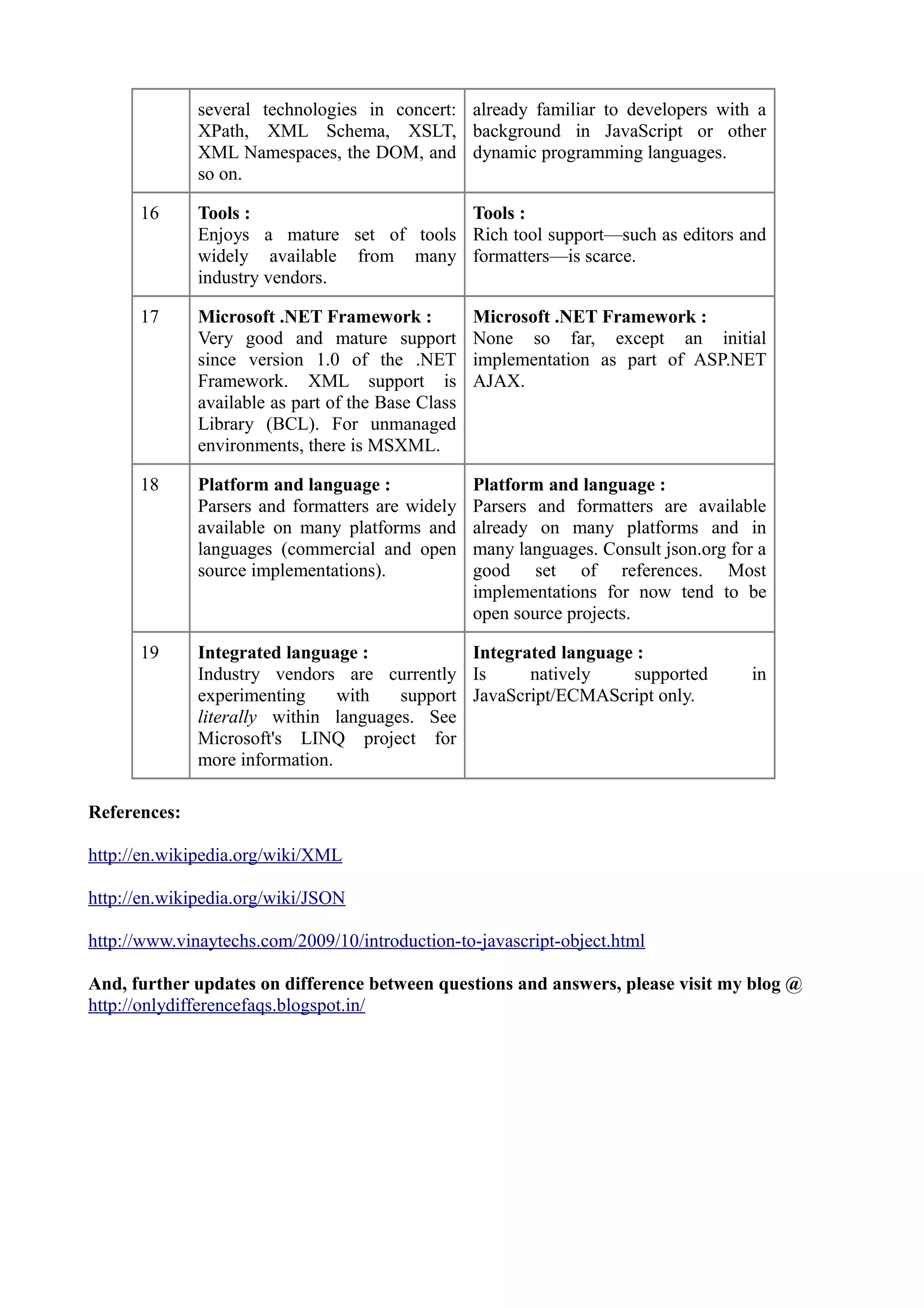
XML and JSON are both commonly used data formats, but they have key differences. XML is an extensible markup language that defines rules for encoding documents in a human and machine-readable format. It was created by the W3C and supports features like namespaces, comments, and complex data types. JSON is a simpler text format used for data interchange, derived from JavaScript. It supports native representation of arrays and objects, and is commonly used to transmit data between servers and web apps. JSON has a simpler syntax than XML and is generally easier for developers to work with.