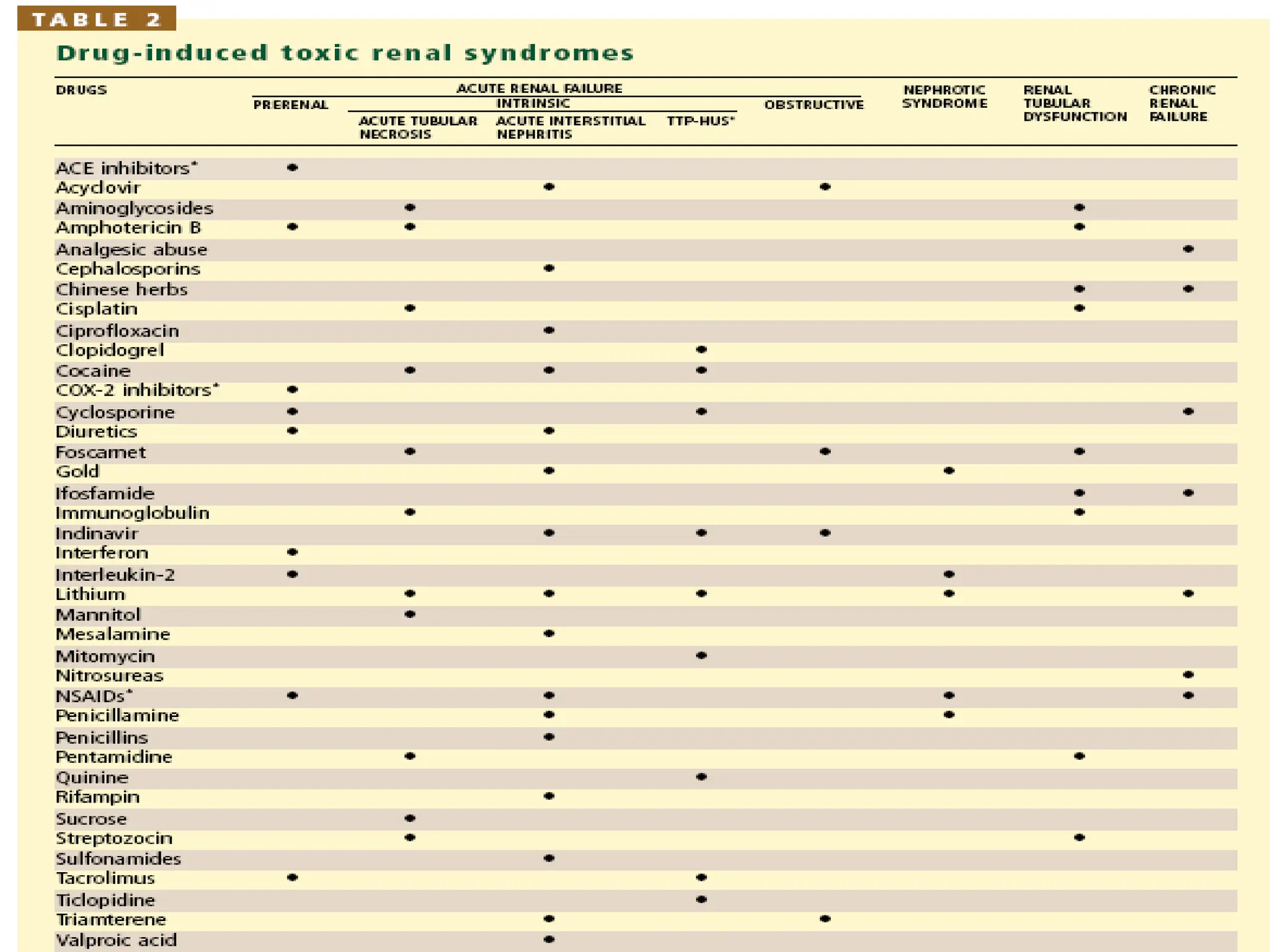
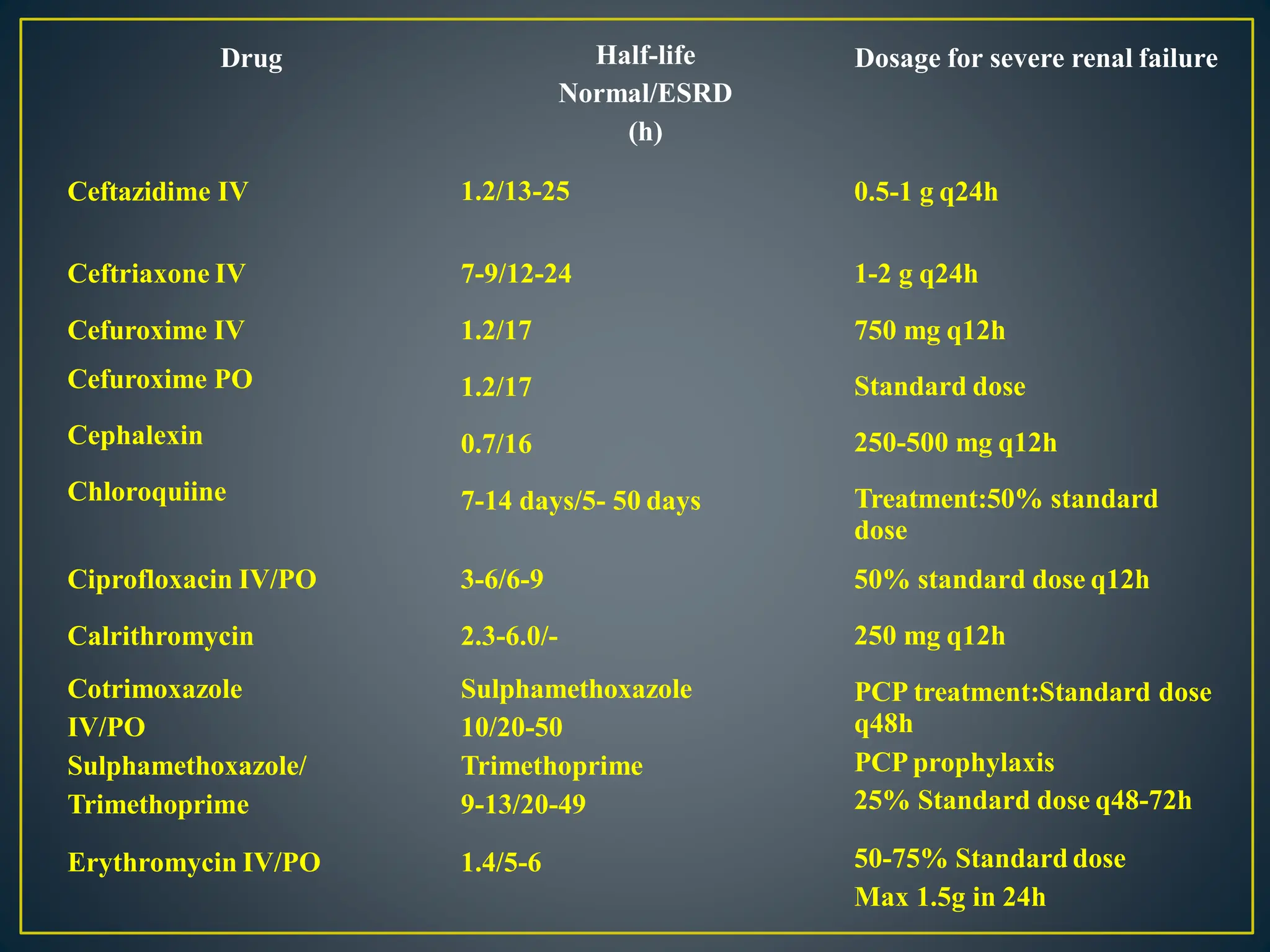
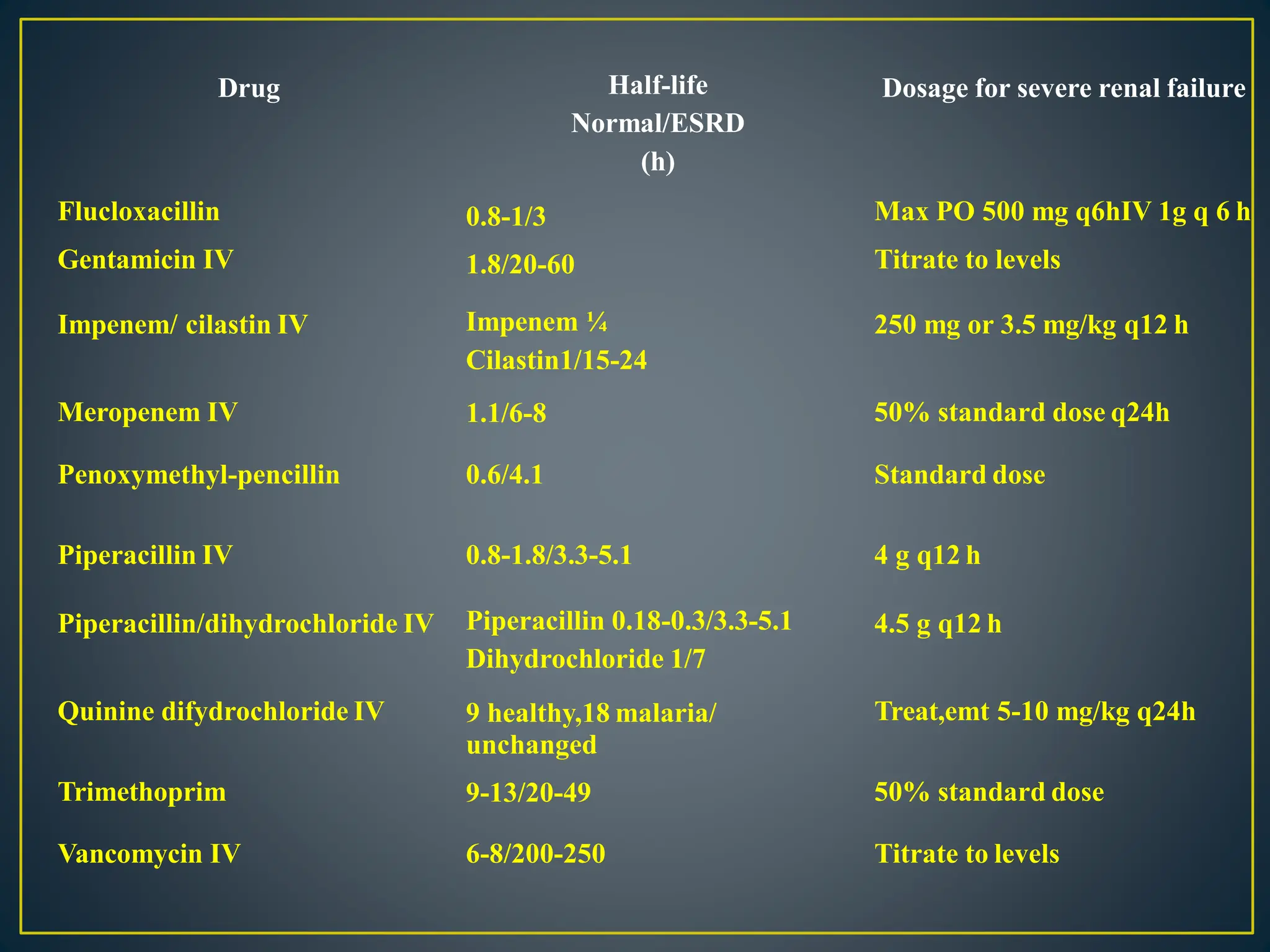
These pharmaceutical agents are capable of being dialyzed through diffusion across dialysis membranes. Whether supplementary dosing is required during or after dialysis depends on the amount of drug that is dialyzed. Several physicochemical characteristics determine a drug's dialyzability, including molecular size, protein binding, volume of distribution, and water solubility. Common drugs that are dialyzable include barbiturates, lithium, isoniazid, salicylates, caffeine, metformin, ethylene glycol, and carbamazepine.