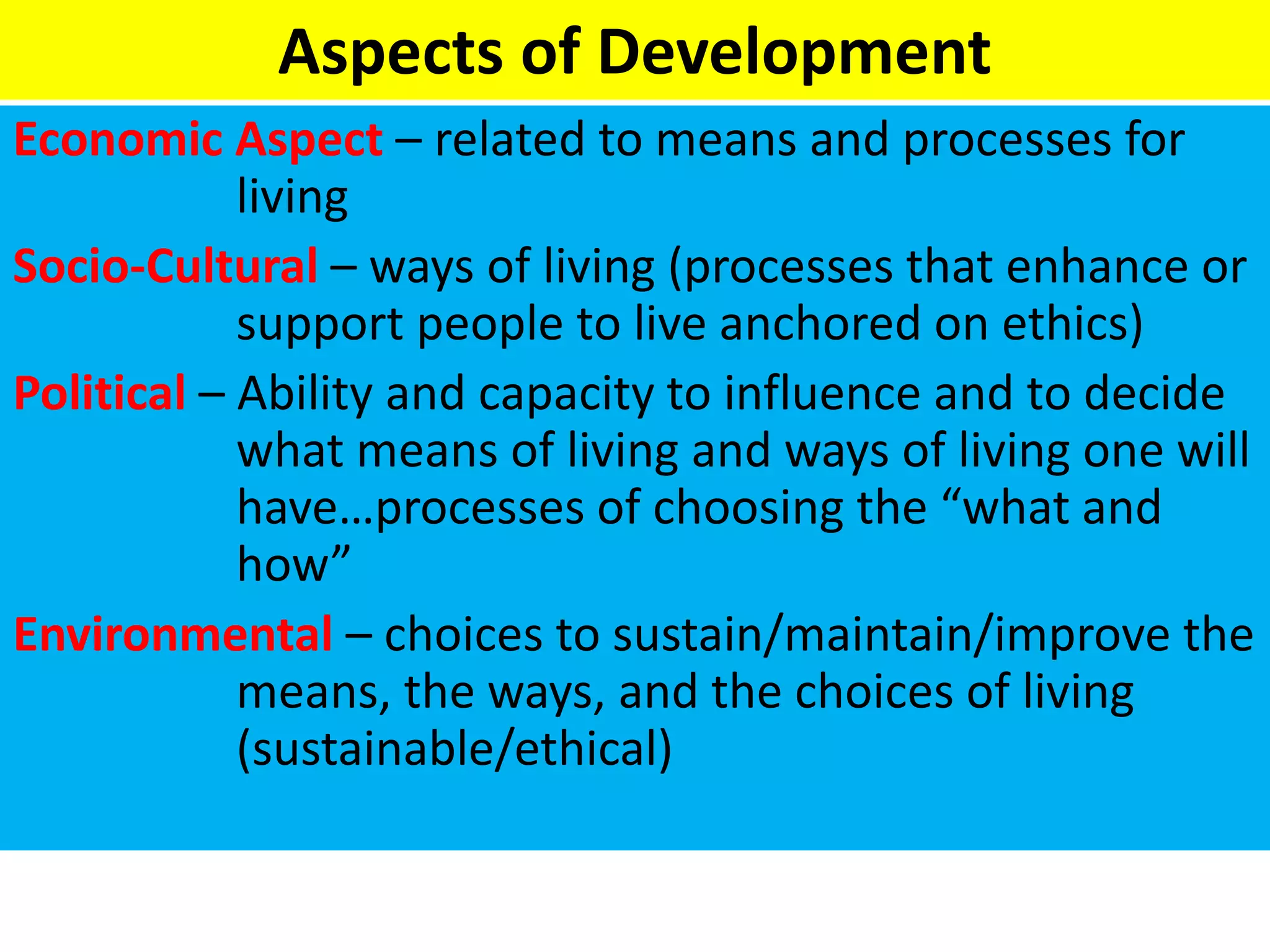
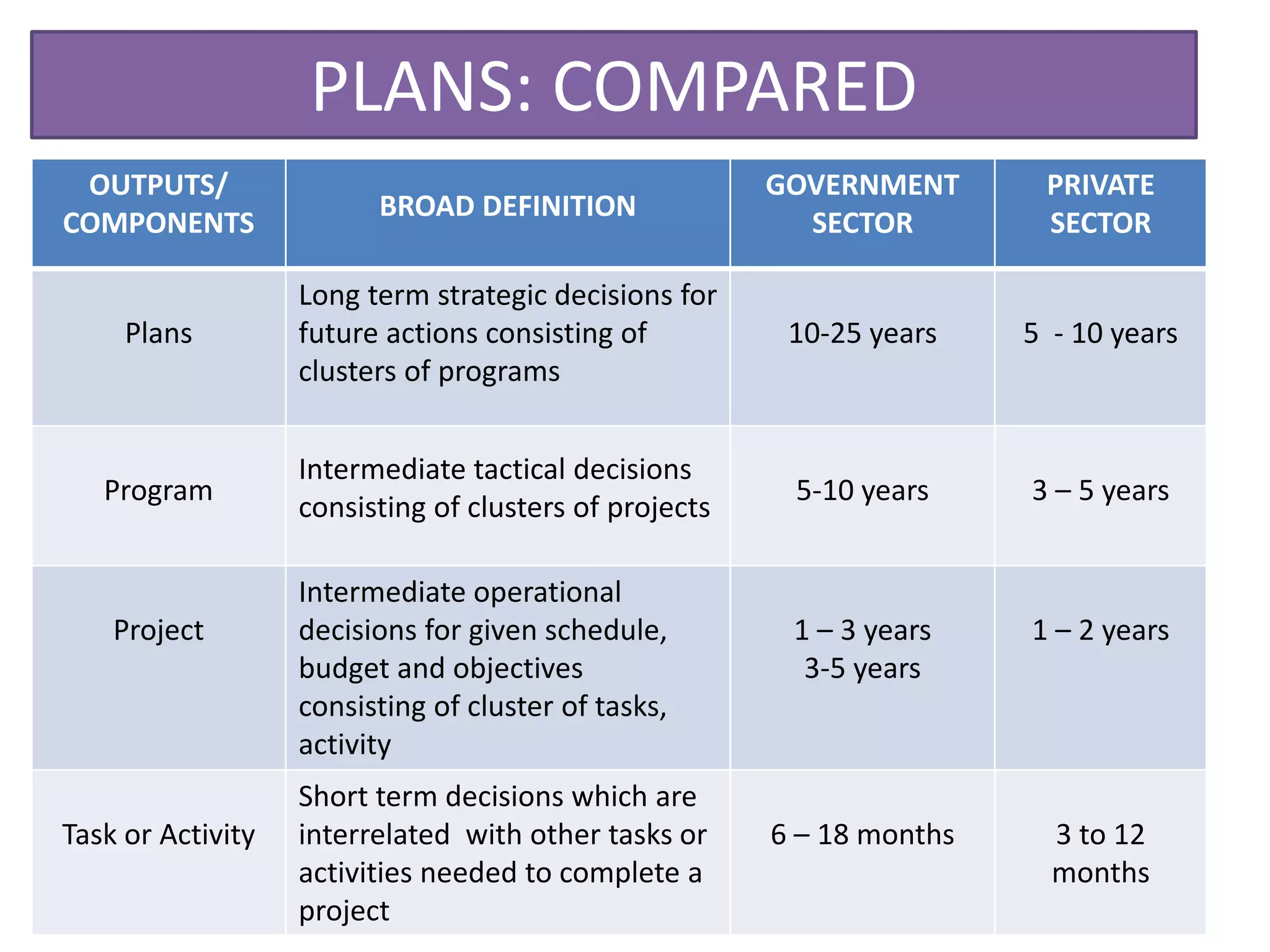
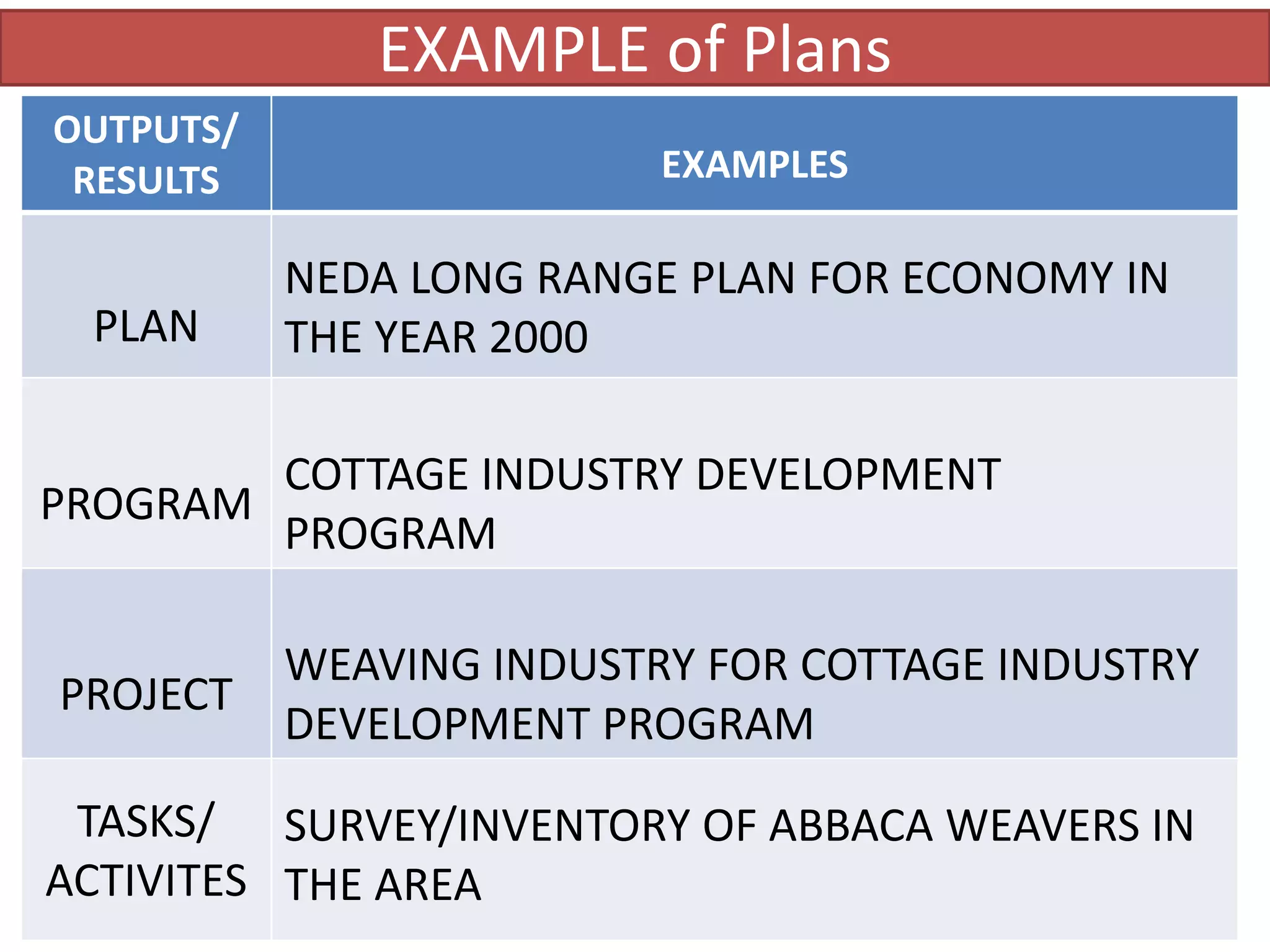
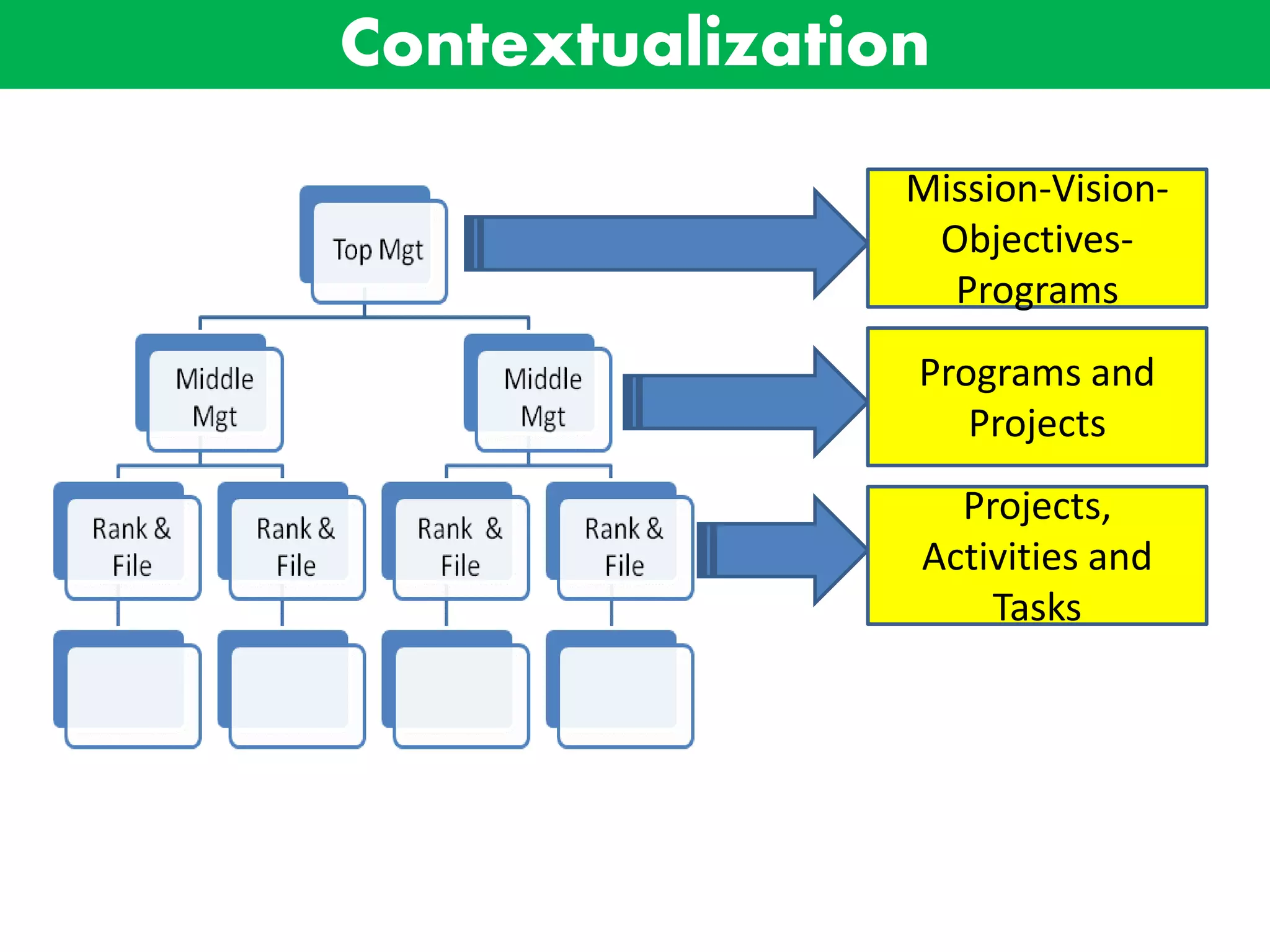
This document discusses basic concepts and frameworks related to project planning and management. It covers aspects of development including economic, socio-cultural, political, and environmental. It also defines key terms like public sector, government sector, public, and public service. Finally, it discusses basic concepts of development planning including long range plans, programs, projects, and contextualizing these within government sector plans.