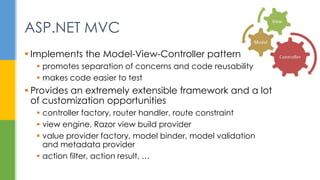
Mark Gu Sungard is developing a next-generation web application aimed at migrating a longstanding asset finance system from Windows to a web-based framework while ensuring extensive customization capabilities. Key challenges include managing per-client customizations, navigating a complex codebase with over 3.5 million lines of code, and addressing the skill gap of existing staff familiar with desktop applications. Strategies to overcome these challenges involve adopting model-view-controller design, using metadata for UI logic, and advocating for TypeScript to facilitate web development.










![Pluggable Website
public interface ISiteRegistration
{
string SiteName { get; }
void RegisterDependencies(IDependencyManager dependencyManager);
void LoadResources(ResourceGateway resourceGateway);
void RegisterIgnoreRoutes(RouteCollection routes);
void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes);
}
[Export(typeof(ISiteRegistration))]
[ExportMetadata("SiteName", SiteConsts.SITE_NAME)]
public class ClientSiteRegistration : ISiteRegistration
{
public string SiteName
{
get { return SiteConsts.SITE_NAME; }
}
...
}
internal static class SiteCompositionManager
{
private static CompositionContainer _compositionContainer;
public static void Initialize()
{
var catalog = new AggregateCatalog();
catalog.Catalogs.Add(new AssemblyCatalog(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly()));
var fullPath = HttpContext.Current.Server.MapPath("~/Sites");
if (Directory.Exists(fullPath))
{
foreach (DirectoryCatalog dirCatalog in GetDirectoryCatalogsRecursive(fullPath))
{
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.AppendPrivatePath(dirCatalog.Path);
catalog.Catalogs.Add(dirCatalog);
}
}
var filteredCatalog = new FilteredCatalog(catalog, ...);
_compositionContainer = new CompositionContainer(filteredCatalog);
}
public static void Compose(params object[] parts)
{
if (_compositionContainer != null)
_compositionContainer.ComposeParts(parts);
}
...
public class MyControllerFactory : DefaultControllerFactory
{
[ImportMany(RequiredCreationPolicy = CreationPolicy.Shared)]
private IEnumerable<Lazy<ISiteRegistration, ISiteRegistrationMetadata>> _sites;
public MyControllerFactory()
{
SiteCompositionManager.Compose(this);
...
public class MyRazorViewEngine : RazorViewEngine { ... }
[BuildProviderAppliesTo(BuildProviderAppliesTo.All)]
public class MyRazorBuildProvider : RazorBuildProvider { ... }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developingnext-genenterprisewebapplication-140528171524-phpapp02/85/Developing-Next-Gen-Enterprise-Web-Application-12-320.jpg)




![ .NET attributes attached to properties to
declaratively express UI logic
Metadata
[ReadOnly(true)]
public string A { get; set; }
[Visible(Property="A", Is="Foo")]
public int B { get; set; }
[OnChange(Send="Currency,Amount", Refresh="Rate,CalculationDate")]
public string D { get; set; }
[Enabled(Property="B", IsGreaterThan=1)]
public string C { get; set; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developingnext-genenterprisewebapplication-140528171524-phpapp02/85/Developing-Next-Gen-Enterprise-Web-Application-17-320.jpg)


![ .NET attributes aren’t expressive enough
only suitable for extremely simple conditions
difficult to read and understand
Lots of magic strings
difficult to refactor and results in run-time error
Same logic needs to be repeated for multiple properties
Slows page load & increase memory usage (IE8)
Problems Introduced by Metadata
[Visible(Property="Amount" IsGreaterThan=100 And=true
Property2="Code" Property2StartsWith="ISO-")]
public int A { get; set; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developingnext-genenterprisewebapplication-140528171524-phpapp02/85/Developing-Next-Gen-Enterprise-Web-Application-20-320.jpg)
![ Attributes now only specifies the name of a method that
provides the actual logic
The actual logic can now be written in plain C#
statements
Use Roslyn & code generation to parse method bodies
and generate equivalent JavaScript statements
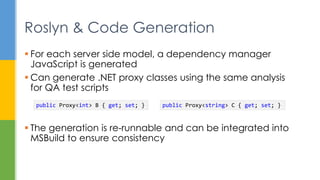
Roslyn & Code Generation
[Visible("IsBVisible")]
public int B { get; set; }
[Enabled("IsCEnabled")]
public string C { get; set; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developingnext-genenterprisewebapplication-140528171524-phpapp02/85/Developing-Next-Gen-Enterprise-Web-Application-21-320.jpg)
![Roslyn & Code Generation
[Enabled(“IsDepartmentTypeEnabled")]
public DepartmentType DepartmentType { get; set; }
public bool IsDepartmentTypeEnabled()
{
return WarehouseState == WarehouseState.SelfWH && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(DepartmentName);
}
data.DepartmentType.extend({
enable: () => {
return data.WarehouseState() === Models.WarehouseState.SelfWH && data.DepartmentName();
}
});
ko.extenders.enable = (function (target, evaluator) {
target.enable = ko.computed(evaluator);
return target;
});
ko.bindingHandlers['meta'] = {
init: function (element, valueAccessor, allBindingsAccessor, viewModel, bindingContext) {
var value = valueAccessor();
if (!ko.isObservable(value)) {
return;
}
if (_.has(value, 'enabled')) {
ko.applyBindingsToNode($(element).find('.form-control')[0],
{ enable: value['enable'] },
bindingContext);
}
}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developingnext-genenterprisewebapplication-140528171524-phpapp02/85/Developing-Next-Gen-Enterprise-Web-Application-22-320.jpg)










![ High level constructs: module, interface, class, enum
Accessibility: public, private, protected
Inheritance: implements, extends, super, overrides
Types: boolean, number, string, null, any, {}
Anonymous type support: { id: number; name: string }
Generic support: Array<string>, Promise<T>
Casting: id: number = <number>obj.Id;
Function overloading and optional parameters: (extraData?: any)
Variable amounts of arguments: format(pattern: string, …args: any[])
Lambda expression: (str1: string, str2: string) => str1 + str2
CommonJS and AMD support: import, export, require
TypeScript – Language Features](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developingnext-genenterprisewebapplication-140528171524-phpapp02/85/Developing-Next-Gen-Enterprise-Web-Application-34-320.jpg)


