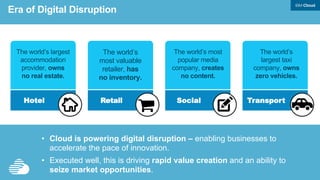
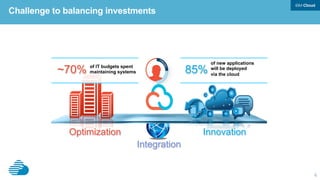
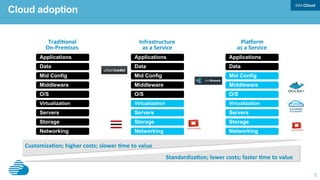
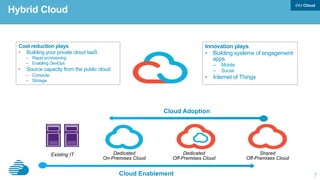
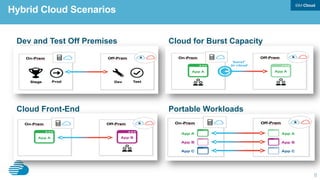
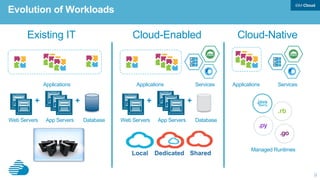
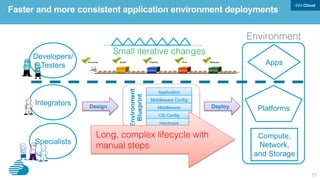
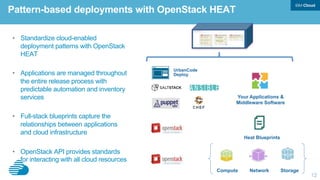
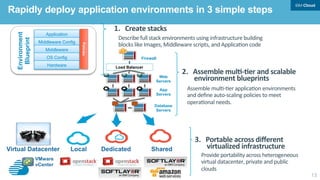
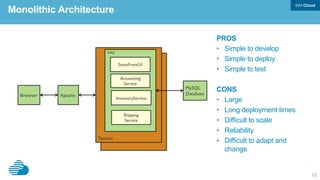
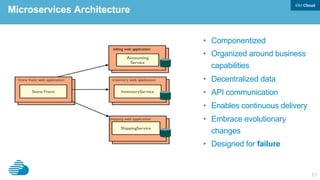
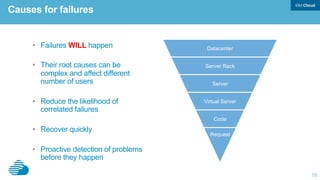
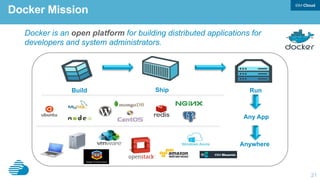
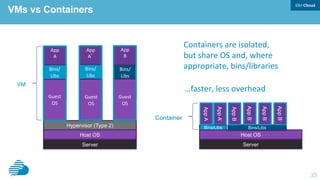
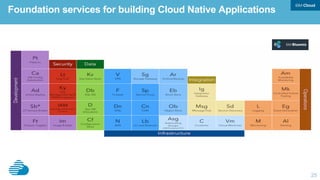
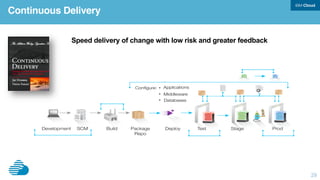
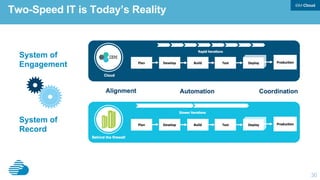
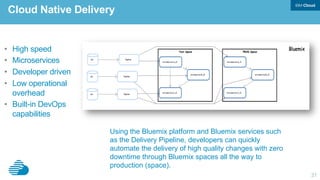
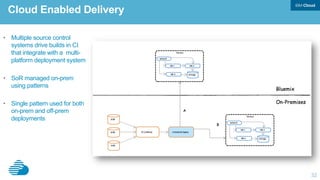
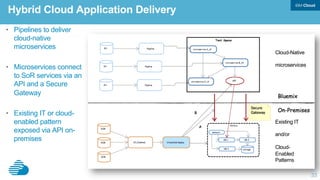
This document discusses developing hybrid cloud applications. It notes that cloud is enabling digital disruption and rapid innovation. It then discusses challenges around balancing investments in innovation and optimization. It outlines the evolution from traditional on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based platforms and services. It also summarizes strategies for using hybrid cloud to reduce costs while enabling innovation through new applications and integration with existing IT.