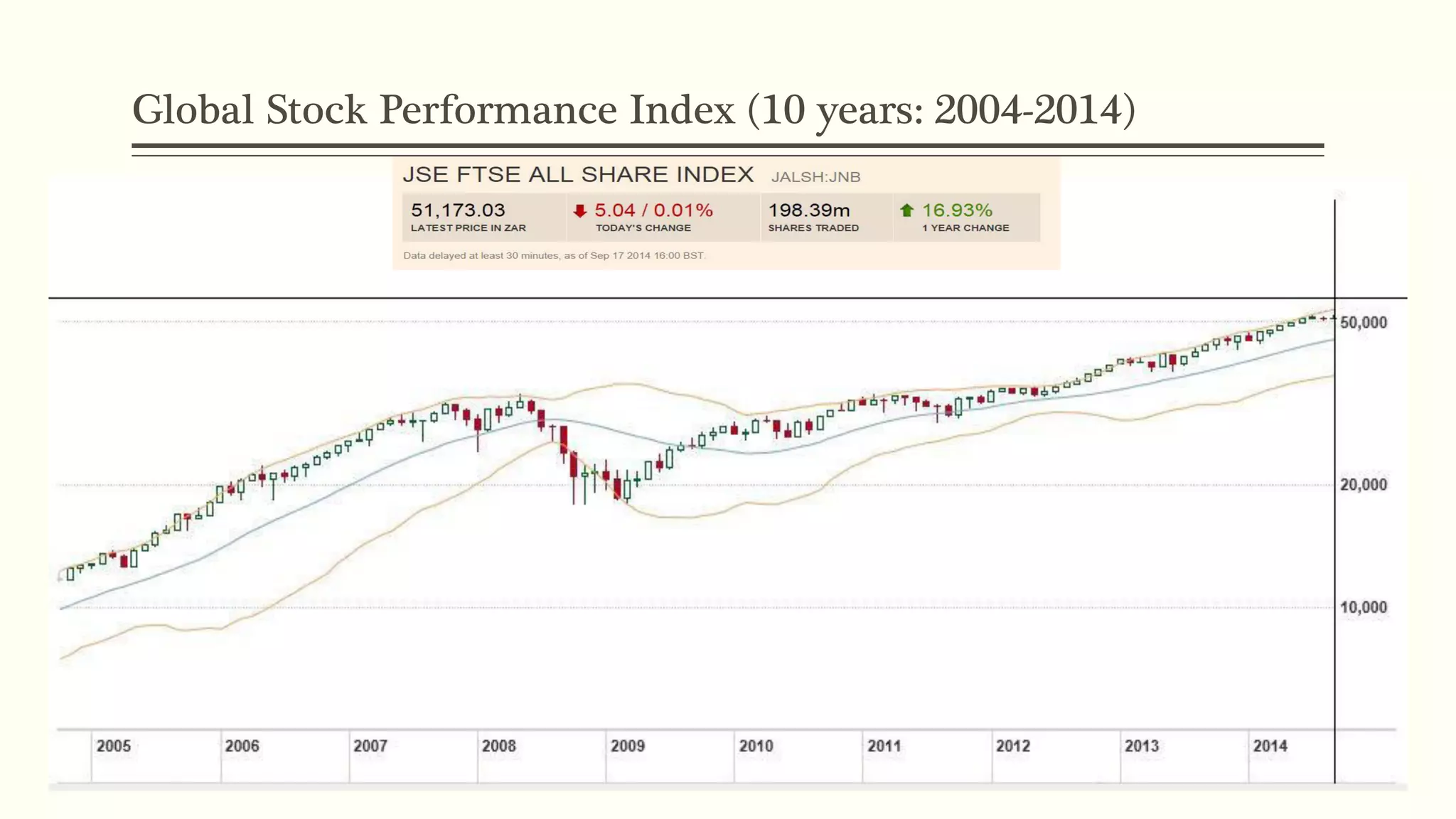
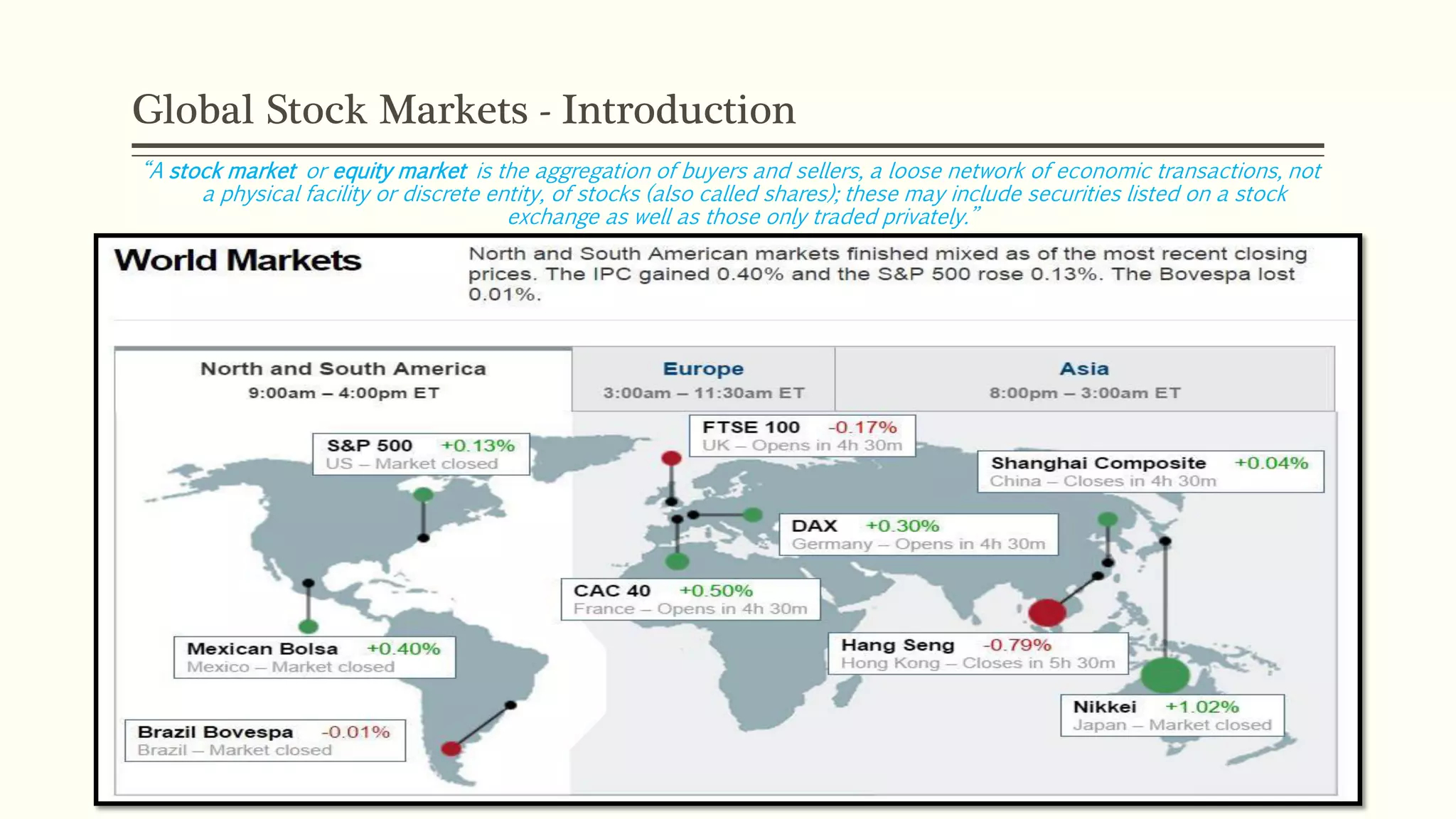
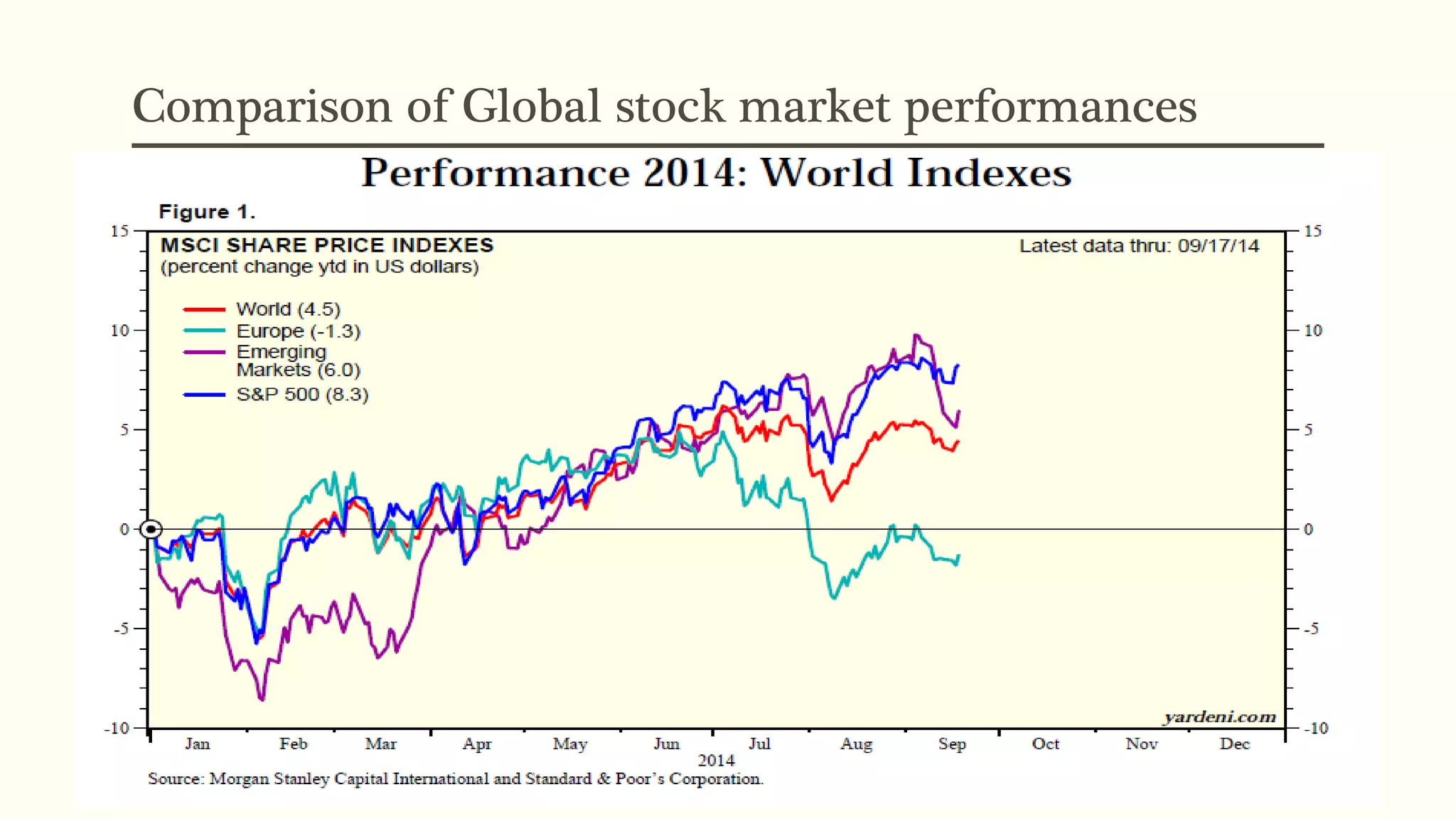
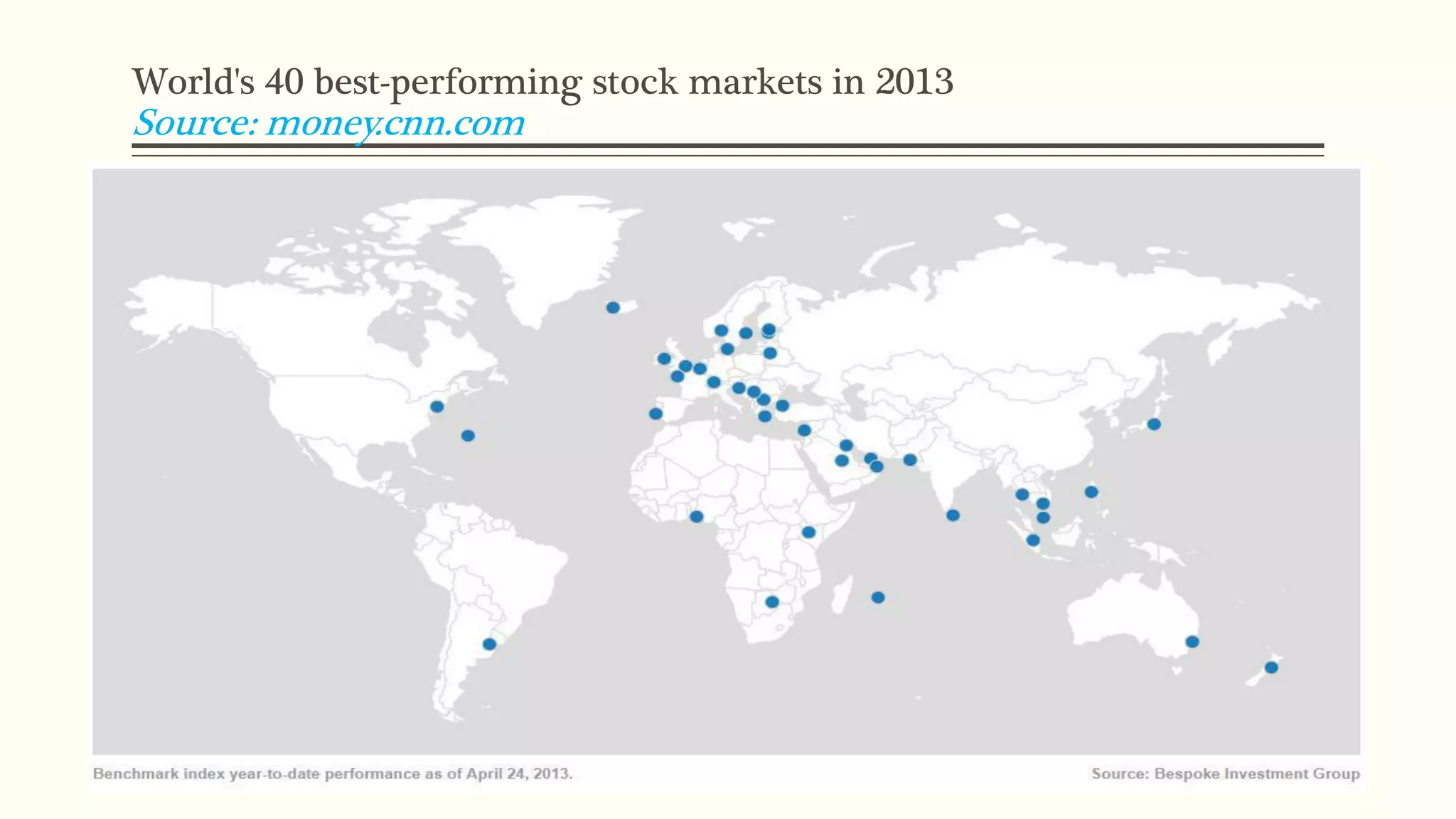
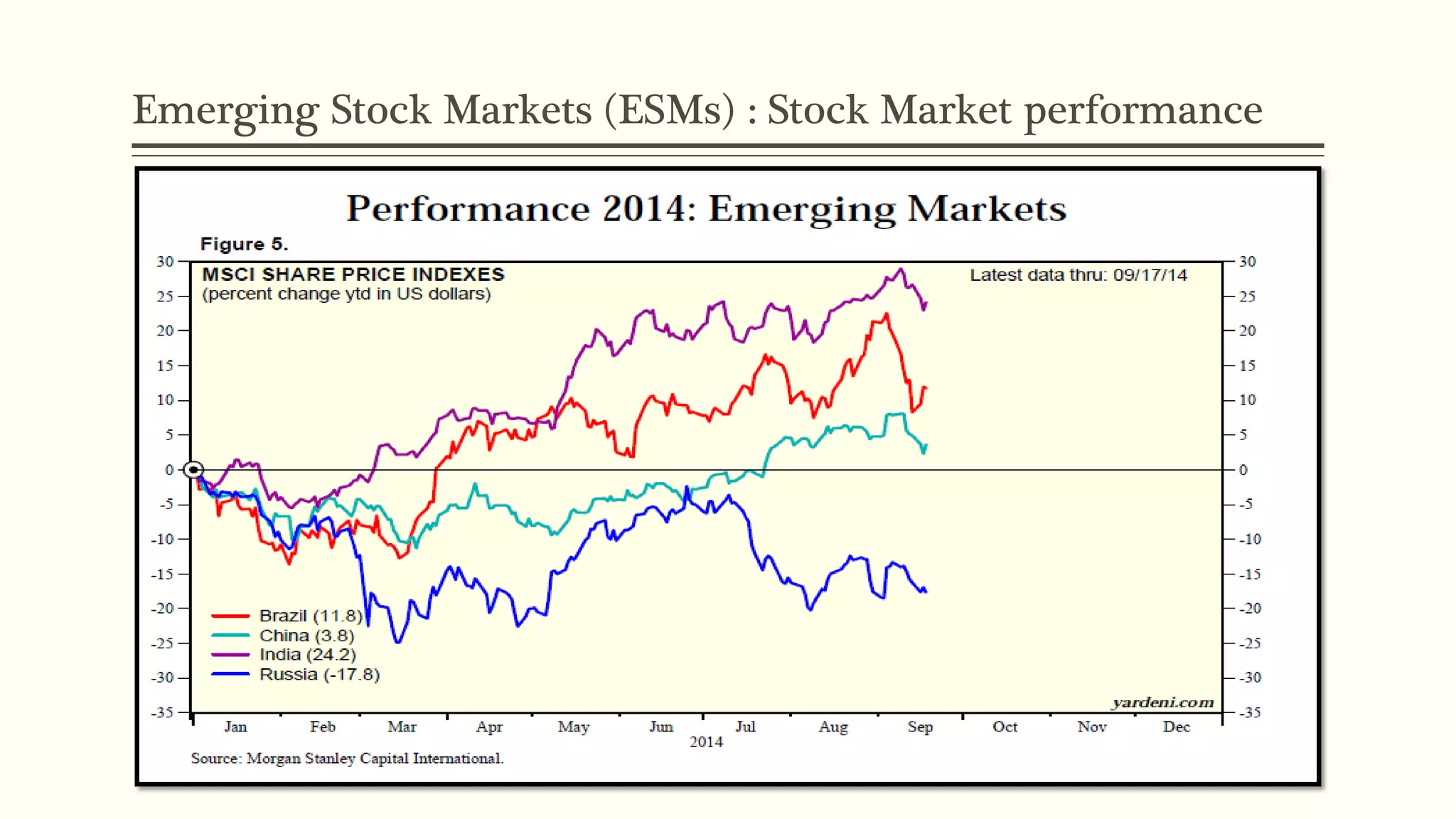
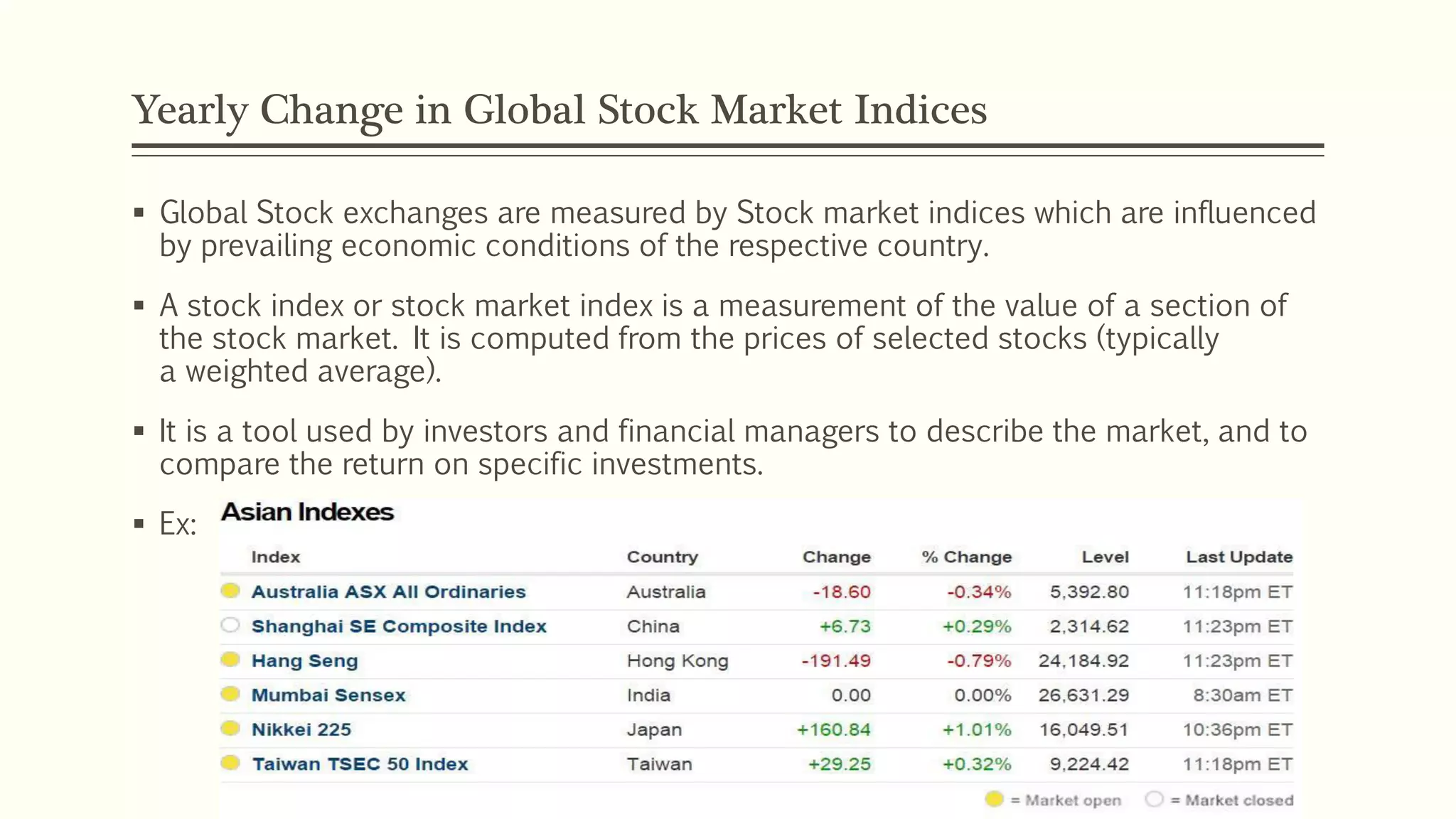
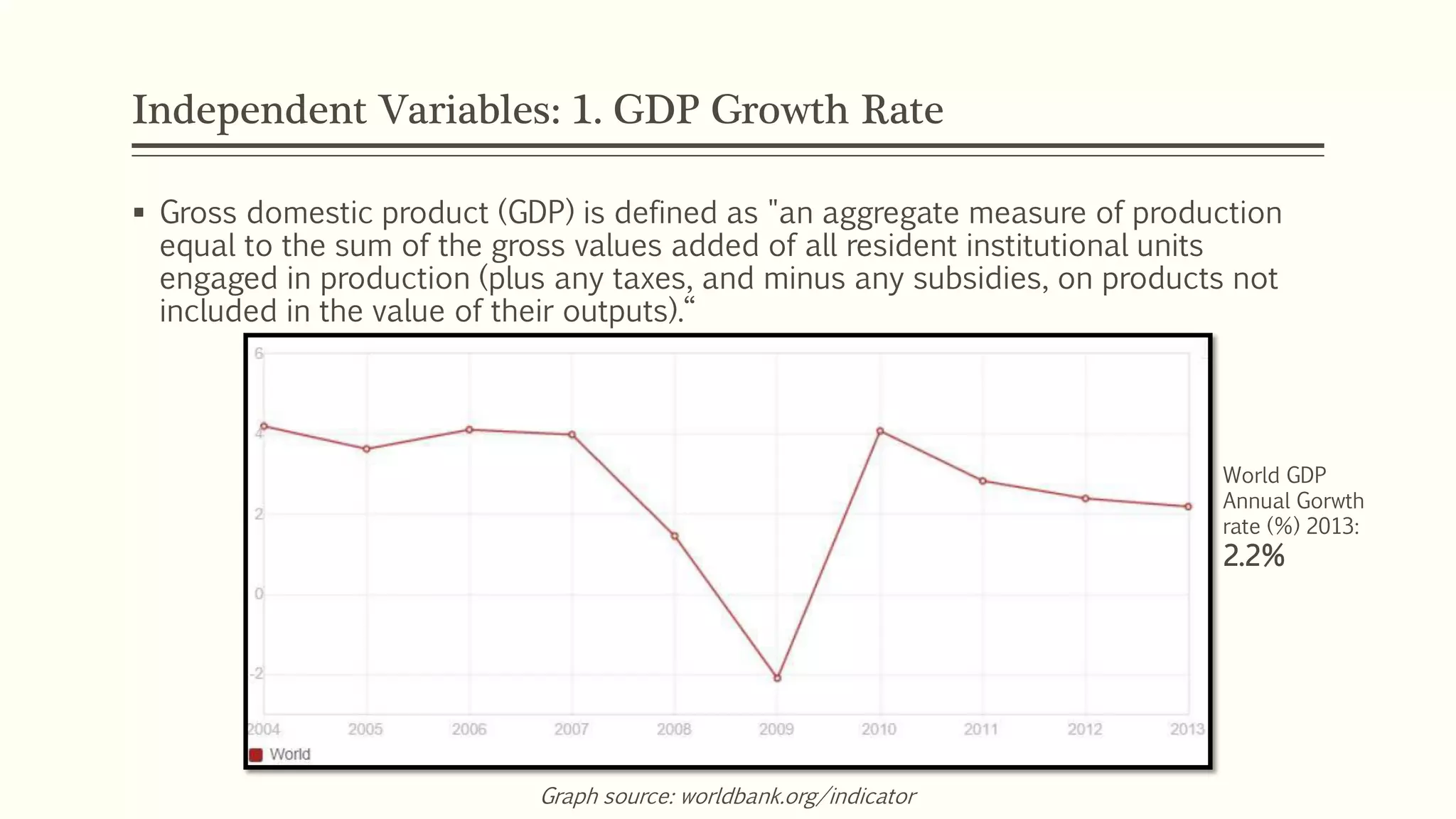
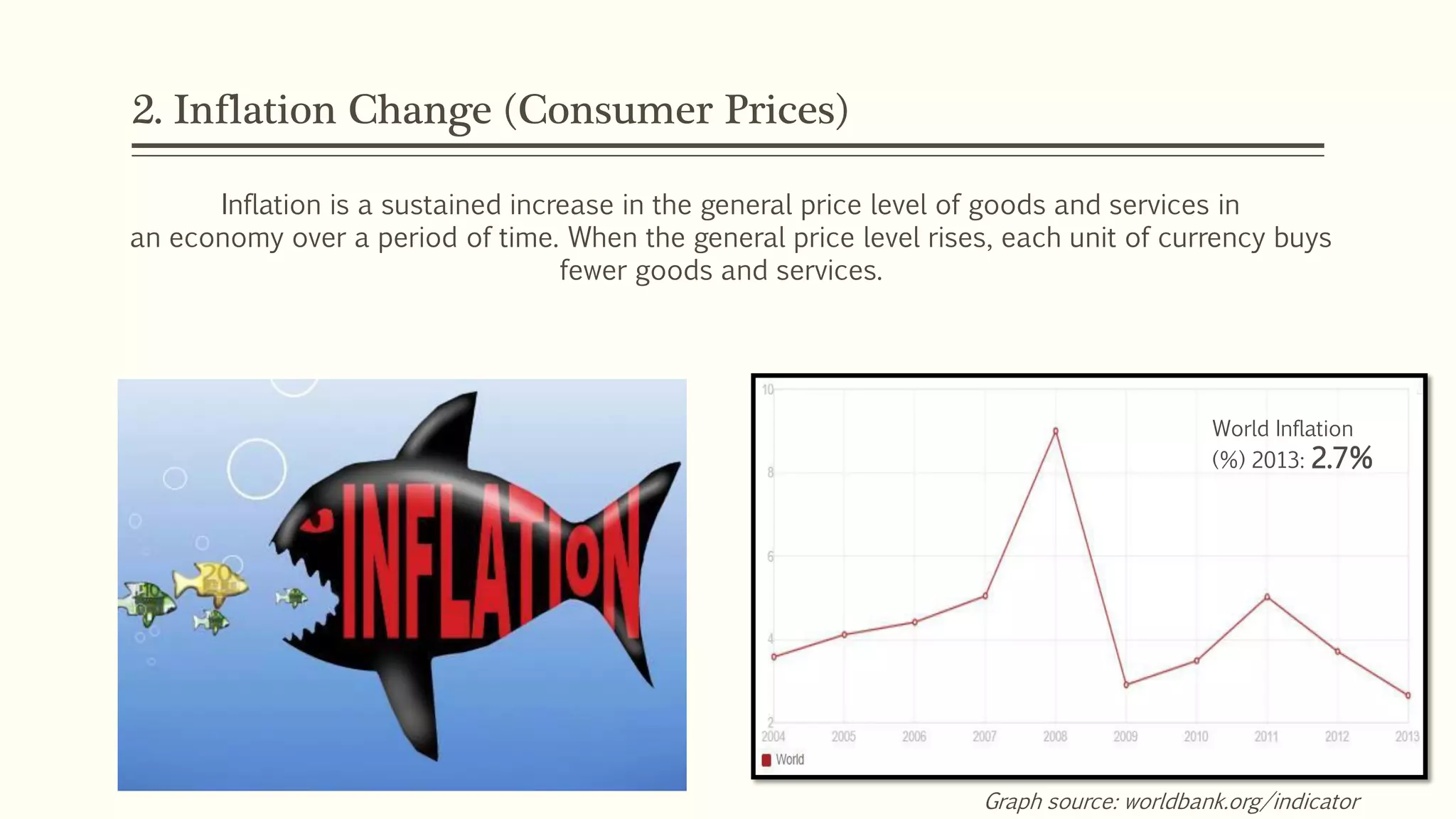
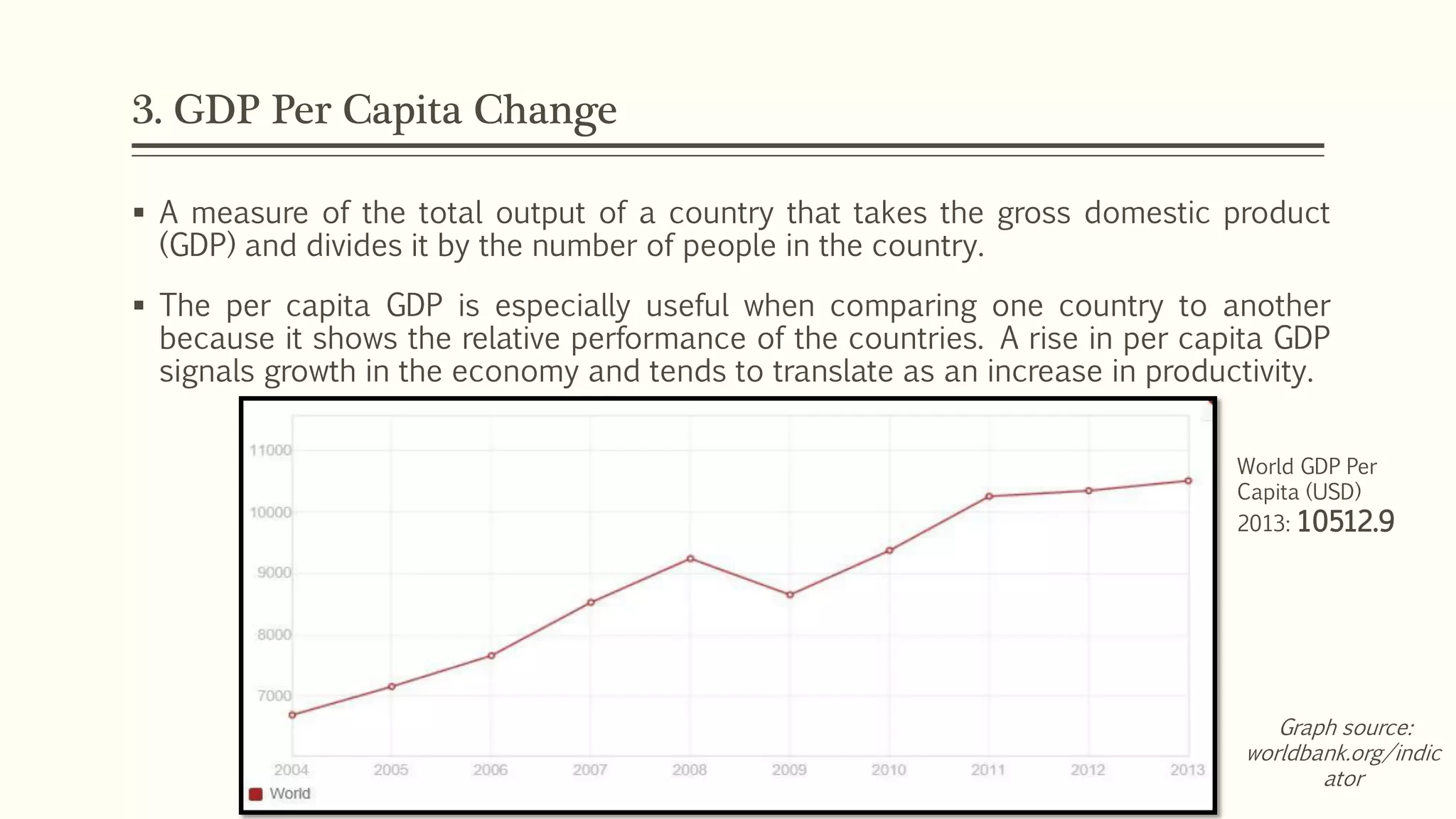
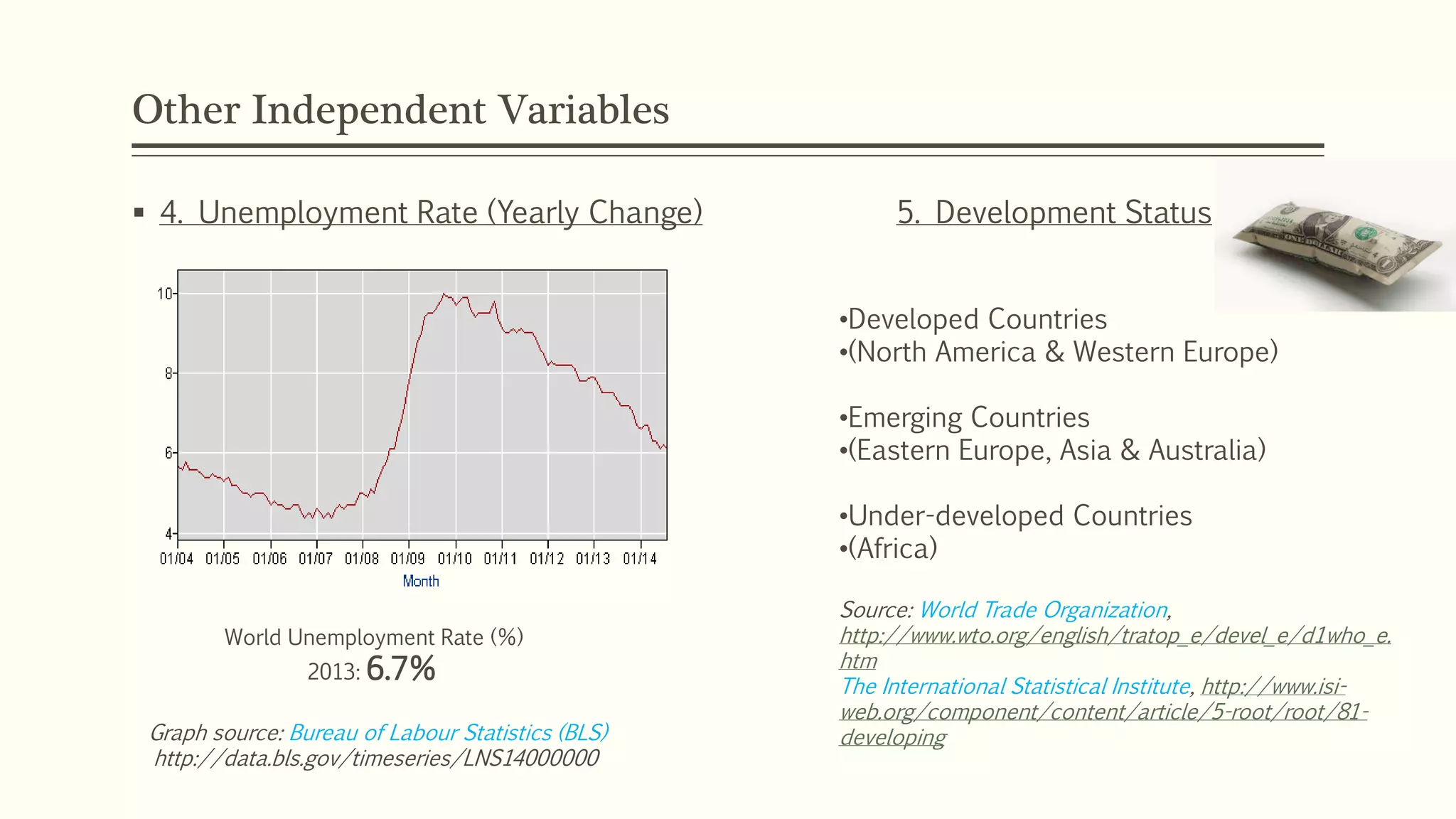
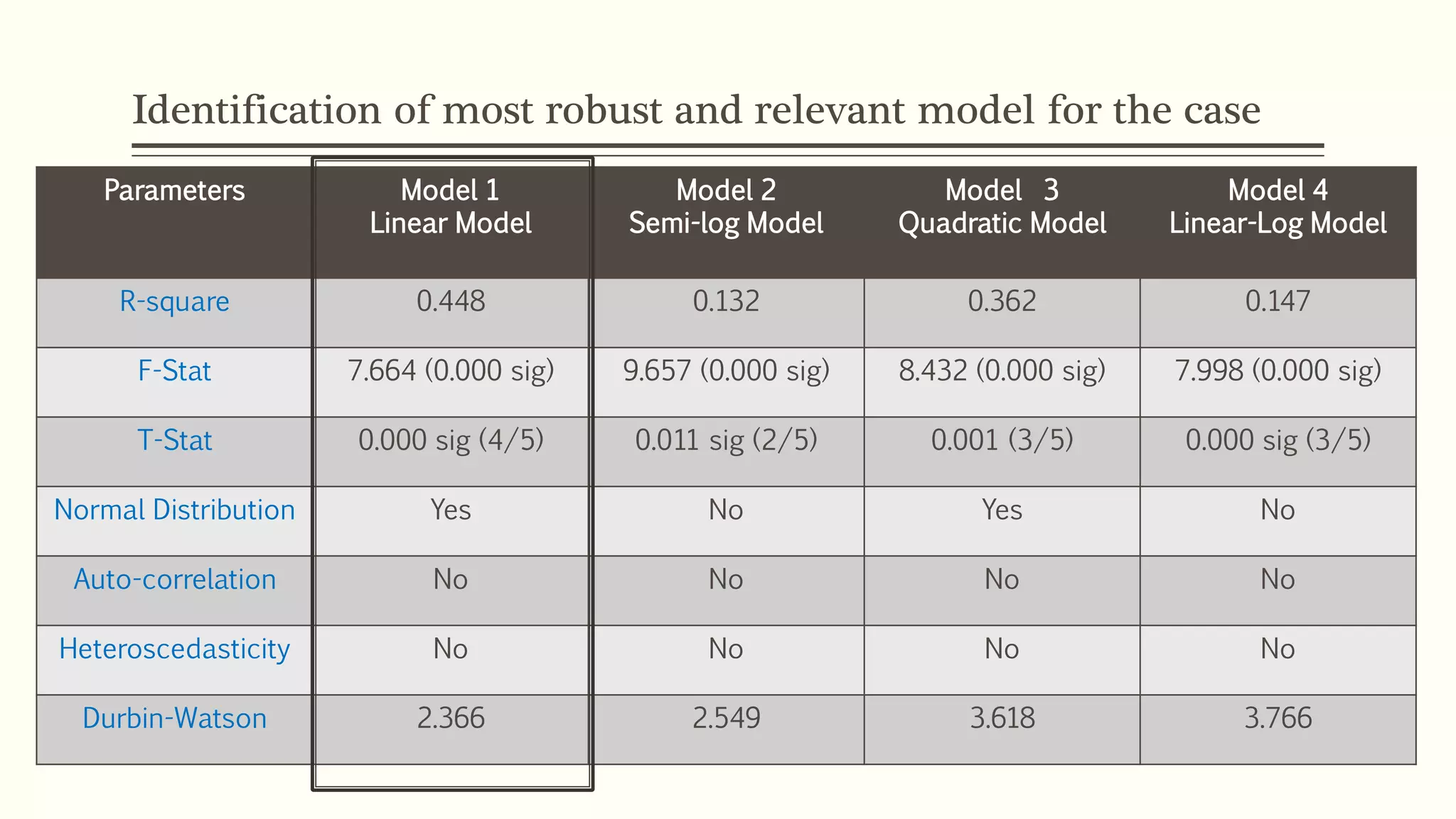
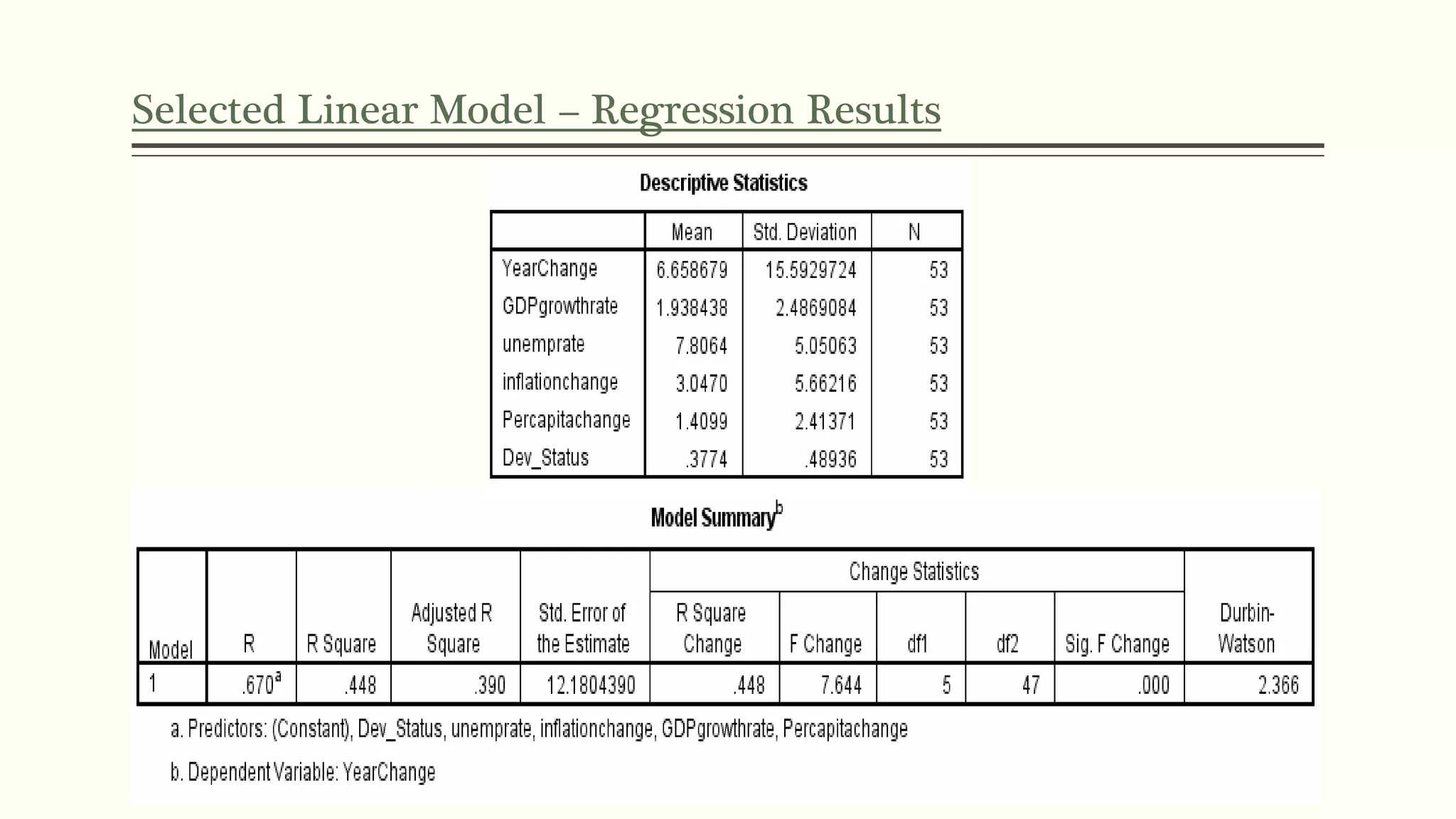
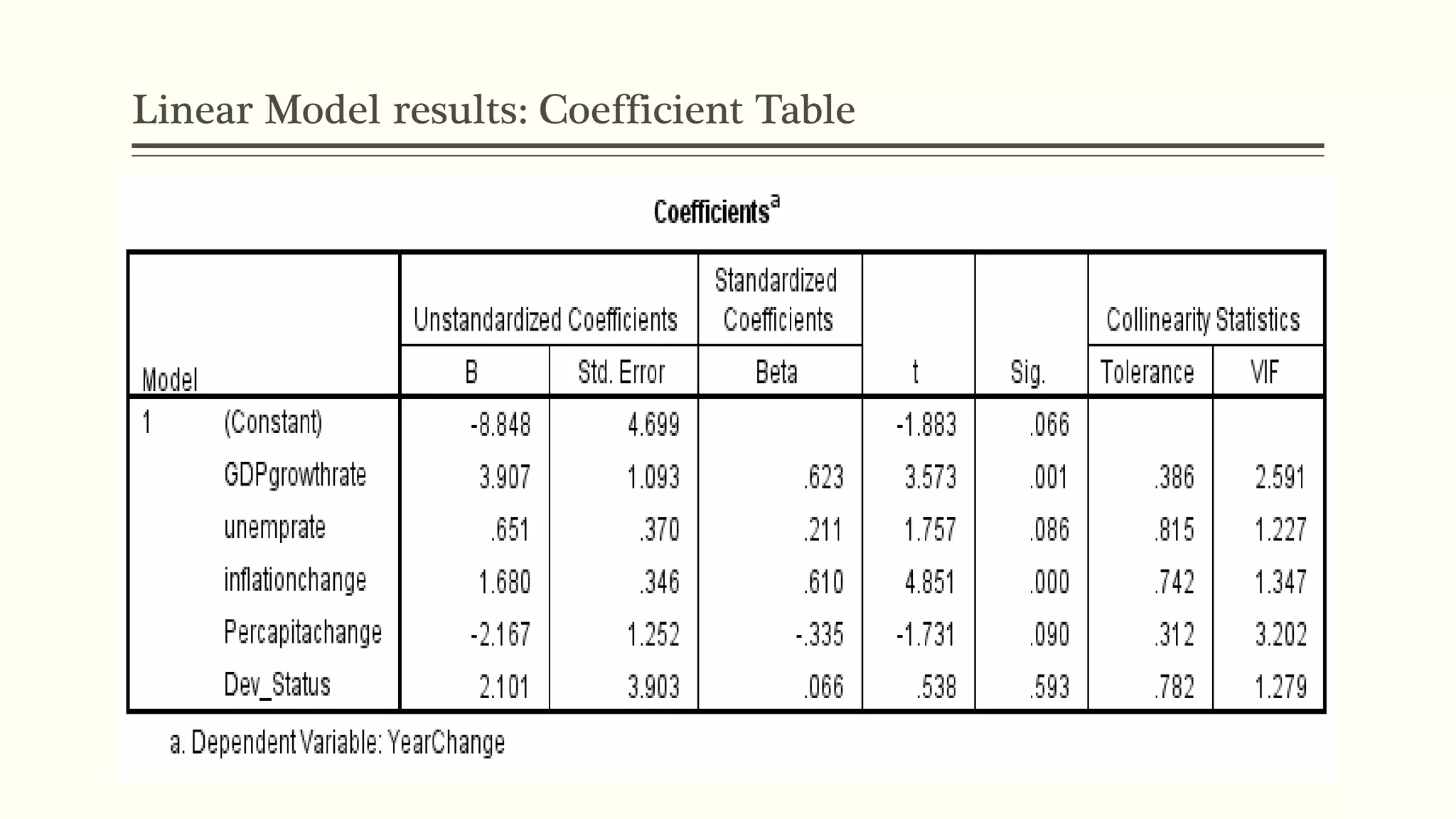
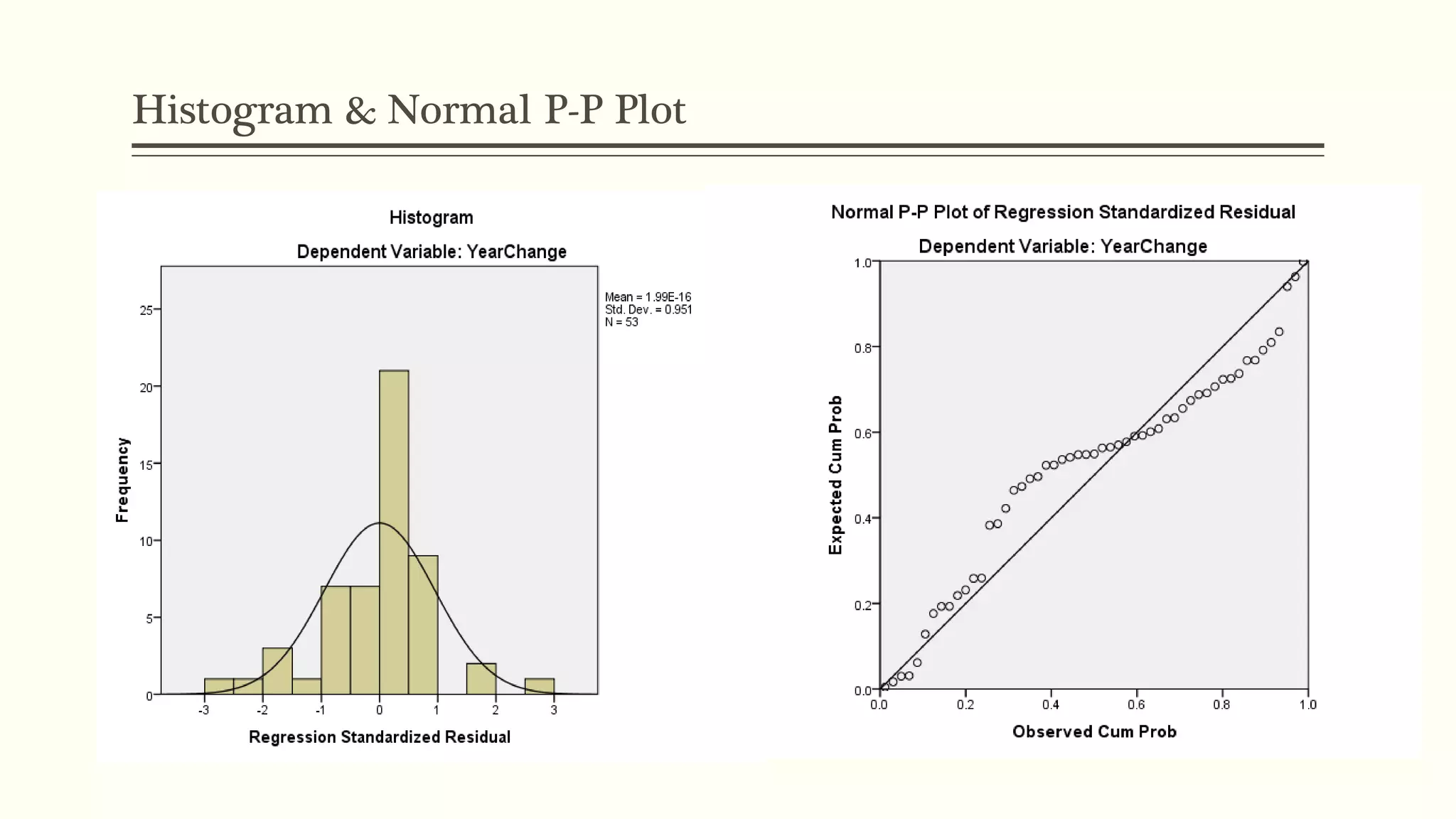
The document presents a study analyzing the impact of macroeconomic variables on global stock market performance. It tests the hypothesis that GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment significantly impact stock market indices. Regression models show GDP growth and inflation have a significant, direct relationship with stock market changes. The study concludes macroeconomic factors robustly explain parts of stock market performance, allowing better understanding and guidance for investors.