More Related Content
PPT
NTUgr(high performance global routing).ppt PPT
fps(techniques of fast physical synthesis).ppt PPT
Computer Aided Design: Global Routing PPT
Placement and routing in full custom physical design PPTX
Routing and Algorithms For VLSI design.pptx PPTX
Routing_process_in_VLSI_verilogmodeling.pptx PPTX
21EC71_Module-2_Routing PPT Electronics and communication engineering module 2 PPTX
12-detailed-routing_techniques_for VLSI.pptx Similar to design-difficult-to-route(design-difficult-to-route).ppt
PPT
Mod3-Lect1-placement-cadforvlsidomainmtech PPT
Placement-and-RoutingPlacement-and-RoutingPlacement-and-Routing.ppt PPT
PPTX
Vlsi physical design (Back End Process) PPTX
Module-2-Routing.pptx department of computer PPT
Lecture20 asic back_end_design PPTX
19ECX25-CAD for VLSI Circuits Unit-1.pptx PDF
PDF
Routing and placement in semicondoctor vlsi .pdf PPTX
VLSI_CAD_Introductionxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.pptx PDF
CS612 Lecture Notes - Bilkent University PPT
PPT
lecture1_intro_vlsi_design_tkmt_digital.ppt PDF
MODULE2-Routing ADVANVECD VLSI VTU2024.pdf PPT
lecture25_fpga-conclude.ppt PDF
A Review on Channel Routing On VLSI Physical Design PDF
AN EFFICIENT APPROACH FOR FOUR-LAYER CHANNEL ROUTING IN VLSI DESIGN DOCX
Detailed routing algorithms for advanced technology nodes PDF
PPT
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Track & Monitor Preventive Maintenance — Best Practices with MaintWiz CMMS PPTX
Preventive Maintenance Program for Compressors – Complete Guide PDF
Modeltomodel_Transformation_with_ATL (1).pdf PPTX
How to Implement Kaizen in Your Organization for Continuous Improvement Success PPTX
Engineering Economics CHAPTER 4.pptx - R PPTX
Transportation Engineering- Modes of Transport, Types of roads, Components of... PDF
3rd International Conference on AI & Civil Engineering (AICiViL 2025) PDF
PROPEX-RAG: Prompt-Driven GraphRAG for Multi-Hop QA PPTX
Network Security v1.0 - Module 2.pptx PDF
Sensor & Instrument MODULE 3 REVISION PPT.pdf PPTX
MODULE 1-UNIT_1.pptx MODULE 1-UNIT_1.pptx MODULE 1-UNIT_1.pptx PPTX
22PEOIT4C Session 7 A searching algorithm.pptx PPTX
Fiber reinforced concrete (FRC) is a composite material made from Portland ce... PPTX
Environmental and Ecology UNIT 4 - Global Warming-1.pptx PPTX
22PEOIT4C Session 1 Introduction to AI and intelligent agents.pptx PPTX
KTU 2024 SCHEME -PEMET 413 COMPOSITE MATERIALS MODULE 1 LECTURE 1.pptx PDF
chapter 30 inductance chương trình tiên tiến bách khoa.pdf PPTX
Industrial Smart Ventilation system.pptx PPTX
UNIT -3 -DIGITAL AND MOBILE FORENSICS FORENSIC READINESS-.pptx DOCX
Buy Facebook Ads Accounts_ Boost Your Professional ....docx design-difficult-to-route(design-difficult-to-route).ppt
- 1.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
1
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
Charles J. Alpert, Zhuo Li, Michael D. Moffitt, Gi-Joon Nam, Jarrod A. Roy,
Gustavo Tellez
Presented by Zhicheng Wei
- 2.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
2
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUNDS
COMMON CONGESTION METRICS
GLOBAL ROUTING CONSTRAINTS
DETAILED ROUTING CONSTRAINTS
PLACEMENT TECHNIQUES
LOGIC SYNTHESIS TECHNIQUES
REPEATER INSERTION TECHNIQUES
CONCLUSION
- 3.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
3
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
INTRODUCTION
Modern technology requires complex wire spacing rules and constraints
High performance routing requires multiple wire width (even same layer)
Local problems including via spacing rules, switchbox inefficiency, intra-gcell
routing
All of these problems make routing hard to model and lead to huge congestion
issues!
- 4.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
4
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
BACKGROUNDS
Routing problems should be considered in 3D instead of 2D
Meet congestion constraints during global routing
Try to satisfy capacity in detailed routing with a given global routing solution
Over-the-cell routing breaks traditional channel/switchbox model
- 5.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
5
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
COMMON CONGESTION METRICS
Total Overflow
Average worst X%
average worst 20% routing edges below 80% is routable
Total routed wirelength (RWL)
significantly above Steiner tree may indicate routing difficulties
Number of scenic nets
wirlelength/minimum Steiner tree length
ratio > 1.3 is generally considered scenic
Number of nets over X%
nets passing through gcells whose congestion is over X%
Number of violations
Routing runtimes
- 6.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
6
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
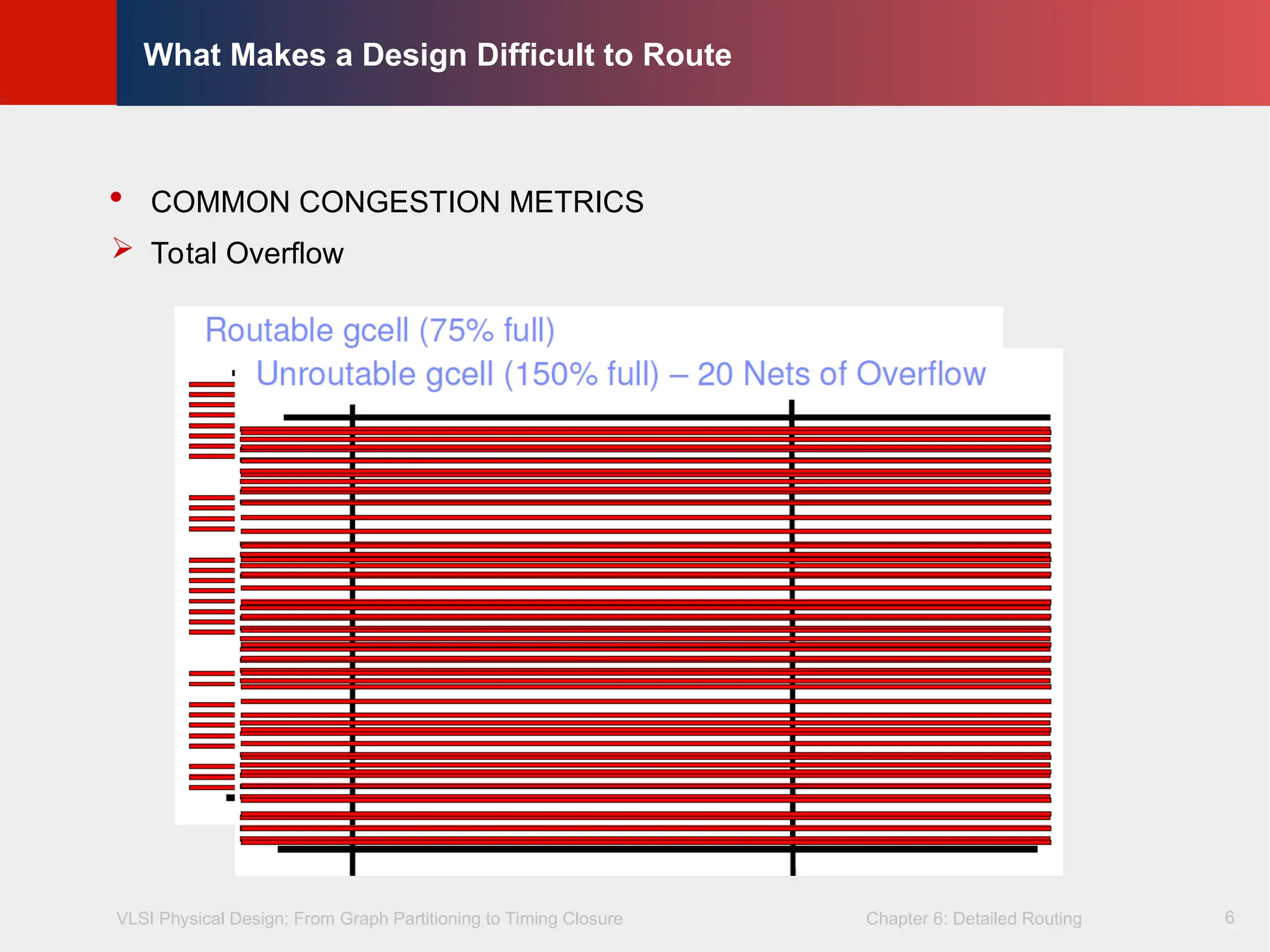
COMMON CONGESTION METRICS
Total Overflow
- 7.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
7
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
GLOBAL ROUTING CONSTRAINTS
Choice of gcell size
gcell size too small
large global routing space and takes more time to route
gcell size too large
not able to expose congestion problems and shift burden to detail routing
Handling scenic nets
go very scenic = bad timing performance
impose scenic constrains on the router
- 8.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
8
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
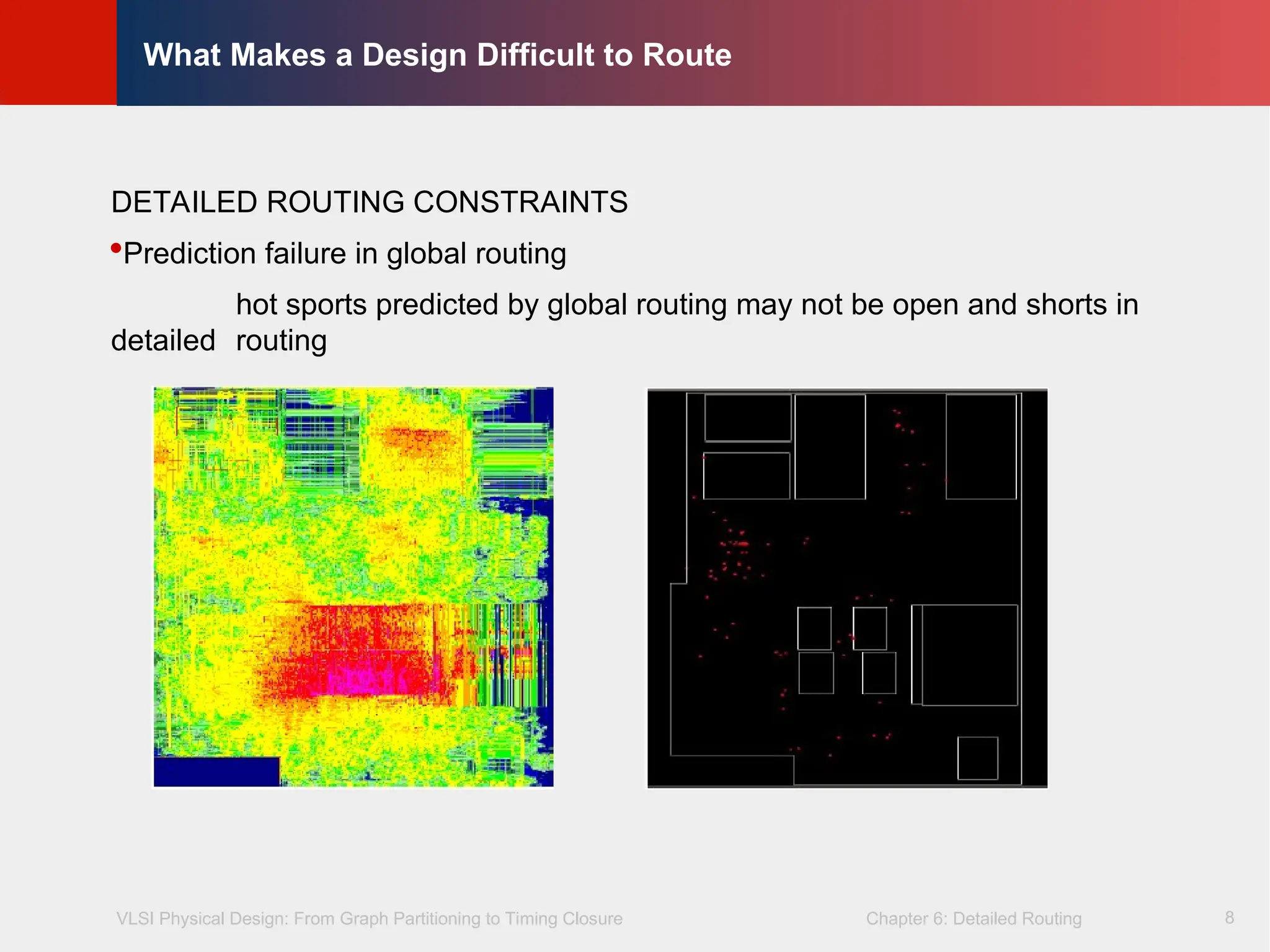
DETAILED ROUTING CONSTRAINTS
Prediction failure in global routing
hot sports predicted by global routing may not be open and shorts in
detailed routing
- 9.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
9
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
DETAILED ROUTING CONSTRAINTS
Pin access problem
certain configurations make accessing pin from higher metal layer
impossible
Via modeling challenge
Vias do not scale as well as device at each technology node
Vias serve as routing blockages which impact local congestion
Via modeling becomes non-trivial, esp with different metal pitches
- 10.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
10
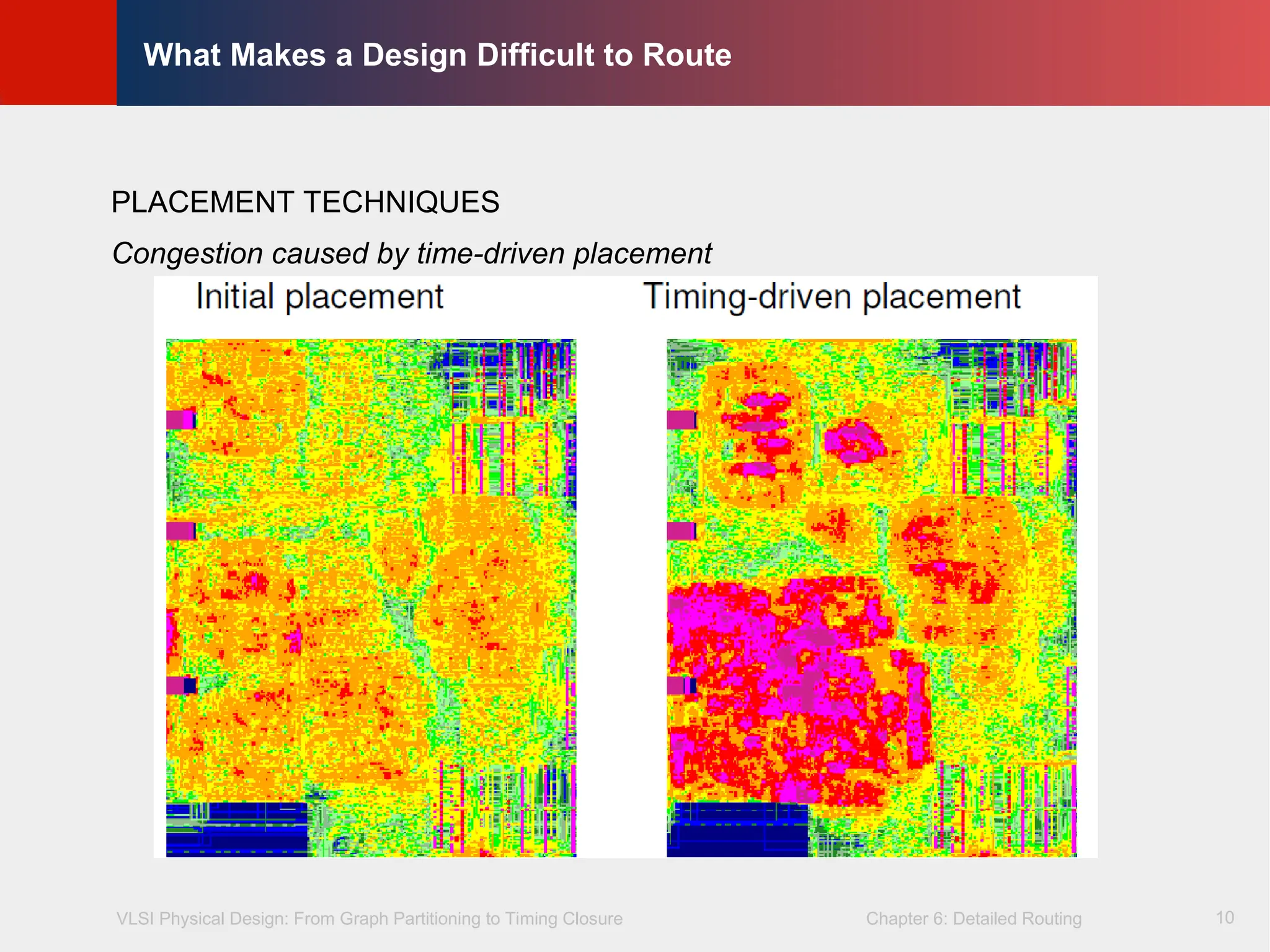
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
PLACEMENT TECHNIQUES
Congestion caused by time-driven placement
- 11.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
11
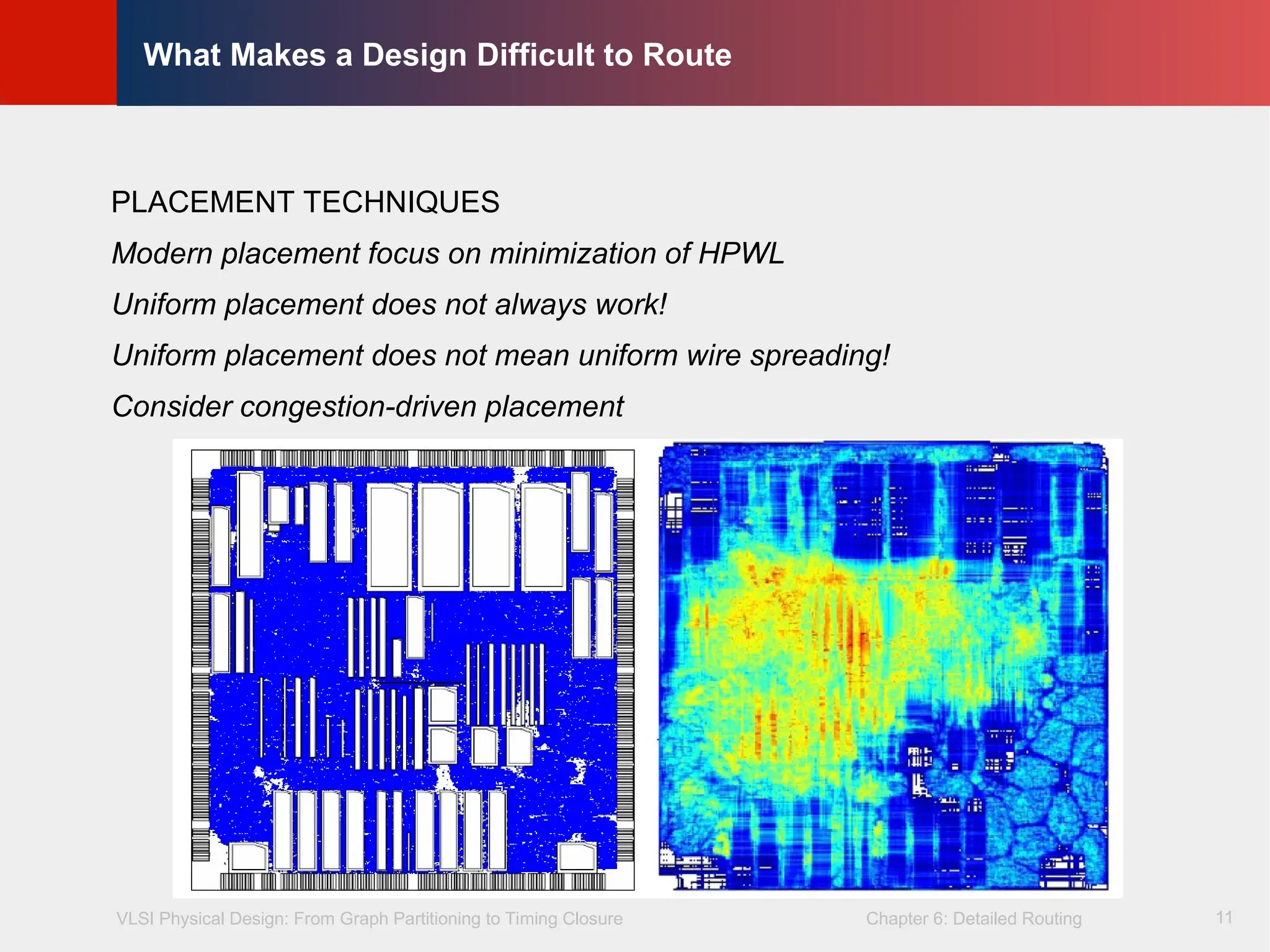
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
PLACEMENT TECHNIQUES
Modern placement focus on minimization of HPWL
Uniform placement does not always work!
Uniform placement does not mean uniform wire spreading!
Consider congestion-driven placement
- 12.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
12
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
PLACEMENT TECHNIQUES
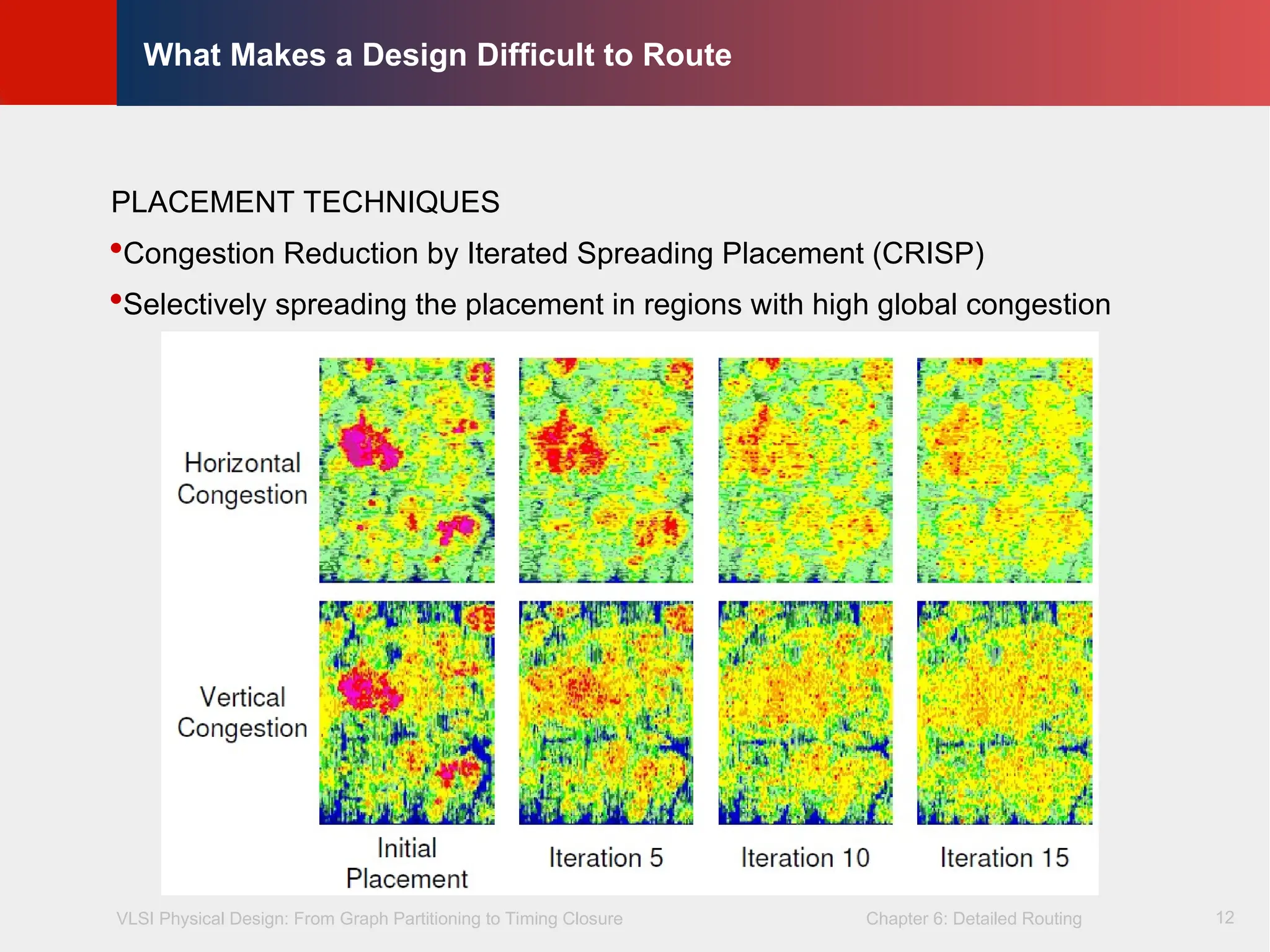
Congestion Reduction by Iterated Spreading Placement (CRISP)
Selectively spreading the placement in regions with high global congestion
- 13.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
13
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
LOGIC SYNTHESIS TECHNIQUES
Logic synthesis generally ignores placement information
Create structures good for timing closure but bad for routing
Logic synthesis transforms to alleviate local congestions
identify logic fan-in tree which is physically wirelength inefficient
rebuild logic tree and place new synthesized gates
wirelength is minimized and congestion alleviated
- 14.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
14
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
REPEATER INSERTION TECHNIQUES
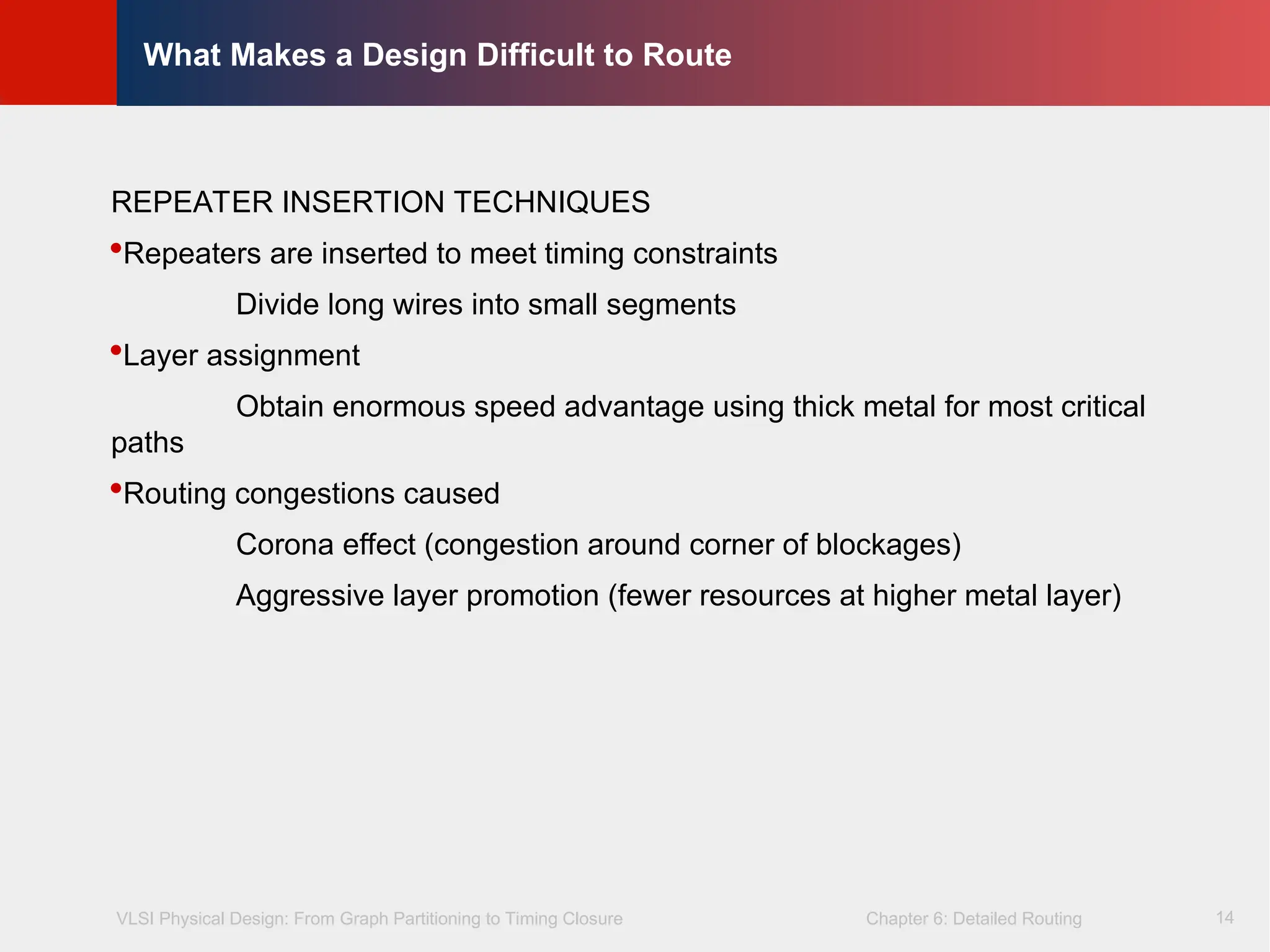
Repeaters are inserted to meet timing constraints
Divide long wires into small segments
Layer assignment
Obtain enormous speed advantage using thick metal for most critical
paths
Routing congestions caused
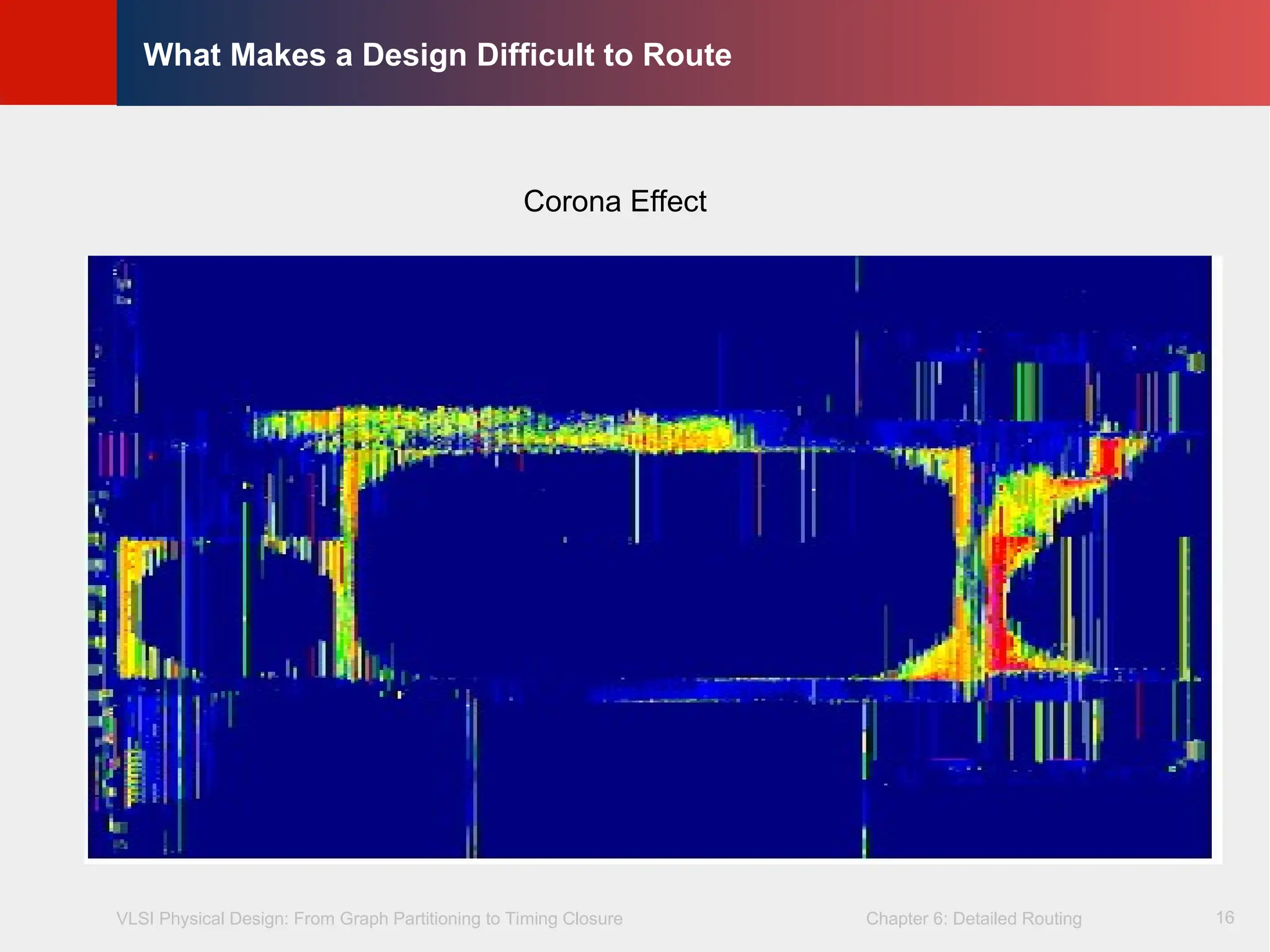
Corona effect (congestion around corner of blockages)
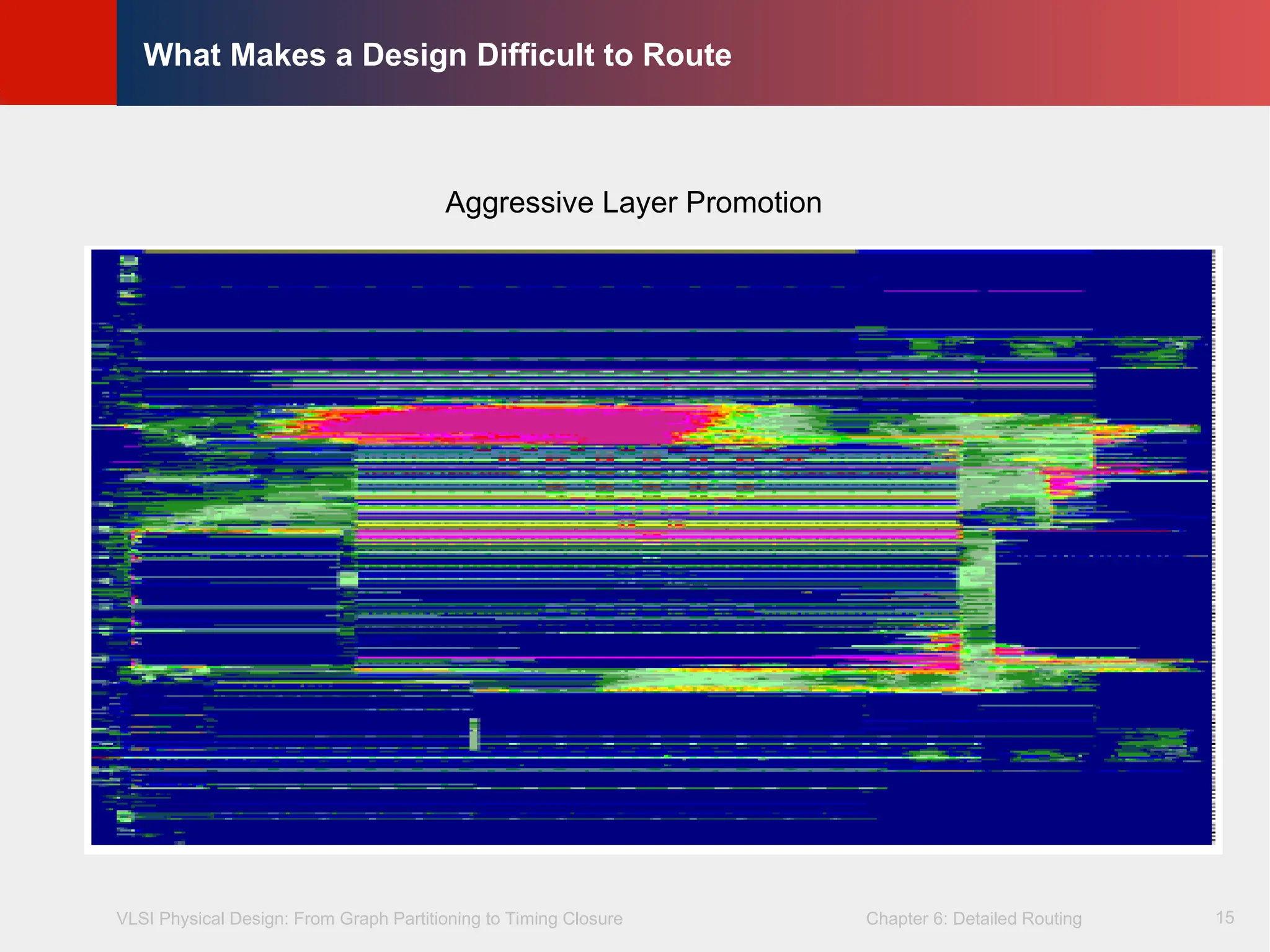
Aggressive layer promotion (fewer resources at higher metal layer)
- 15.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
15
Aggressive Layer Promotion
- 16.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
16
Corona Effect
- 17.
VLSI Physical Design:From Graph Partitioning to Timing Closure Chapter 6: Detailed Routing
©
KLMH
Lienig
17
What Makes a Design Difficult to Route
CONCLUSION
Physical synthesis issues in placement, global/detail routing, logic
synthesis
Advanced technologies require more complicated modeling plan
Capture more detailed routing effects in global routing stage
Estimation techniques need to be fast to optimize routing fast