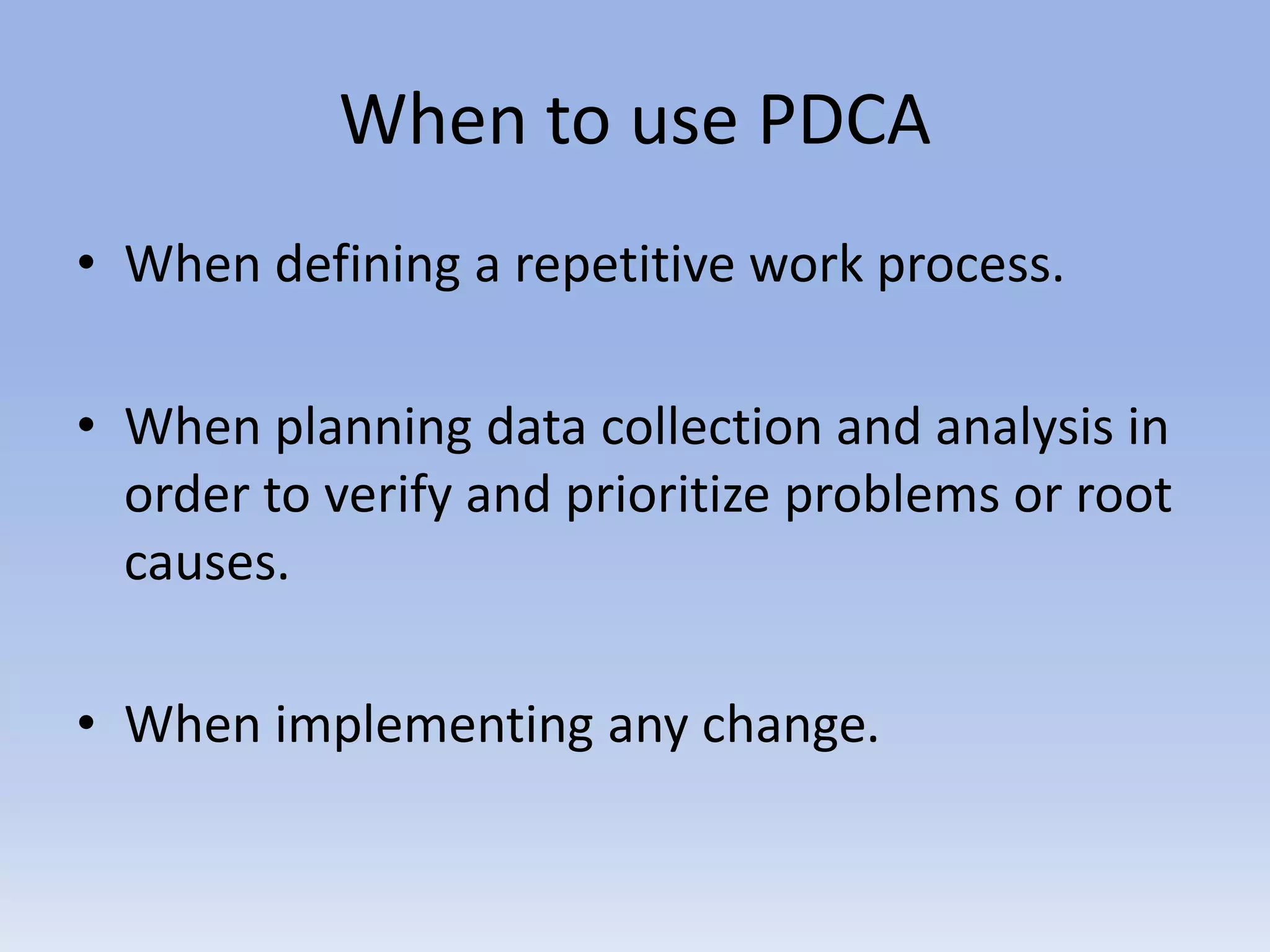
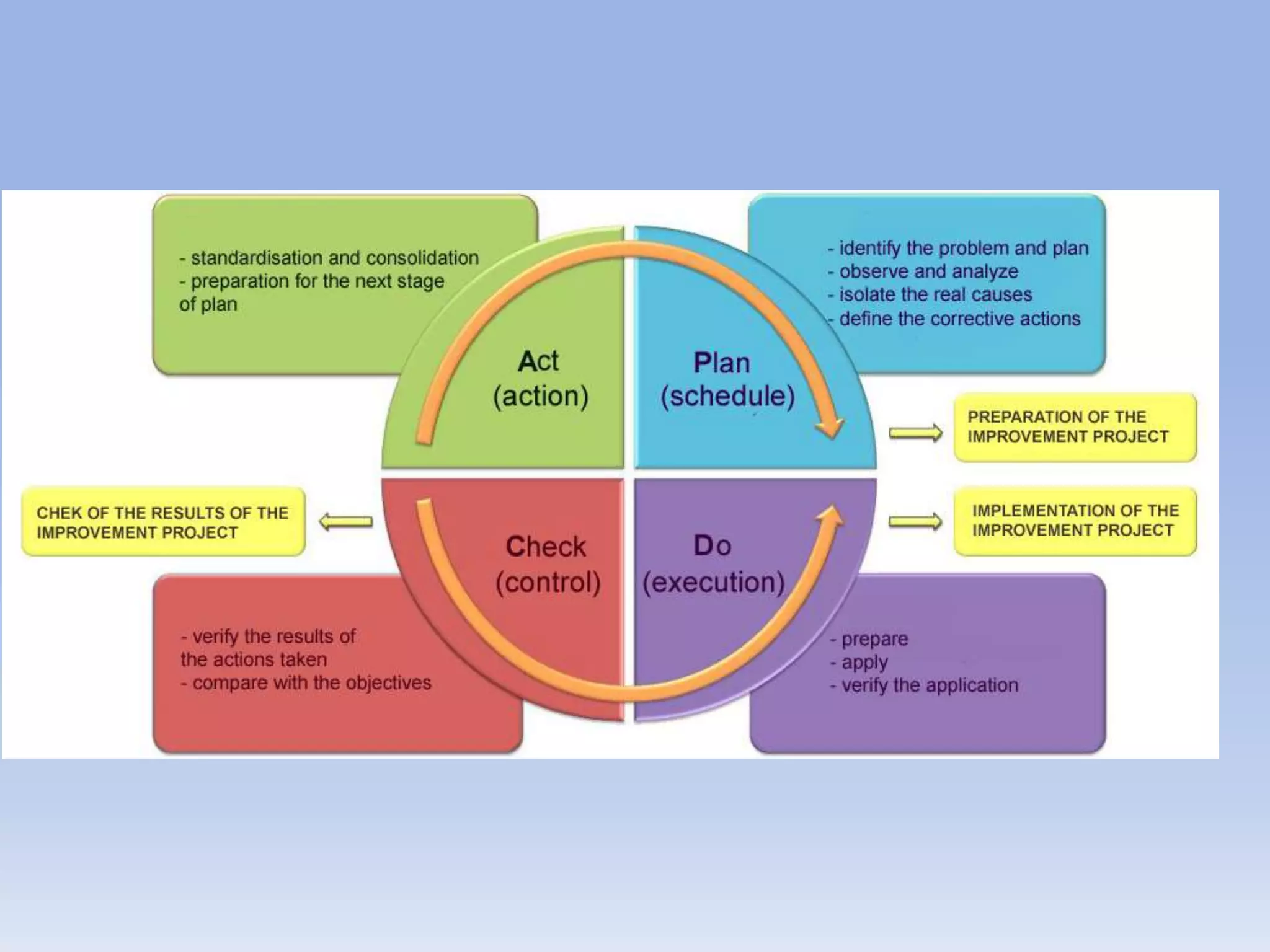
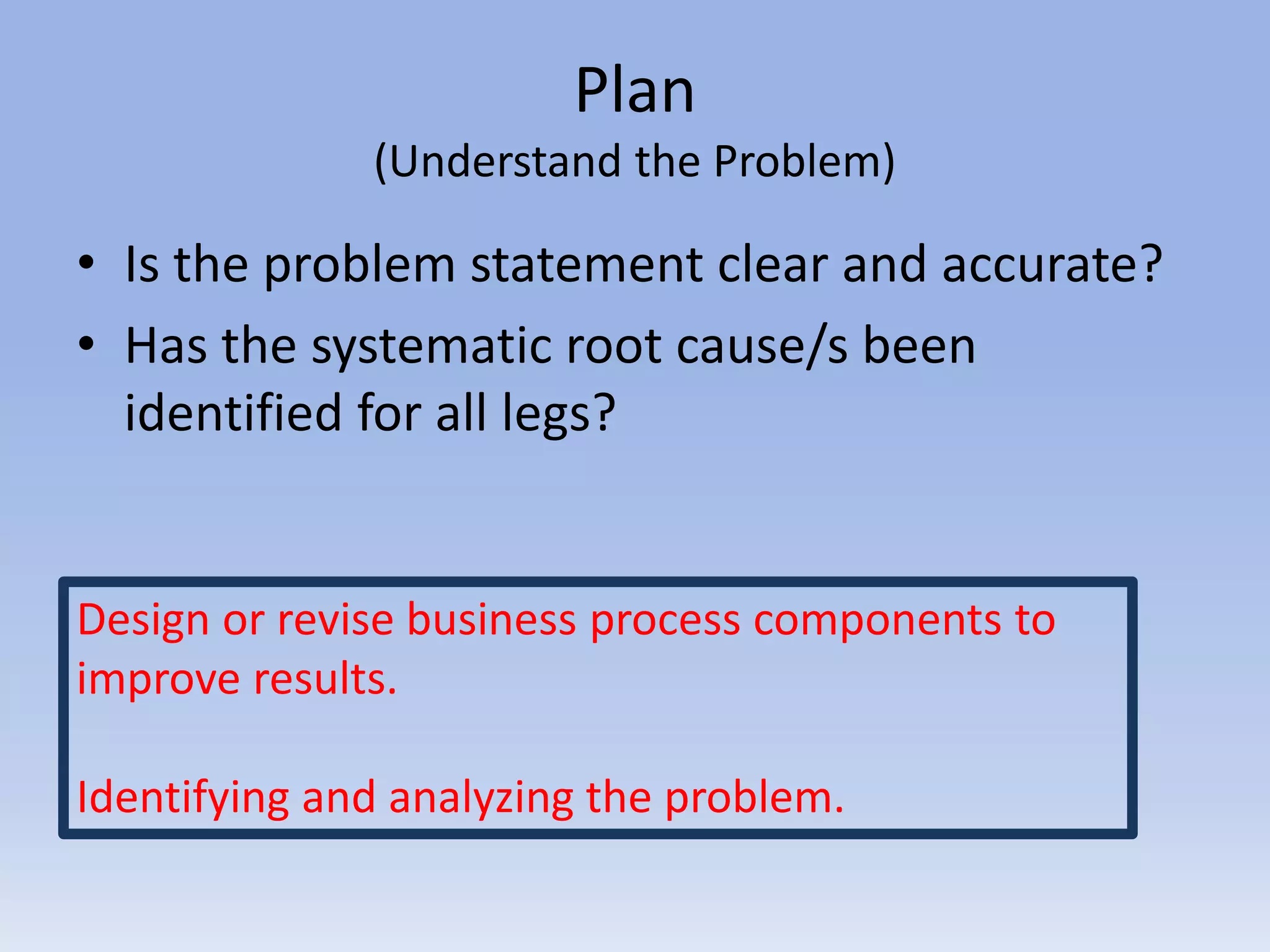
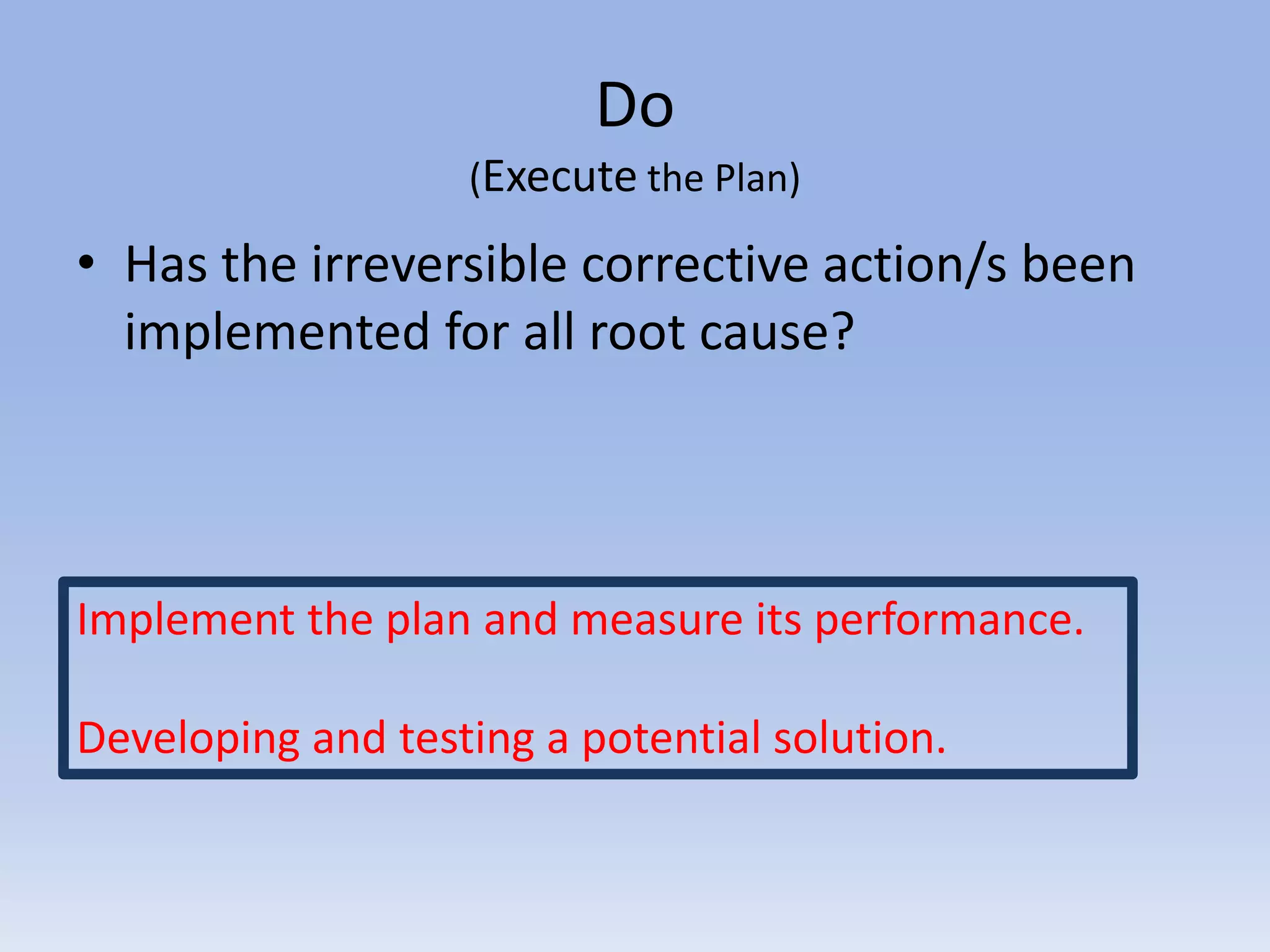
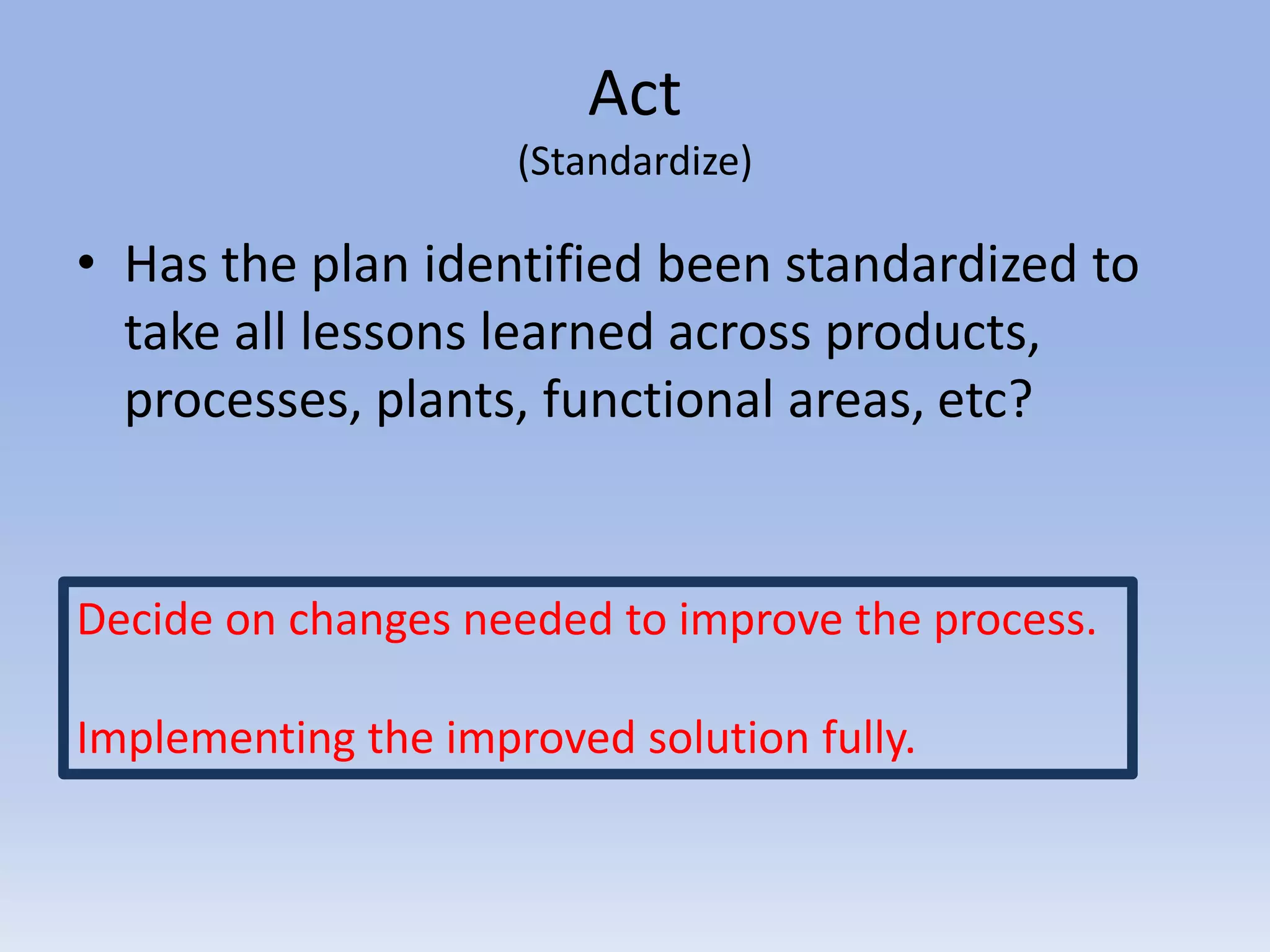
This document discusses Deming's PDCA cycle and message of constant learning. It provides an overview of Deming's philosophy that inefficiency and poor quality are usually due to systemic problems rather than employees. It also outlines Deming's message to Japanese management to see production as a system, make quality a priority set by management, and continuously learn and improve using the PDCA (plan-do-check-act) cycle. The PDCA cycle is described as a four-step model for continuous improvement: plan potential solutions, implement the plan, check the results, and act to standardize successful changes. Guiding questions for each step are provided. The document concludes with discussing Deming's views on constant learning through rigorous screening,