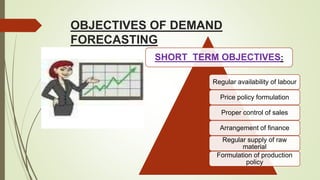
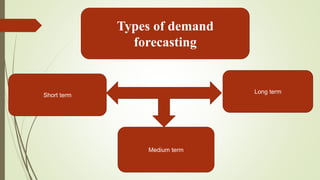
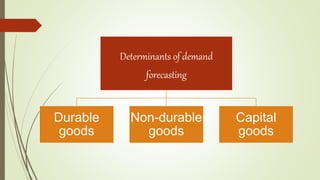
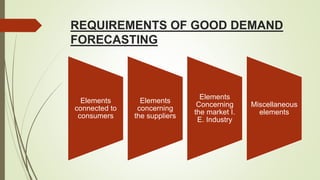
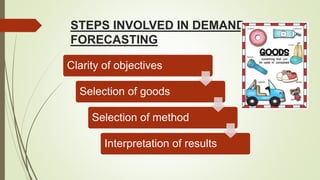
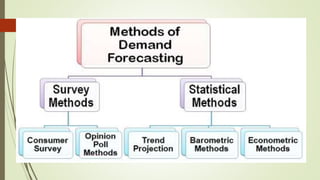
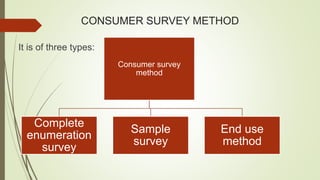
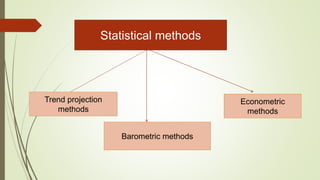
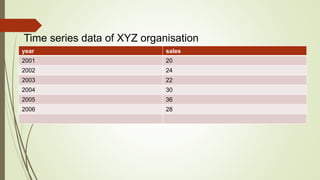
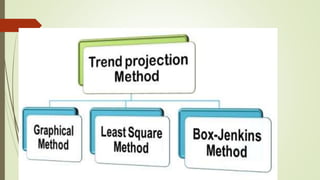
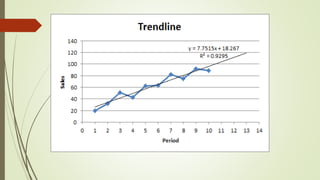
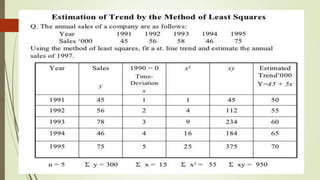
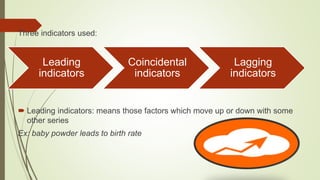
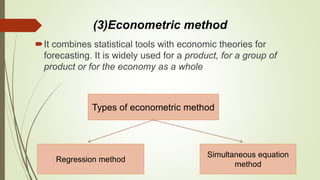
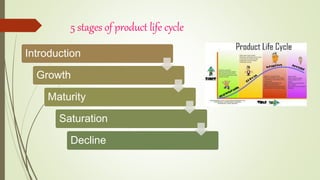
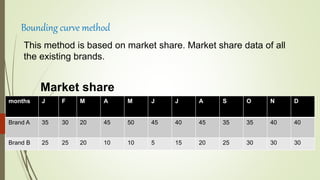
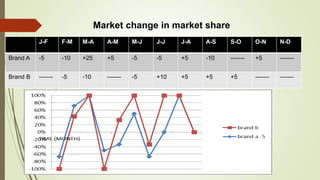
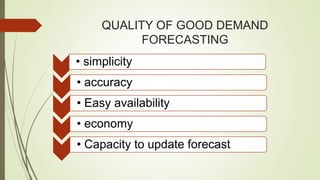
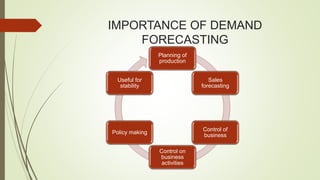
The document discusses demand forecasting, including its meaning, objectives in the short and long term, types including short, medium and long term forecasting, determinants for different goods, requirements for good forecasting, techniques like consumer surveys and opinion methods, and steps involved in the forecasting process. It provides details on objectives like arranging labor, finances and production, as well as factors that influence demand for different goods and methods for collecting information and opinions to forecast future demand.