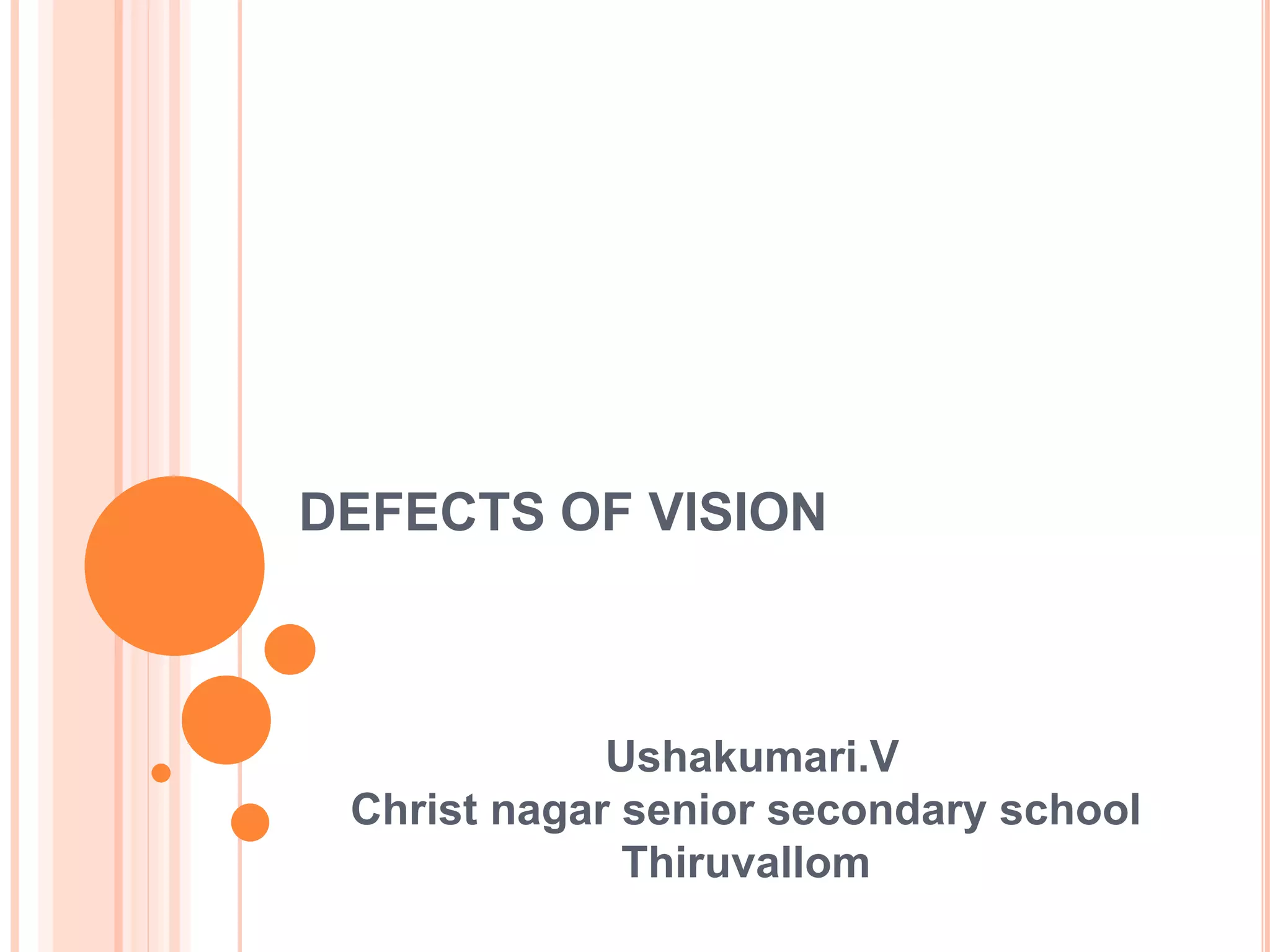
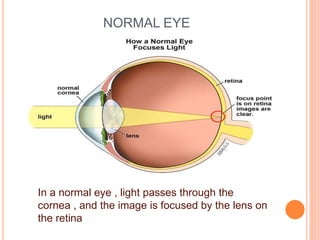
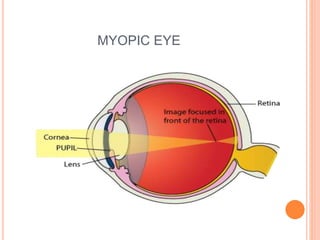
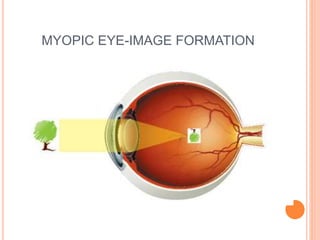
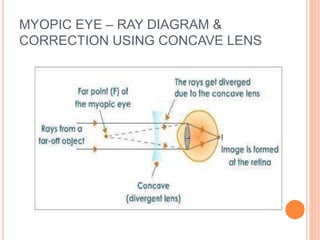
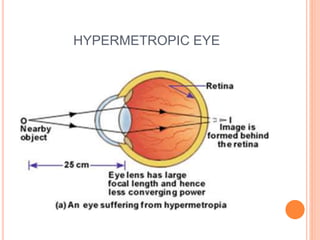
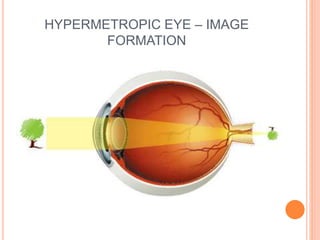
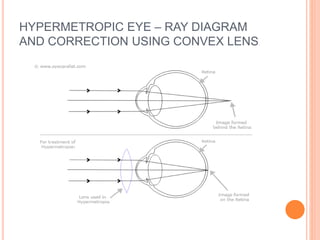
There are two main types of vision defects: myopia and hypermetropia. Myopia, or nearsightedness, causes a person to see nearby objects clearly but not distant objects, because the image is focused in front of the retina. It is caused by elongation of the eyeball or a decrease in the lens's focal length. Hypermetropia, or farsightedness, has the opposite effect - distant objects are seen clearly but not nearby ones, as the image is focused behind the retina, due to shortening of the eyeball or an increase in the lens's focal length. Both conditions can be corrected using convex or concave lenses, respectively, to properly focus the image on the retina