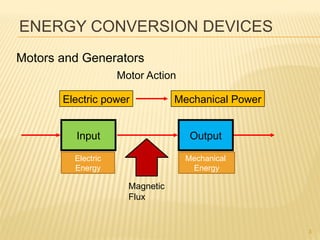
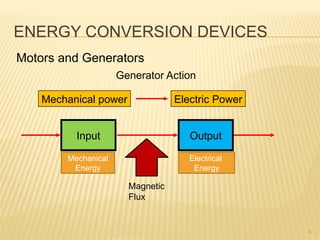
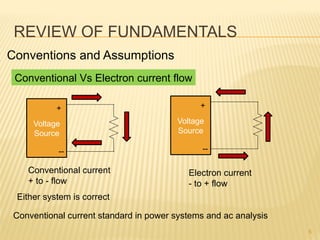
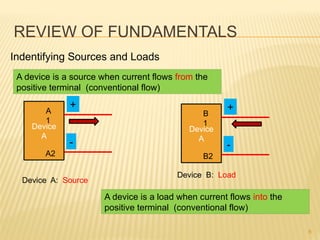
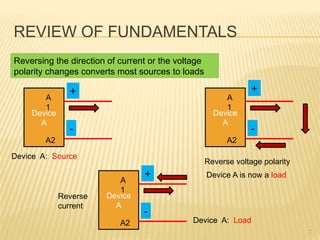
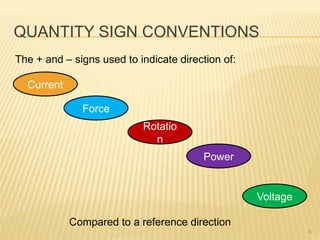
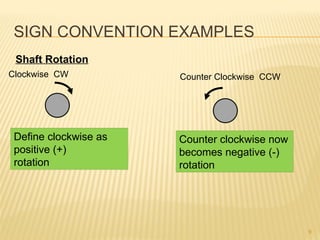
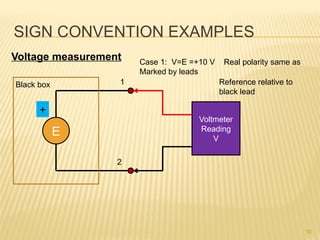
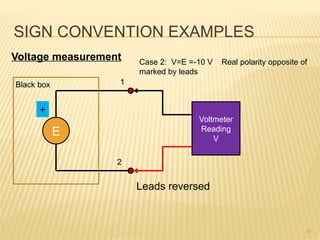
This document introduces concepts related to energy conversion devices like motors and generators. It explains that motors convert electric power to mechanical power, while generators convert mechanical power to electric power using magnetic flux. It also discusses the differences between conventional and electron current flow and how to identify power sources and loads in electric circuits. Finally, it reviews sign conventions for quantities like current, voltage, and rotation to establish a reference for positive and negative values.