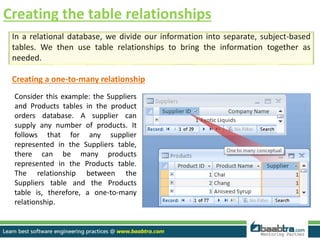
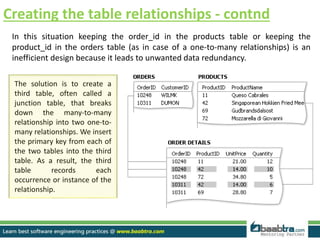
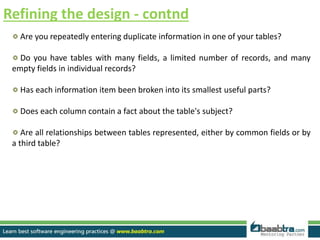
A properly designed database divides information into subject-based tables to reduce redundancy and link information together. The design process includes determining the database purpose, finding required information, dividing it into tables and fields, specifying primary keys, and setting relationships. Tables should be in first normal form with single values per field. Relationships like one-to-many are created by adding a primary key as a foreign key in another table. The design is then refined, sample data added, and normalization rules applied to achieve higher normal forms.