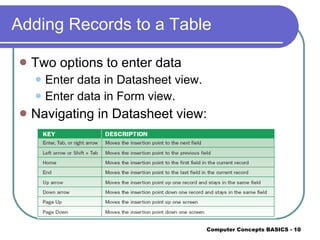
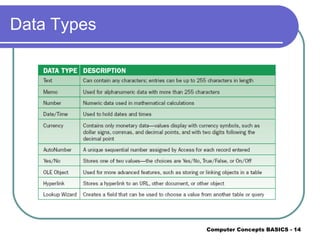
Databases allow for organizing, storing, maintaining, retrieving, and sorting data. The components of a database are tables, queries, forms, and reports. You should plan the database structure first by defining fields and tables before creating it. After creating tables, you add records and can sort them in ascending or descending order. Forms simplify data entry into tables, while queries find records meeting criteria and reports print organized data.