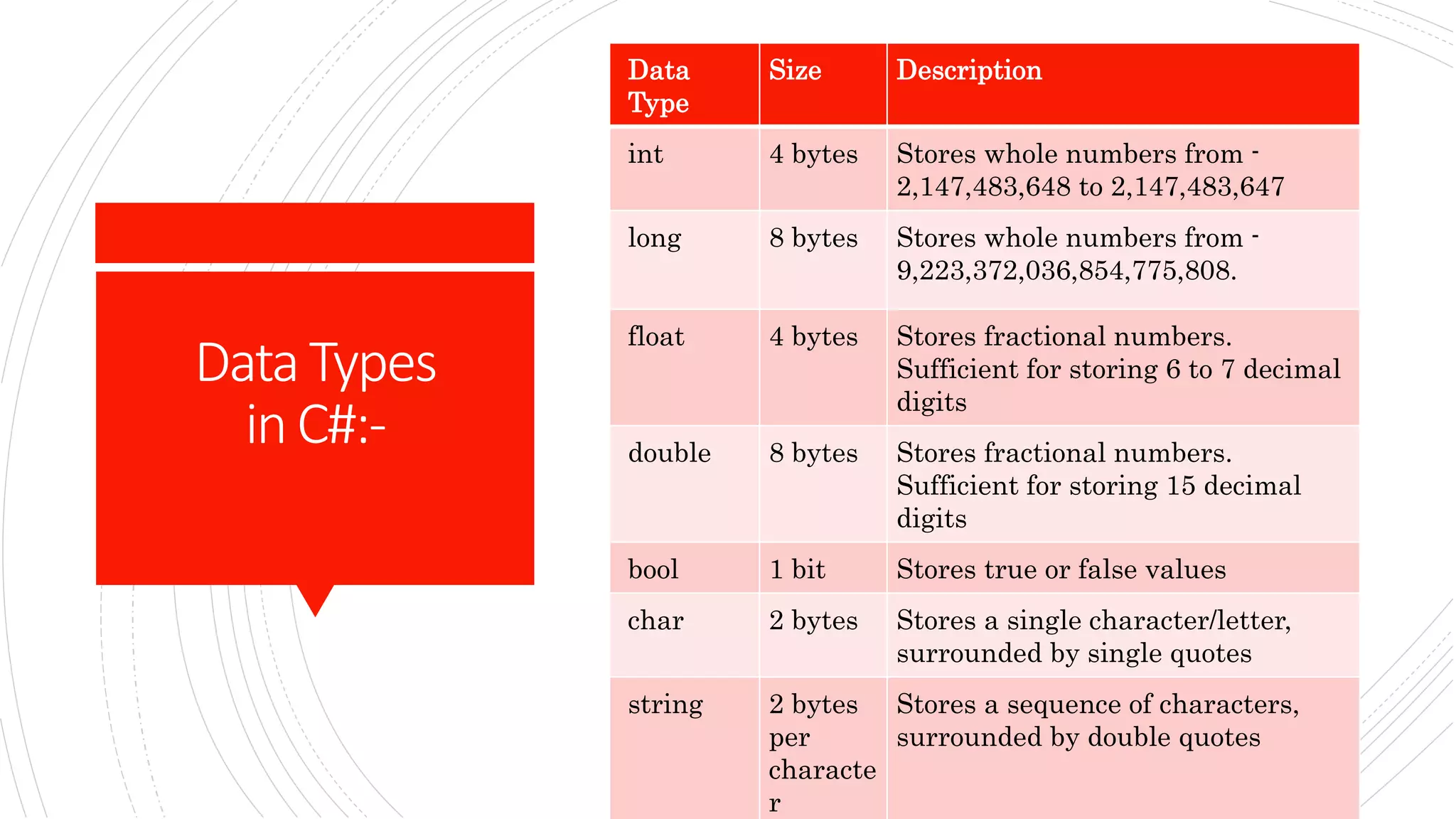
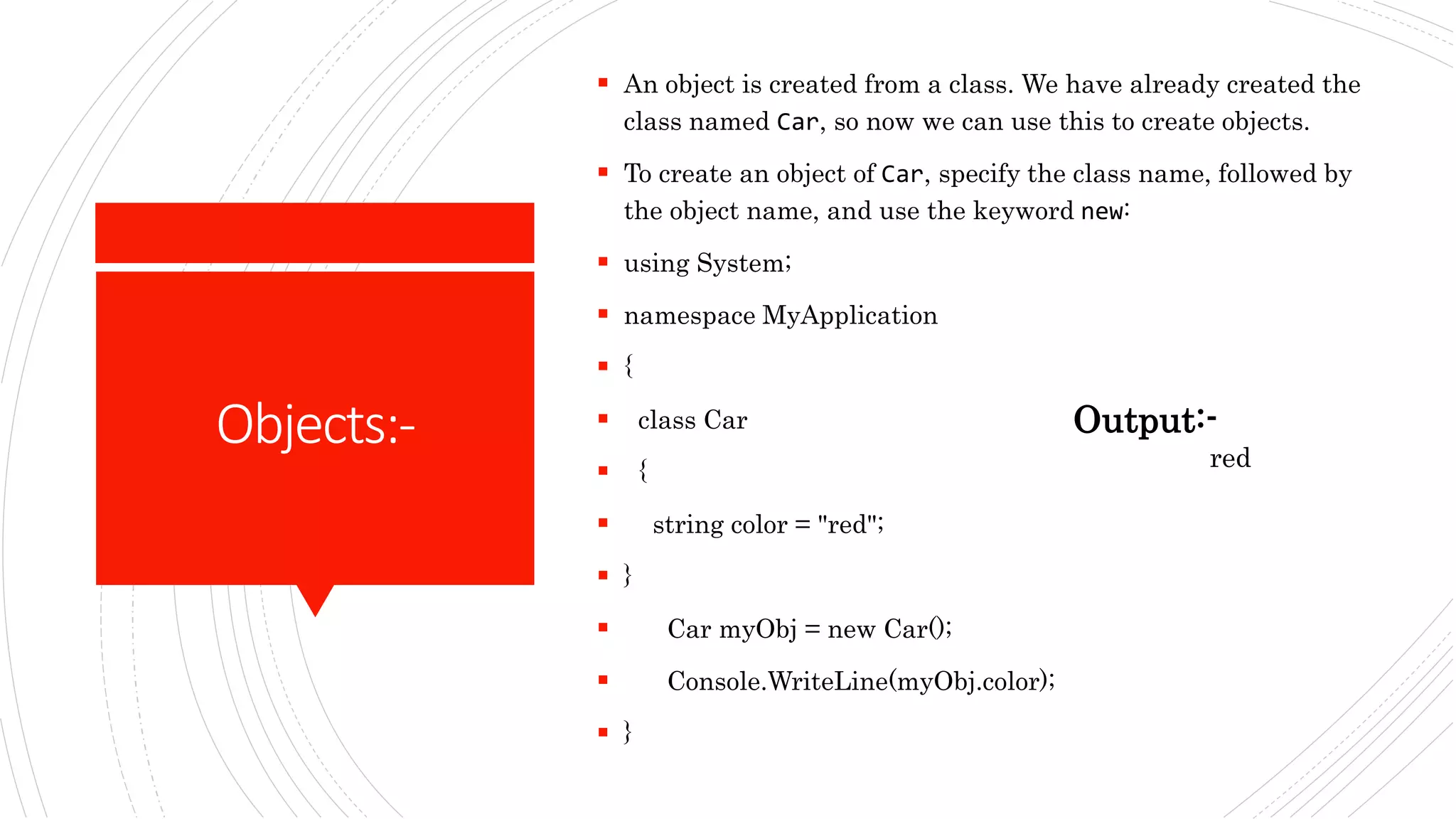
This document discusses data types and objects in C#. It describes the different data types in C# like int, long, float, double, bool, char, and string. It explains that a data type specifies the size and type of variable values. It also discusses that everything in C# is associated with classes and objects, and that a class acts as a blueprint for creating objects. It provides an example of creating a Car class with a color variable, and then creating a Car object from the class to access the color property.