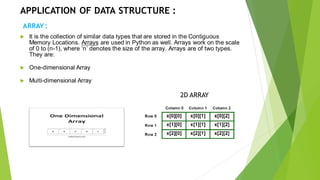
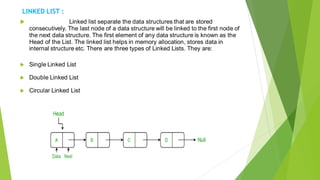
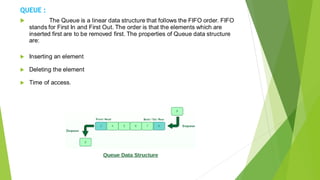
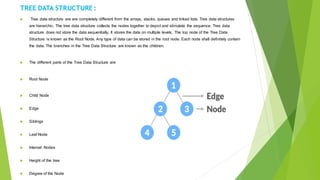
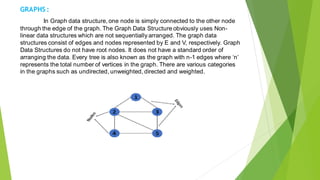
This document discusses various data structures and their applications. It describes linear data structures like arrays, linked lists, stacks, and queues. It also covers nonlinear data structures like trees and graphs. Arrays store similar data types in contiguous memory locations. Linked lists link data structures non-consecutively. Stacks and queues follow LIFO and FIFO ordering respectively. Trees store data hierarchically with parent and child nodes. Graphs connect nodes through edges in a non-sequential manner. These data structures are important for efficient program design and development.