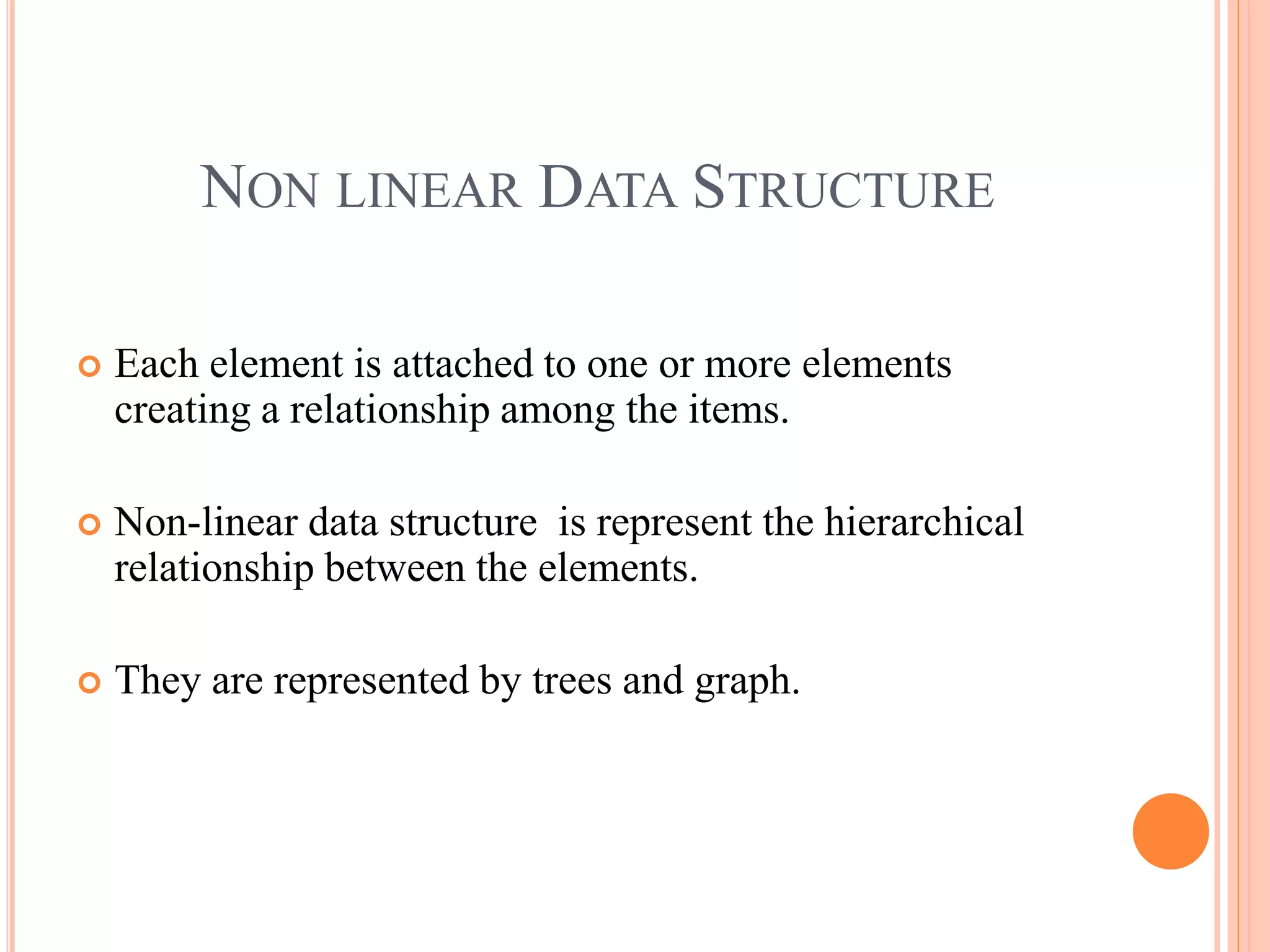
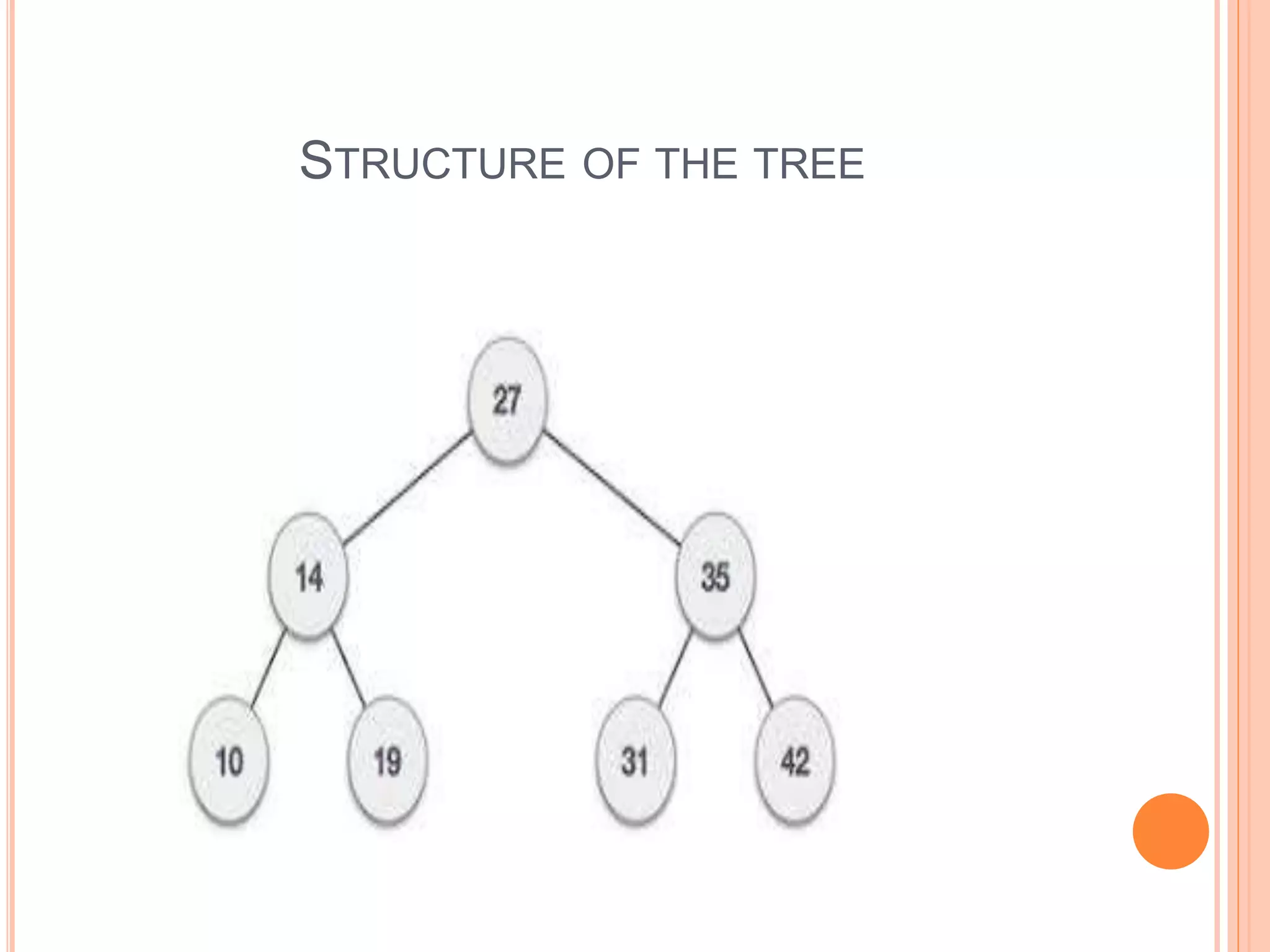
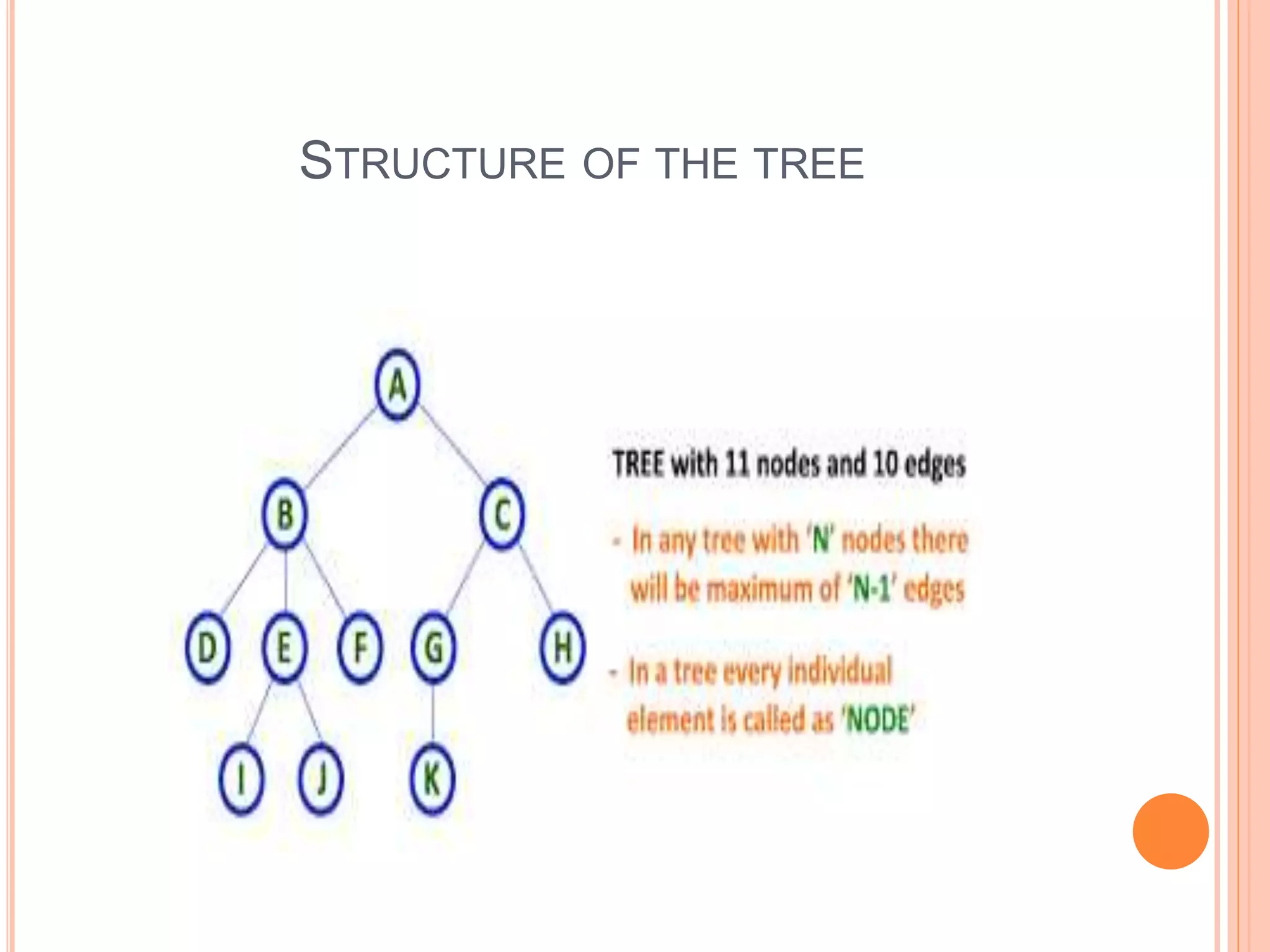
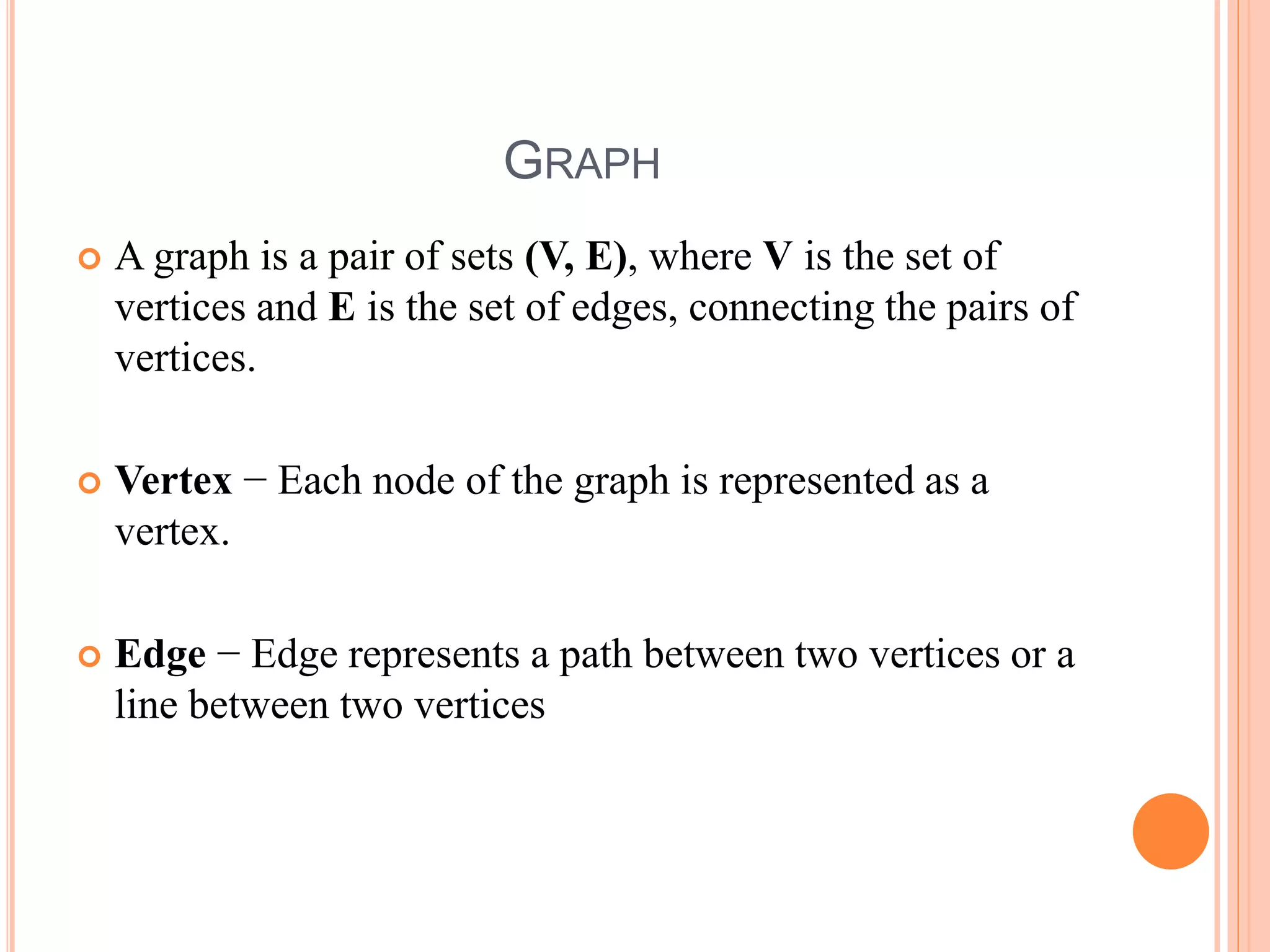
This document provides information about a data structures and algorithms class given to third year BSc IT students at Bon Secours College for Women in Thanjavur, India. It discusses non-linear data structures like trees and graphs, as well as linear data structures like arrays. Key points covered include the structure and representation of trees, types of graphs, and basic operations on data structures like traversal, searching, insertion and deletion.







![ARRAY REPRESENTATION
Fetching element:
Array[0]=35, array[1]=33, array[2]=42,array[3]=10,
Array[4]=14,Array[5]=19,Array[6]=27,Array[7]=44,Arra
y[8]=26,Array[9]=31.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructure-230213081149-f7591e7e/75/Data-Structure-pptx-15-2048.jpg)
![WHY DOES ARRAY INDEXING START WITH 0?
int a[10];
Here a itself is a pointer which contains the memory
location of the first element of the array. Now for
accessing the first element, we will write a[0] which is
internally decoded by the compiler as *(a + 0).
In the same way, the second element can be accessed
by a[1] or *(a + 1). As a contains the address of the first
element so for accessing the second element we have to
add 1 to it. That's why here we have written *(a +1). In
an array, the index describes the offset from the first
element, i.e. the distance from the first element.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructure-230213081149-f7591e7e/75/Data-Structure-pptx-16-2048.jpg)
![REPRESENTATION OF LINEAR ARRAY IN MEMORY
Let LA be a linear array that the memory of the
computer is simply a sequence of address.
Loc(LA[K])= address of the element
LA[K] of the array LA.
1000
1001
1002
1003](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructure-230213081149-f7591e7e/75/Data-Structure-pptx-17-2048.jpg)
