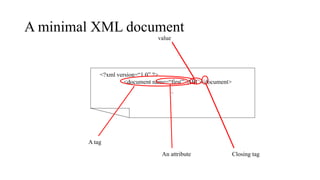
The document discusses the challenges of data integration in the life sciences due to incompatible data sources and the absence of standard naming conventions. It highlights the use of XML for representing biological data, emphasizing its extensibility, ease of modification, and ability to support interoperability across platforms and applications. Additionally, it outlines the significance of XML in the bioinformatics field, including self-describing data and the potential for transforming the web into a unified database.