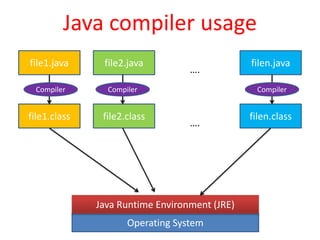
C++ and Java are both object-oriented languages that derive from C, but they have some key differences. C++ supports operator overloading and explicit memory management using pointers, references, and destructors. It also does not check array bounds. Java uses automatic garbage collection, does not support operator overloading, and always checks array bounds. While C++ applications run directly on the operating system, Java applications run on the Java Runtime Environment (JRE), allowing them to run on any system that supports Java.









![Arrays
• Basic data types and classes are treated the
same way in C++, unlike Java.
C++: ComplexNumber numbers[5];
Java: nothing equivalent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cvsjava-220725042155-20957a66/85/C-vsJava-pptx-11-320.jpg)
![C++ array version #2
ComplexNumber *numbers;
numbers = new ComplexNumber[5];
Java: nothing equivalent for classes,
but possible for basic data types:
int numbers[];
numbers = new int[5];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cvsjava-220725042155-20957a66/85/C-vsJava-pptx-12-320.jpg)
![C++ array version #3
ComplexNumber **numbers;
numbers = new ComplexNumber*[5];
for( index i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++)
numbers[i] = new ComplexNumber(…);
Java:
ComplexNumber numbers[];
numbers = new ComplexNumber [5];
for( index i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++)
numbers[i] = new ComplexNumber(…);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cvsjava-220725042155-20957a66/85/C-vsJava-pptx-13-320.jpg)

