PyCUDA provides a Python interface to CUDA that allows developers to write CUDA kernels in Python and execute them on NVIDIA GPUs. The example loads random data onto the GPU, defines a simple element-wise multiplication kernel in Python, compiles and runs the kernel on the GPU to multiply the arrays in parallel, and verifies the result matches multiplying the arrays on the CPU. PyCUDA handles memory transfers between CPU and GPU and provides tools for kernel definition, compilation and execution that abstract away many low-level CUDA API details.





![__global__ void dot( float *a, float *b, float *c )
{
__shared__ float cache[threadsPerBlock];
int cacheIndex = threadIdx.x;
...
// set the cache values
cache[cacheIndex] = temp;
// synchronize threads in this block
__syncthreads();
...
}
int main( void )
{
...
dot<<<blocksPerGrid,threadsPerBlock>>>( d_a, d_b, d_c );
...
}
shared memory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-6-2048.jpg)


![__constant__ float constFloat;
__device__ float getConstFloat() { return constFloat; }
__global__ void addConstant(float *vec, int N)
{
int i = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i<N)
vec[i] += getConstFloat();
}
#include <cutil_inline.h>
int main( int argc, char** argv)
{
float constValue = 4.0f;
cutilSafeCall( cudaMemcpyToSymbol(constFloat,
&constValue,
sizeof(float), 0,
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice) );
...
}
constant mem.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-9-2048.jpg)

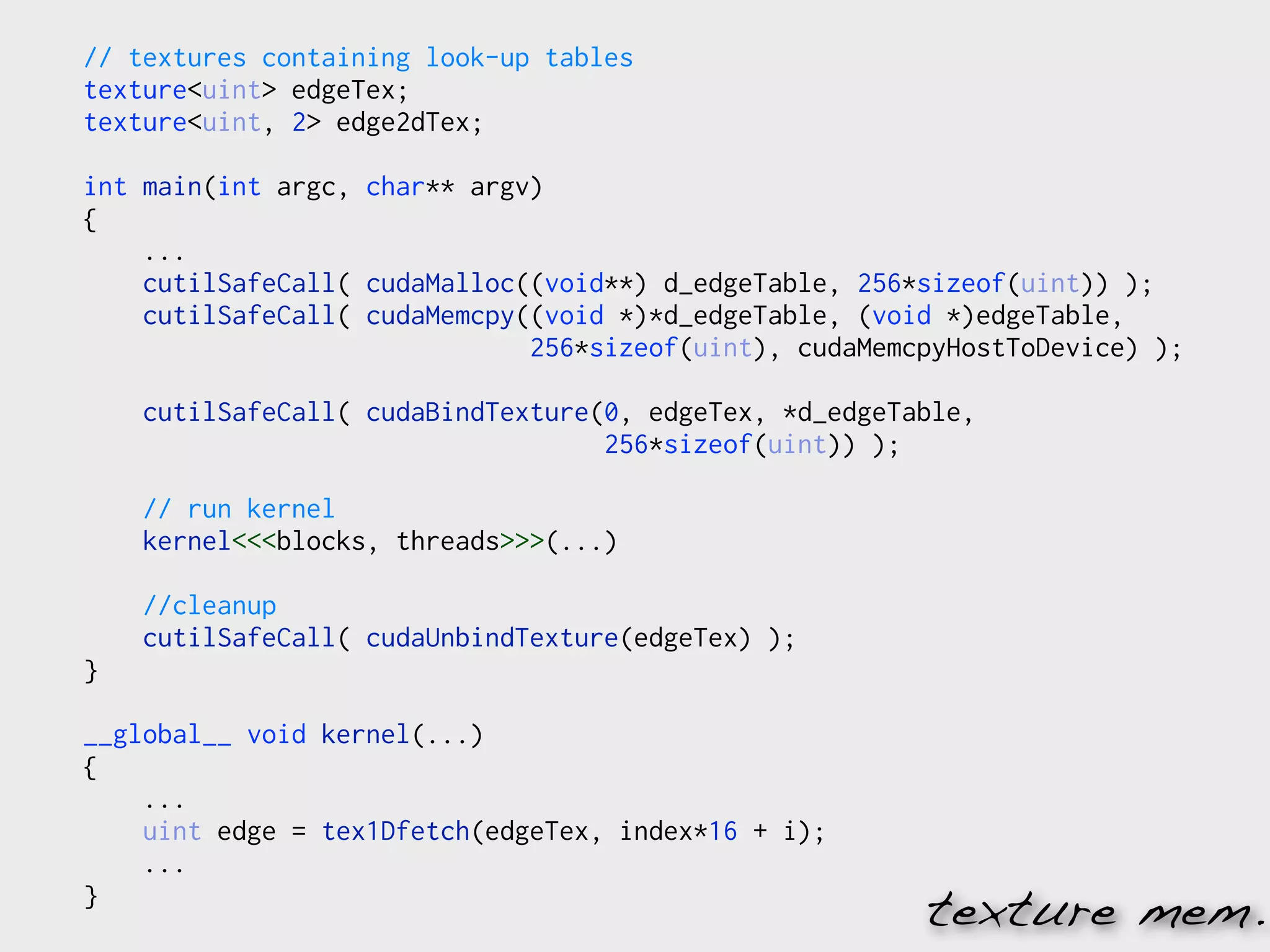

![surface<void, 2> output_surface;
__global__ void surfaceWrite(float* g_idata, int width, int height) {
// calculate surface coordinates
unsigned int x = blockIdx.x*blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
unsigned int y = blockIdx.y*blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
// read from global memory and write to cuarray (via surface reference)
surf2Dwrite(g_idata[y*width+x], output_surface, x*4, y, cudaBoundaryModeTrap);
}
int main( int argc, char** argv) {
...
cudaChannelFormatDesc channelDesc = cudaCreateChannelDesc(32, 0, 0, 0,
cudaChannelFormatKindFloat);
cudaArray* cu_array;
cutilSafeCall( cudaMallocArray(&cu_array, &channelDesc, width, height,
cudaArraySurfaceLoadStore) );
cutilSafeCall( cudaMemcpy( d_data, h_data, size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice) );
cutilSafeCall( cudaBindSurfaceToArray(output_surface, cu_array) );
surfaceWrite<<<dimGrid, dimBlock>>>(d_data, width, height);
...
cutilSafeCall( cudaFree(d_data) );
cutilSafeCall( cudaFreeArray(cu_array) );
}
surface mem.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-13-2048.jpg)





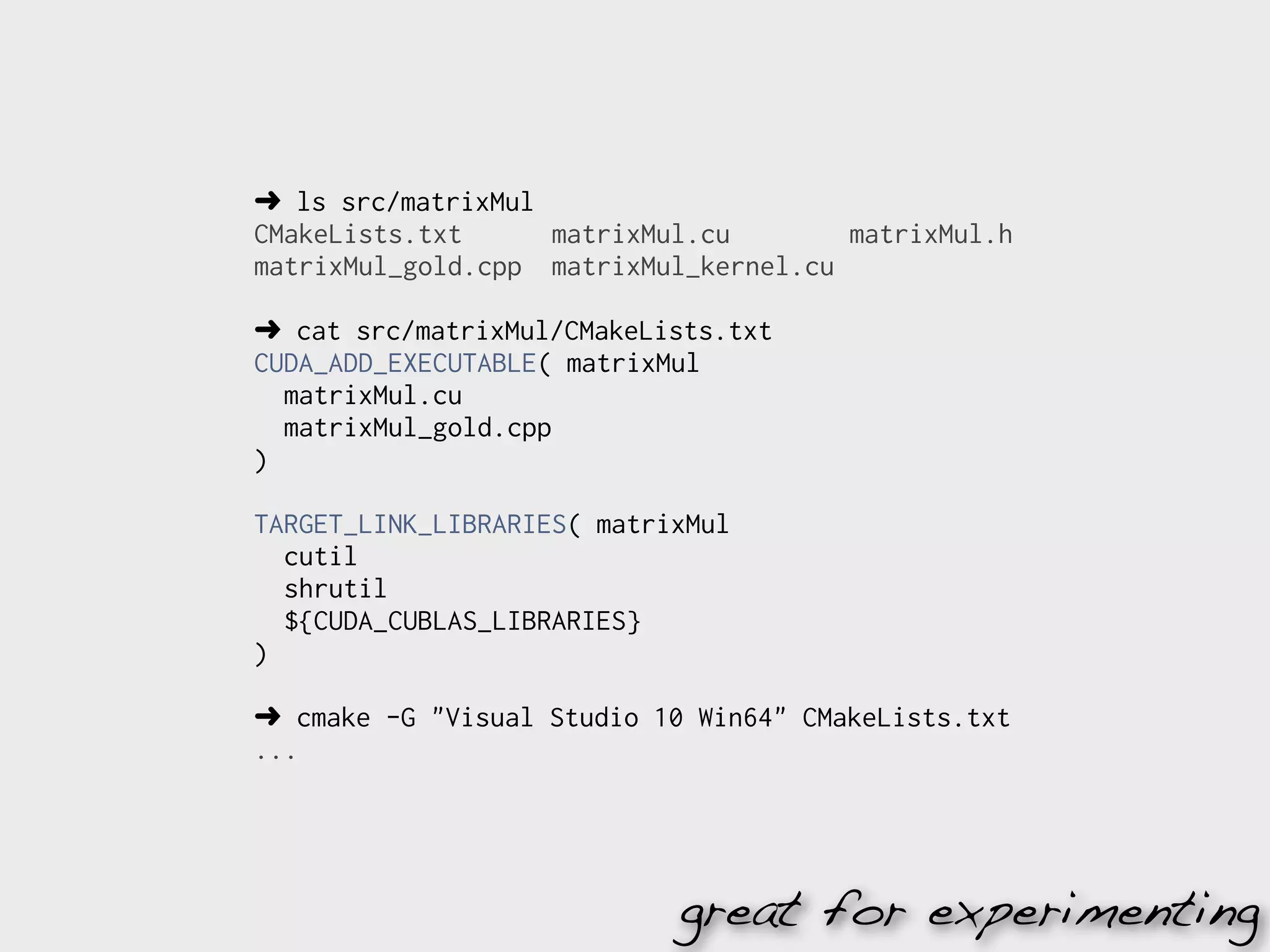
![➜ git clone https://github.com/kashif/cuda-workshop.git
Cloning into cuda-workshop...
...
➜ cd cuda-workshop
➜ cmake CMakeLists.txt
-- The C compiler identification is GNU
...
➜ make
Scanning dependencies of target cutil
[ 5%] Building CXX object cutil/CMakeFiles/cutil.dir/src/bank_checker.cpp.o
...
[100%] Built target matrixMul
➜ ./bin/matrixMul
[ matrixMul ]
bin/matrixMul Starting (CUDA and CUBLAS tests)...
Device 0: "GeForce GTX 480" with Compute 2.0 capability
...
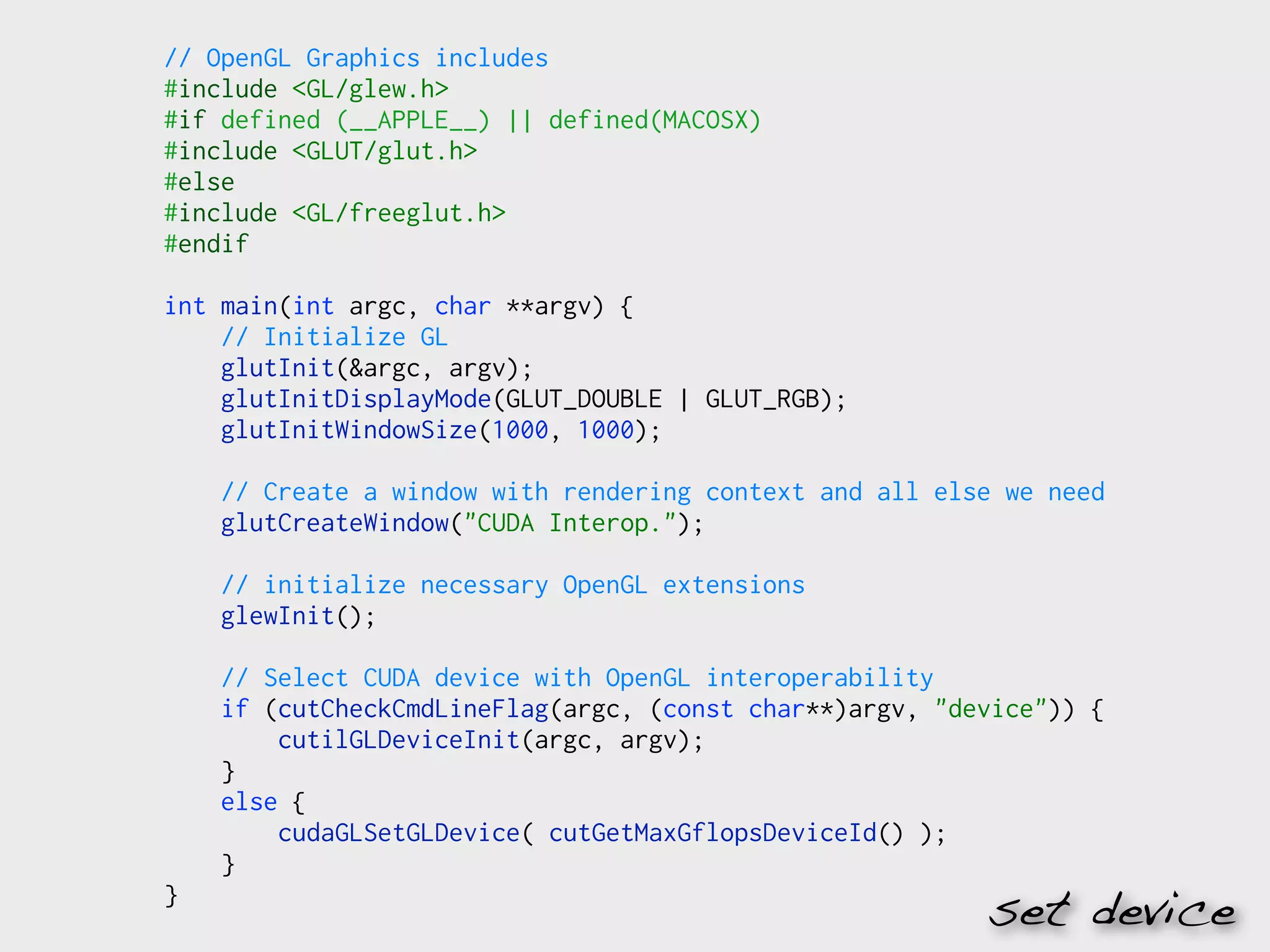
install CMake, glut & glew](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-20-2048.jpg)


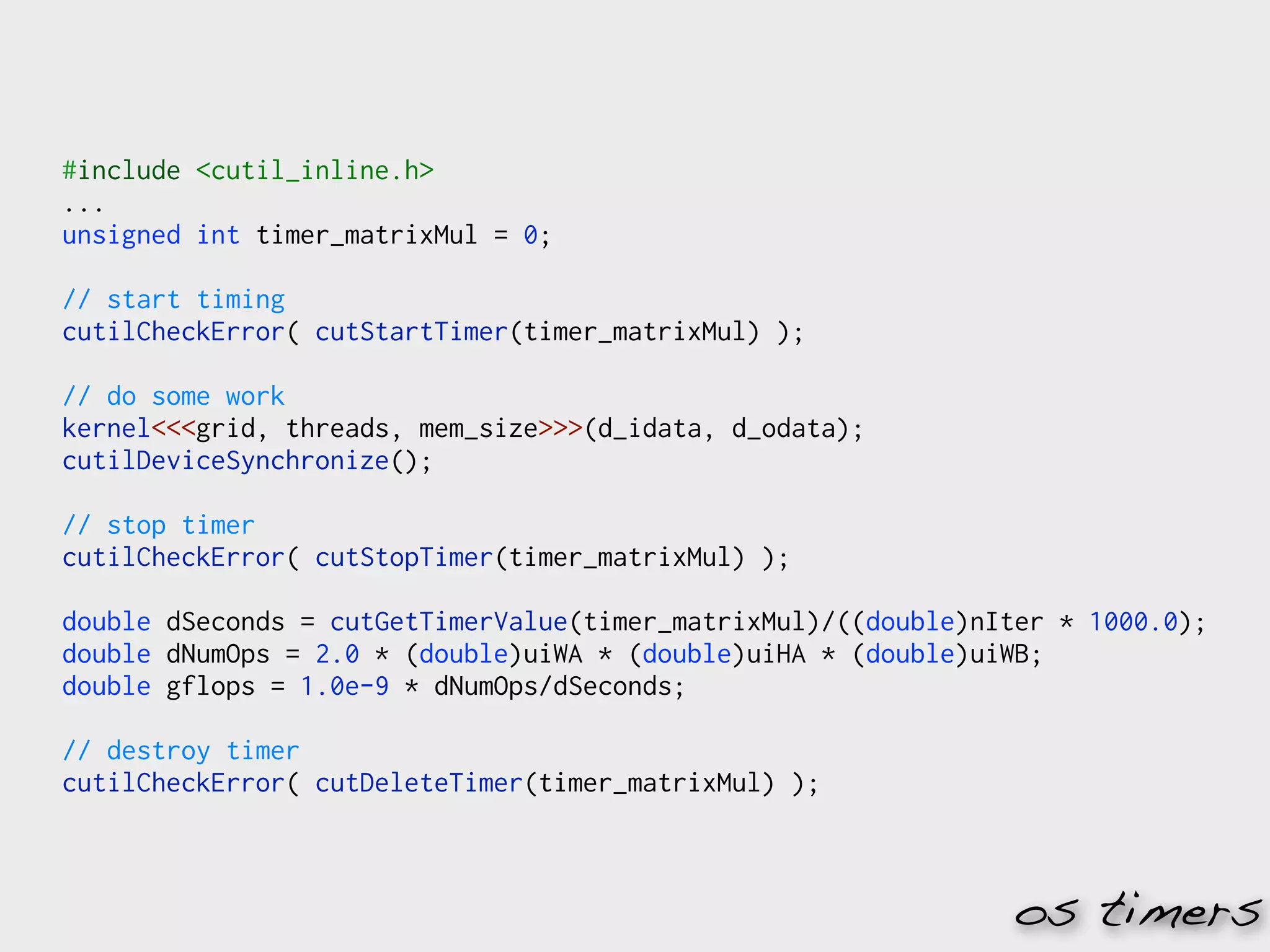


![➜ cat hello_gpu.py
import pycuda.driver as drv
import pycuda.tools
import pycuda.autoinit
import numpy
import numpy.linalg as la
from pycuda.compiler import SourceModule
mod = SourceModule("""
__global__ void multiply_them(float *dest, float *a, float *b)
{
const int i = threadIdx.x;
dest[i] = a[i] * b[i];
}
""")
multiply_them = mod.get_function("multiply_them")
a = numpy.random.randn(400).astype(numpy.float32)
b = numpy.random.randn(400).astype(numpy.float32)
dest = numpy.zeros_like(a)
multiply_them(
drv.Out(dest), drv.In(a), drv.In(b),
block=(400,1,1))
print dest-a*b
pycuda](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-27-2048.jpg)
![➜ python hello_gpu.py
[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.
0. 0. 0. 0.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-28-2048.jpg)
![// Initialize the driver and create a context for the first device.
cuInit(0);
CUdevice device = new CUdevice(); cuDeviceGet(device, 0);
CUcontext context = new CUcontext(); cuCtxCreate(context, 0, device);
// Create the PTX file by calling the NVCC and load it
String ptxFileName = preparePtxFile("JCudaVectorAddKernel.cu");
CUmodule module = new CUmodule(); cuModuleLoad(module, ptxFileName);
// Obtain a function pointer to the "add" function.
CUfunction function = new CUfunction(); cuModuleGetFunction(function, module, "add");
// Allocate the device input data
float hostInputA[] = new float[numElements]; CUdeviceptr deviceInputA = new CUdeviceptr();
cuMemAlloc(deviceInputA, numElements * Sizeof.FLOAT);
cuMemcpyHtoD(deviceInputA, Pointer.to(hostInputA), numElements * Sizeof.FLOAT);
...
// Set up the kernel parameters
Pointer kernelParameters = Pointer.to(Pointer.to(deviceInputA),...);
// Call the kernel function
int blockSizeX = 256; int gridSizeX = (int)Math.ceil((double)numElements / blockSizeX);
cuLaunchKernel(function,
gridSizeX, 1, 1, // Grid dimension
blockSizeX, 1, 1, // Block dimension
0, null, // Shared memory size and stream
kernelParameters, null); // Kernel- and extra parameters
cuCtxSynchronize();
jcuda](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-29-2048.jpg)
![➜ ls
License.txt jcuda-0.4.0-beta1.jar
jcurand-0.4.0-beta1.jar libJCublas-apple-x86_64.dylib
libJCudaRuntime-apple-x86_64.dylib libJCurand-apple-x86_64.dylib
jcublas-0.4.0-beta1.jar jcufft-0.4.0-beta1.jar
jcusparse-0.4.0-beta1.jar libJCudaDriver-apple-x86_64.dylib
libJCufft-apple-x86_64.dylib libJCusparse-apple-x86_64.dylib
JCudaVectorAdd.java JCudaVectorAddKernel.cu
➜ cat JCudaVectorAddKernel.cu
extern "C"
__global__ void add(float *a, float *b, float *sum, int n)
{
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i<n)
{
sum[i] = a[i] + b[i];
}
}
➜ javac -classpath jcuda-0.4.0-beta1.jar JCudaVectorAdd.java
➜ java -classpath jcuda-0.4.0-beta1.jar:. JCudaVectorAdd
Executing
nvcc -m64 -ptx JCudaVectorAddKernel.cu -o JCudaVectorAddKernel.ptx
Finished creating PTX file
Test PASSED](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-30-2048.jpg)
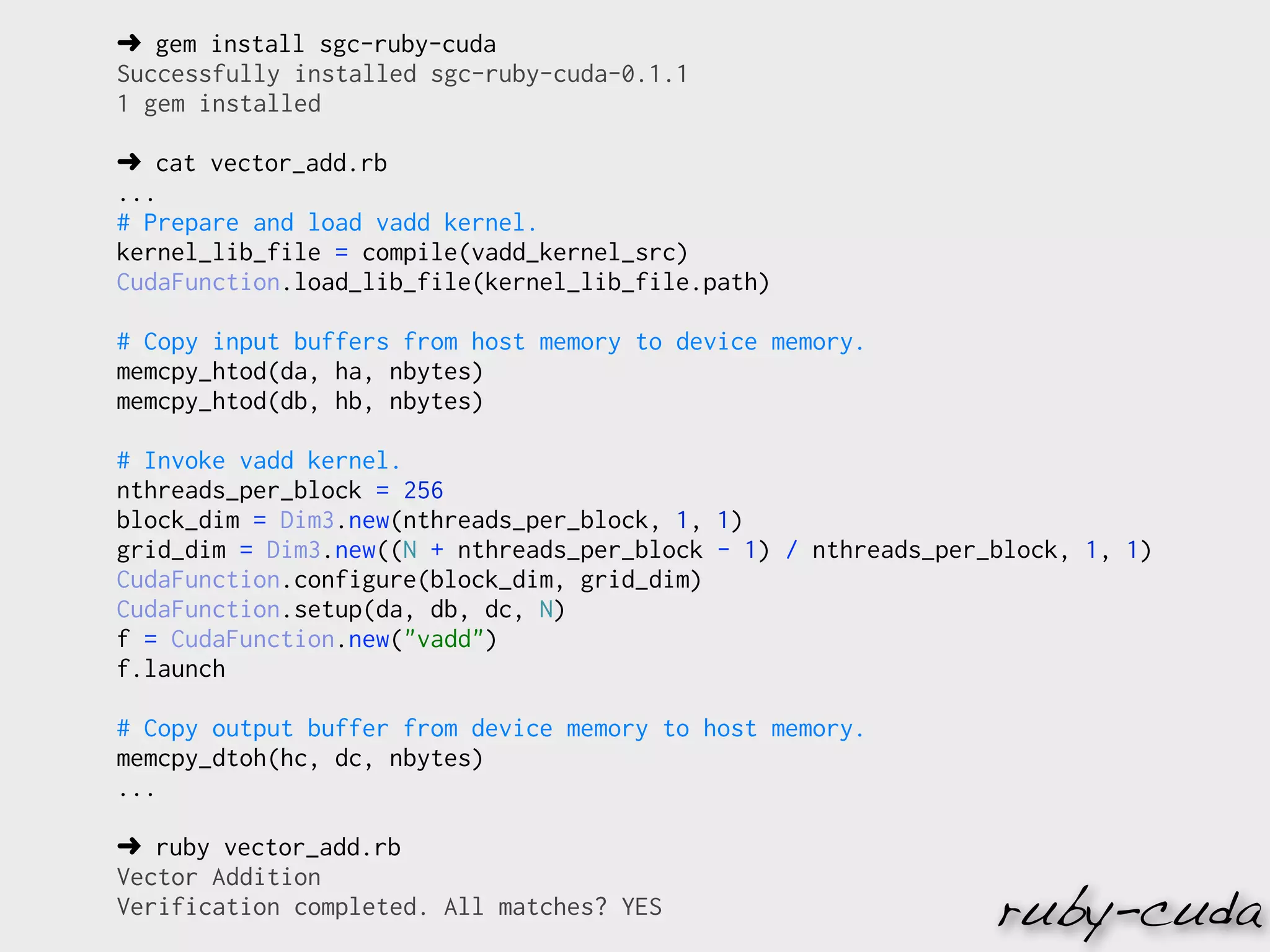

![cublasHandle_t handle;
cublasStatus_t status = cublasCreate(&handle);
float* h_A = (float*)malloc(N * N * sizeof(h_A[0]));
...
/* Fill the matrices with test data */
...
/* Allocate device memory for the matrices */
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_A, N * N * sizeof(d_A[0]));
...
/* Initialize the device matrices with the host matrices */
status = cublasSetVector(N * N, sizeof(h_A[0]), h_A, 1, d_A, 1);
...
/* Performs Sgemm: C <- alphaAB + betaC */
status = cublasSgemm(handle, CUBLAS_OP_N, CUBLAS_OP_N, N, N, N,
&alpha, d_A, N, d_B, N, &beta, d_C, N);
/* Allocate host mem & read back the result from device mem */
h_C = (float*)malloc(N * N * sizeof(h_C[0]));
status = cublasGetVector(N * N, sizeof(h_C[0]), d_C, 1, h_C, 1);
/* Memory clean up */
cudaFree(d_A);
...
/* Shutdown */
status = cublasDestroy(handle);
cublas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-33-2048.jpg)







![cudaStream_t *streamArray = 0;
streamArray = (cudaStream_t *)malloc(N * sizeof (cudaStream_t *));
...
for ( int i = 0; i < N ; i++) {
cudaStreamCreate(&streamArray[i]);
...
}
...
for ( int i = 0; i < N ; i++) {
cublasSetMatrix (..., devPtrA[i], ...);
...
}
...
for ( int i = 0; i < N ; i++) {
cublasSetStream(handle, streamArray[i]);
cublasSgemm(handle, ..., devPtrA[i], devPtrB[i], devPtrC[i], ...);
}
cudaThreadSynchronize();
batched computation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-41-2048.jpg)

![// Allocate resources
for( int i =0; i<STREAM_COUNT; ++i ) {
cudaHostAlloc(&h_data_in[i], memsize, cudaHostAllocDefault);
cudaMalloc(&d_data_in[i], memsize);
...
}
int current_stream = 0;
// Do processing in a loop...
{
int next_stream = (current_stream + 1 ) % STREAM_COUNT;
// Ensure that processing and copying of the last cycle has finished
cudaEventSynchronize(cycleDone[next_stream]);
// Process current frame
kernel<<<grid, block, 0, stream[current_stream]>>>(d_data_out[current_stream],
d_data_in[current_stream],
N, ...);
// Upload next frame
cudaMemcpyAsync(d_data_in[next_stream], ..., cudaMemcpyHostToDevice,
stream[next_stream]);
// Download current frame
cudaMemcpyAsync(h_data_out[current_stream], ..., cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost,
stream[current_stream]);
cudaEventRecord(cycleDone[current_stream], stream[current_stream]);
current_stream = next_stream;
}
overlap kernel exec. & memcpy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-43-2048.jpg)


![float *a, *d_a;
...
/* Allocate mapped CPU memory. */
cutilSafeCall( cudaHostAlloc((void **)&a, bytes, cudaHostAllocMapped) );
...
/* Initialize the vectors. */
for(n = 0; n < nelem; n++) { a[n] = rand() / (float)RAND_MAX; ... }
/* Get the device pointers for the pinned CPU memory mapped into the GPU
memory space. */
cutilSafeCall( cudaHostGetDevicePointer((void **)&d_a, (void *)a, 0) );
...
/* Call the GPU kernel using the device pointers for the mapped memory. */
...
kernel<<<grid, block>>>(d_a, d_b, d_c, nelem);
...
/* Memory clean up */
cutilSafeCall( cudaFreeHost(a) );
...
zero-copy host memory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-46-2048.jpg)
![//Create streams for issuing GPU command asynchronously and allocate memory
for(int i = 0; i < GPU_N; i++) {
cutilSafeCall( cudaStreamCreate(&stream[i]) );
cutilSafeCall( cudaMalloc((void**)&d_Data[i], dataN * sizeof(float)) );
cutilSafeCall( cudaMallocHost((void**)&h_Data[i], dataN * sizeof(float)) );
//init h_Data
}
//Copy data to GPU, launch the kernel and copy data back. All asynchronously
for(int i = 0; i < GPU_N; i++) {
//Set device
cutilSafeCall( cudaSetDevice(i) );
// Copy input data from CPU
cutilSafeCall( cudaMemcpyAsync(d_Data[i], h_Data[i], dataN * sizeof(float),
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream[i]) );
// Perform GPU computations
kernel<<<blocks, threads, 0, stream[i]>>>(...)
// Copy back the result
cutilSafeCall( cudaMemcpyAsync(h_Sum_from_device[i], d_Sum[i],
ACCUM_N * sizeof(float),
cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream[i]) );
}
streams](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-47-2048.jpg)
![// Process GPU results
for(i = 0; i < GPU_N; i++) {
// Set device
cutilSafeCall( cudaSetDevice(i) );
// Wait for all operations to finish
cudaStreamSynchronize(stream[i]);
// Shut down this GPU
cutilSafeCall( cudaFreeHost(h_Data[i]) );
cutilSafeCall( cudaFree(d_Data[i]) );
cutilSafeCall( cudaStreamDestroy(stream[i]) );
}
// shutdown
for(int i = 0; i < GPU_N; i++) {
cutilSafeCall( cudaSetDevice(i) );
cutilDeviceReset();
}
process the result](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-48-2048.jpg)

![// Initialize MPI state
MPI_CHECK( MPI_Init(&argc, &argv) );
// Get our MPI node number and node count
int commSize, commRank;
MPI_CHECK( MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &commSize) );
MPI_CHECK( MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &commRank) );
if(commRank == 0) {// Are we the root node?
//initialize dataRoot...
}
// Allocate a buffer on each node
float * dataNode = new float[dataSizePerNode];
// Dispatch a portion of the input data to each node
MPI_CHECK( MPI_Scatter(dataRoot, dataSizePerNode, MPI_FLOAT, dataNode,
dataSizePerNode, MPI_FLOAT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD) );
// if commRank == 0 then free dataRoot...
kernel<<<gridSize, blockSize>>>(dataNode, ...);
// Reduction to the root node
float sumNode = sum(dataNode, dataSizePerNode);
float sumRoot;
MPI_CHECK( MPI_Reduce(&sumNode, &sumRoot, 1, MPI_FLOAT, MPI_SUM, 0,
MPI_COMM_WORLD) );
MPI_CHECK( MPI_Finalize() ); mpi + cuda](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-50-2048.jpg)
![// Enable peer access
cutilSafeCall(cudaSetDevice(gpuid_tesla[0]));
cutilSafeCall(cudaDeviceEnablePeerAccess(gpuid_tesla[1], gpuid_tesla[0]));
...
// Allocate buffers
cudaSetDevice(gpuid_tesla[0]); cudaMalloc(&g0, buf_size);
cudaSetDevice(gpuid_tesla[1]); cudaMalloc(&g1, buf_size);
// Ping-pong copy between GPUs
cudaMemcpy(g1, g0, buf_size, cudaMemcpyDefault);
// Prepare host buffer and copy to GPU 0
cudaSetDevice(gpuid_tesla[0]); cudaMemcpy(g0, h0, buf_size, cudaMemcpyDefault);
// Run kernel on GPU 1, reading input from the GPU 0 buffer, writing
// output to the GPU 1 buffer: dst[idx] = src[idx] * 2.0f
cudaSetDevice(gpuid_tesla[1]); kernel<<<blocks, threads>>>(g0, g1);
cutilDeviceSynchronize();
// Disable peer access (also unregisters memory for non-UVA cases)
cudaSetDevice(gpuid_tesla[0]); cudaDeviceDisablePeerAccess(gpuid_tesla[1]);
cudaSetDevice(gpuid_tesla[1]); cudaDeviceDisablePeerAccess(gpuid_tesla[0]);
cudaFree(g0);
...
P2P & unified virtual address space](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cuda-deep-dive-111109035314-phpapp02/75/CUDA-Deep-Dive-51-2048.jpg)


