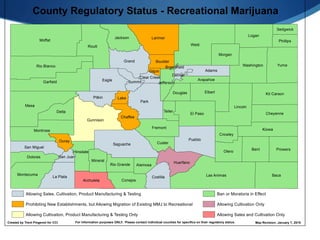
The legal marijuana industry in Colorado has grown rapidly but faces challenges regarding water supply and compliance. Indoor cannabis cultivation requires different types of water rights than traditional irrigation. Federal restrictions ban using water from federal facilities for marijuana. States and localities have implemented solutions like allowing water leasing or requiring cultivation plans. While indoor use can be efficient, outdoor cultivation requires more water but systems vary significantly between operations.