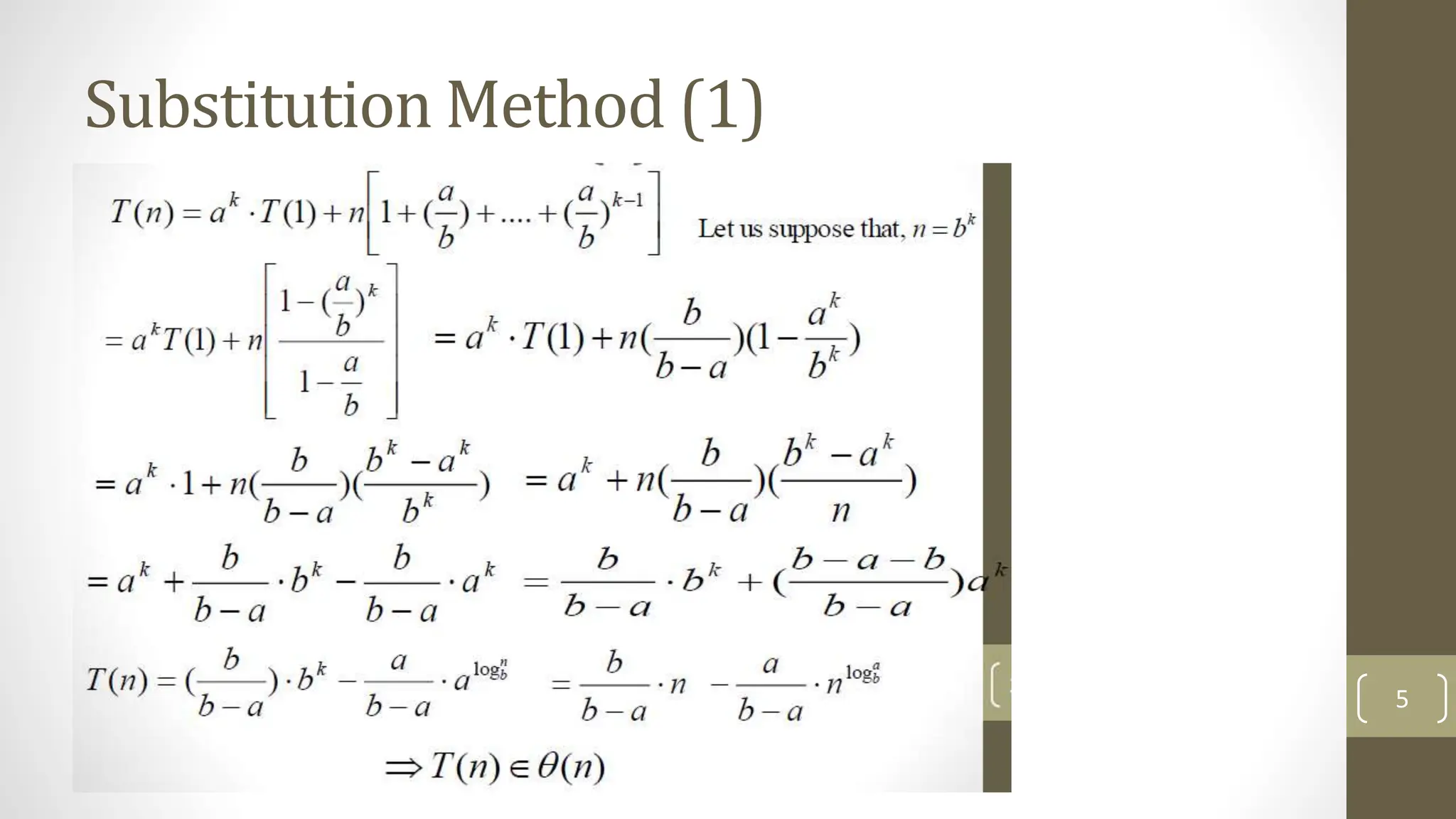
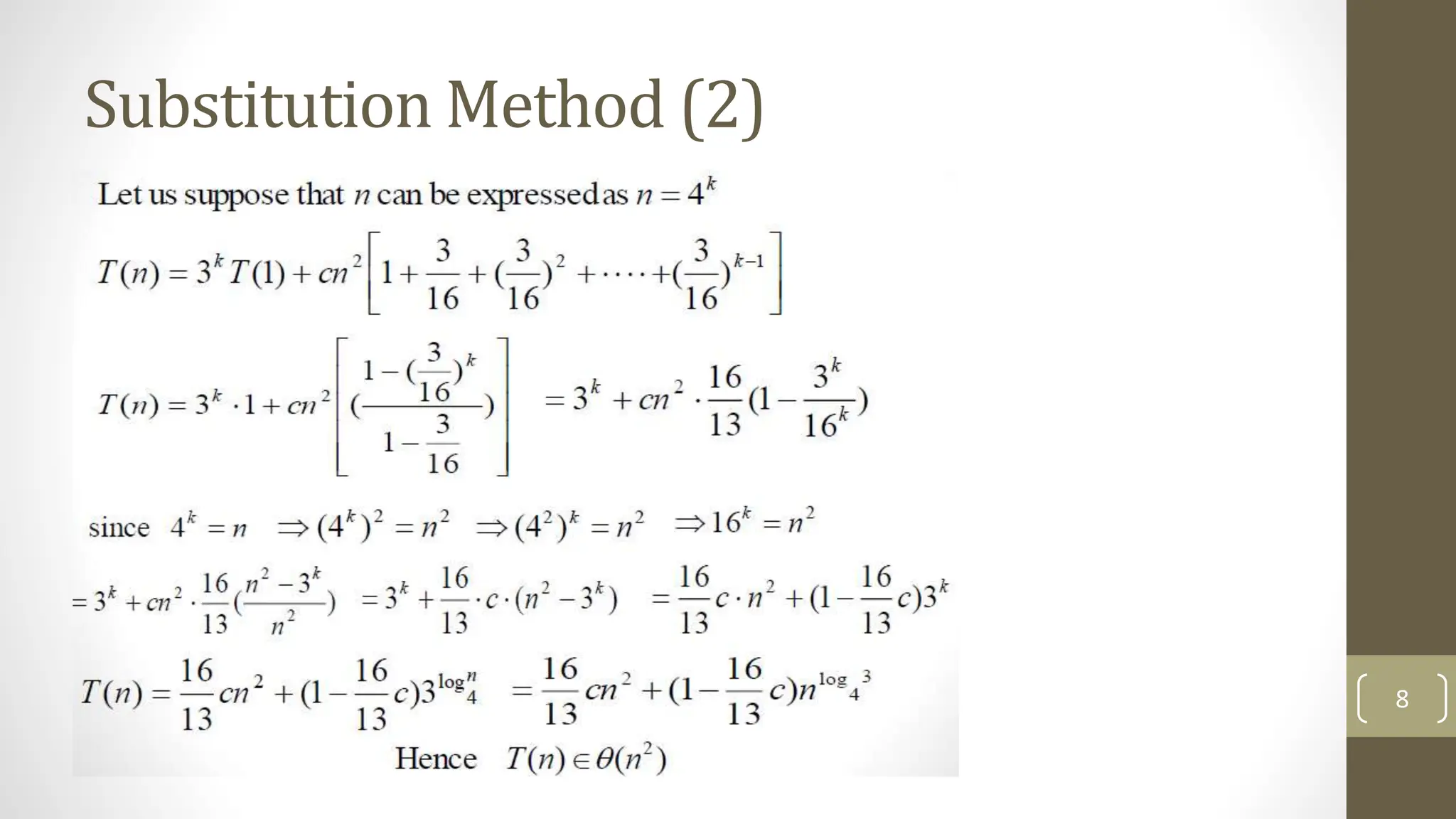
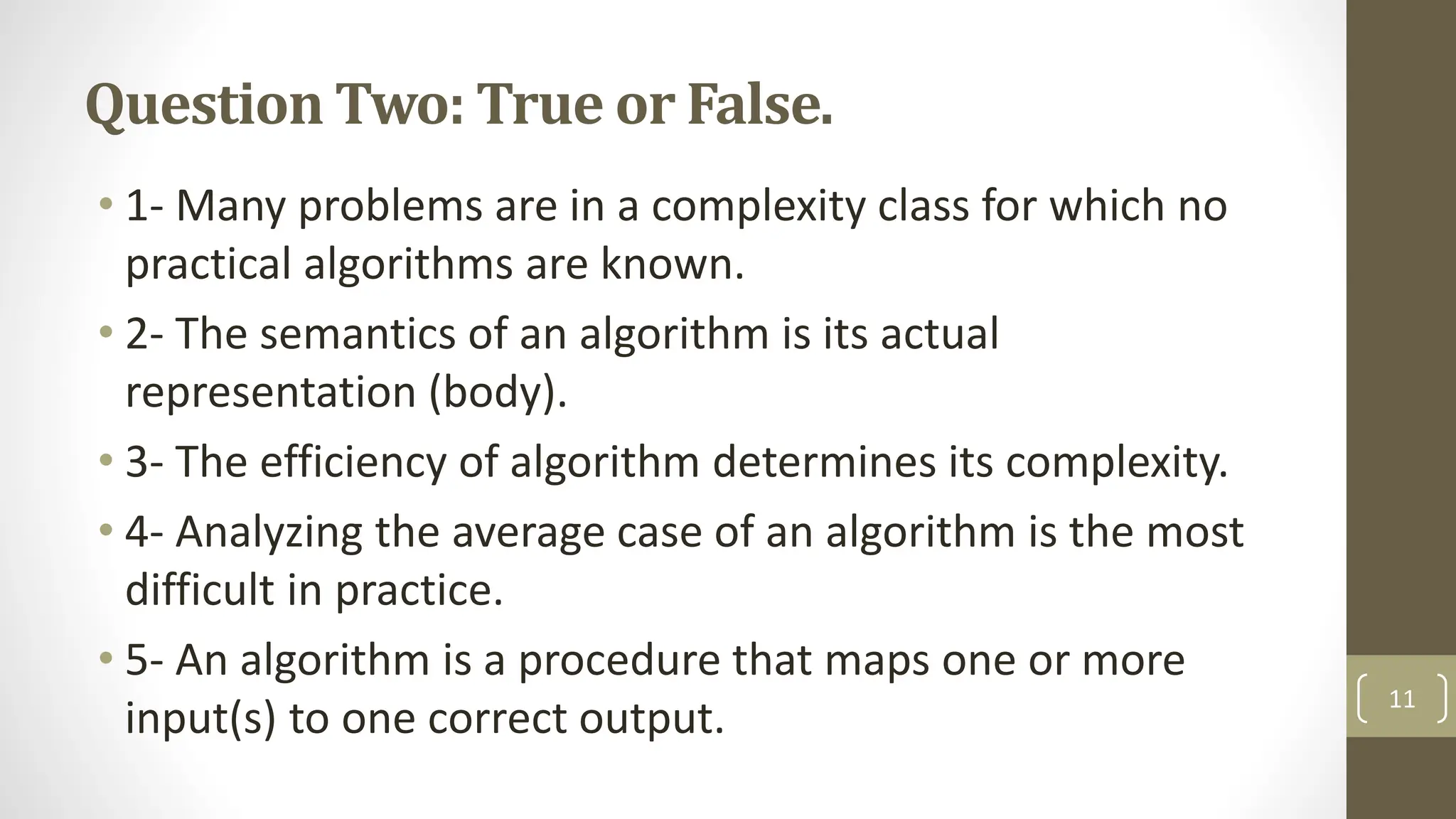
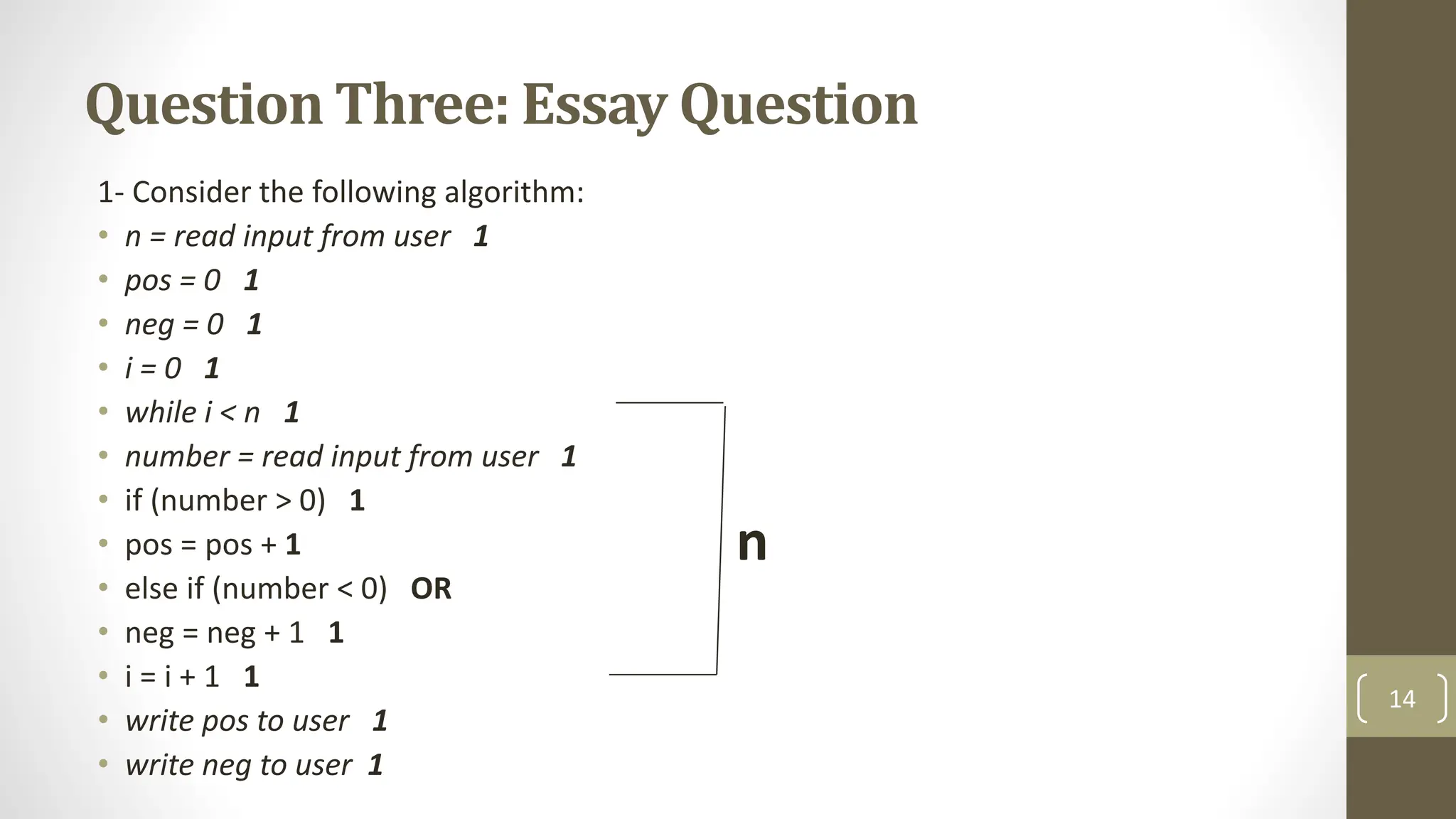
The document discusses three methods to solve recurrences in algorithm analysis: the substitution method, recursion tree method, and master method. It details the substitution method, which involves guessing the form of a solution and proving it by induction. Additionally, there is a midterm exam section with multiple choice and true/false questions evaluating concepts in algorithm analysis and complexity.