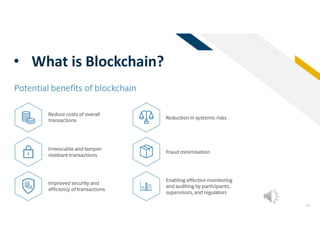
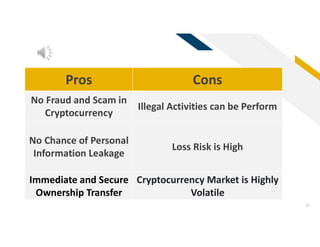
This document provides an overview of cryptocurrency, including definitions and explanations of key concepts. It discusses the history and development of cryptocurrency from early concepts like Bitcoin to more recent innovations. Major topics covered include blockchain technology, different types of cryptocurrencies like coins and tokens, cryptocurrency mining processes, potential pros and cons, and criticisms. It also presents visions of cryptocurrency's future role and potential to disrupt traditional financing systems through features like low-cost international payments. In under 3 sentences.