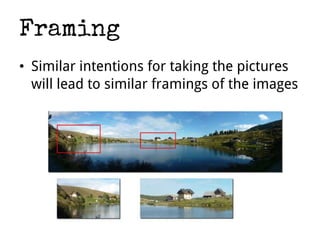
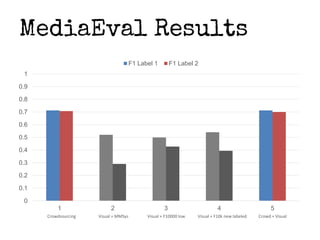
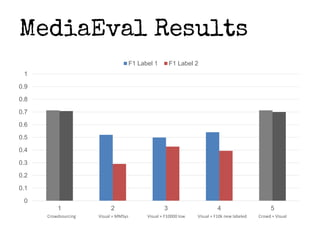
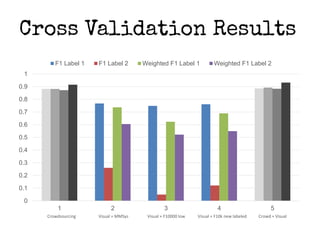
This document presents a method for improving image classification using crowdsourcing and global visual features. It calculates worker reliability to weight crowd votes and uses these weighted votes to label images. Visual classifiers are then trained on the newly labeled data. Experimental results show that combining crowdsourcing with visual features leads to good classification performance, even with small labeled datasets. Worker reliability measures perform well, and transfer learning is effective. However, some concepts are better detected visually than others.