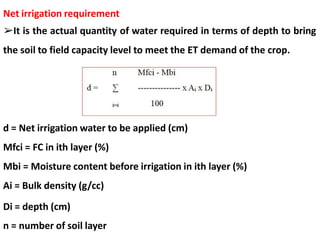
This document discusses factors that affect crop water requirement and how to calculate irrigation requirements. It outlines that crop water requirement includes transpiration, evaporation, and water used for plant metabolism. It also lists factors like crop variety, growth stage, soil type, climate, and irrigation methods that influence water needs. The document defines net and gross irrigation requirements, noting that gross requirement includes losses. It further explains how to calculate irrigation period based on soil moisture levels and crop water usage during peak consumption periods. Critical irrigation stages are identified as periods when moisture stress can severely reduce yields.