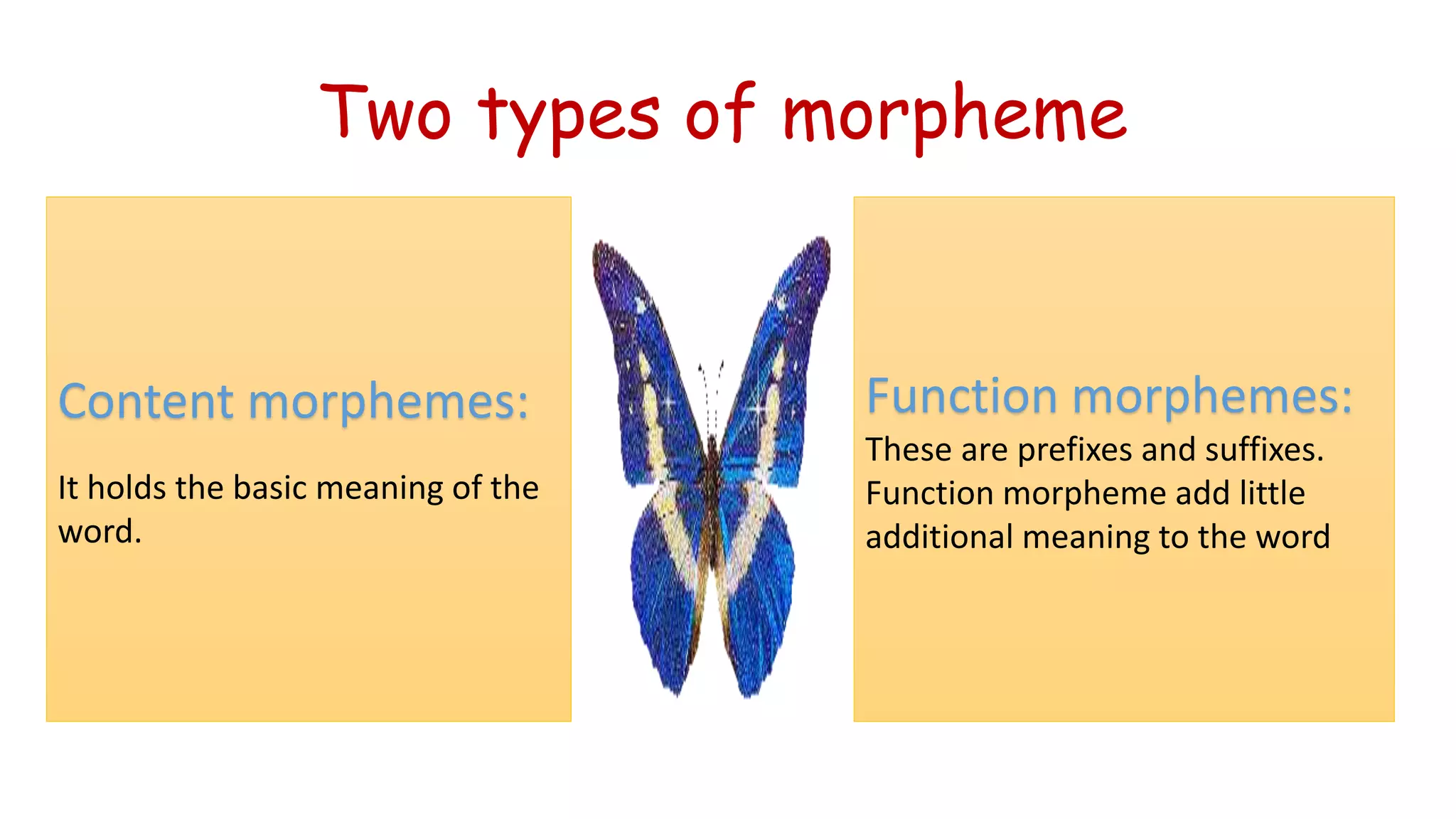
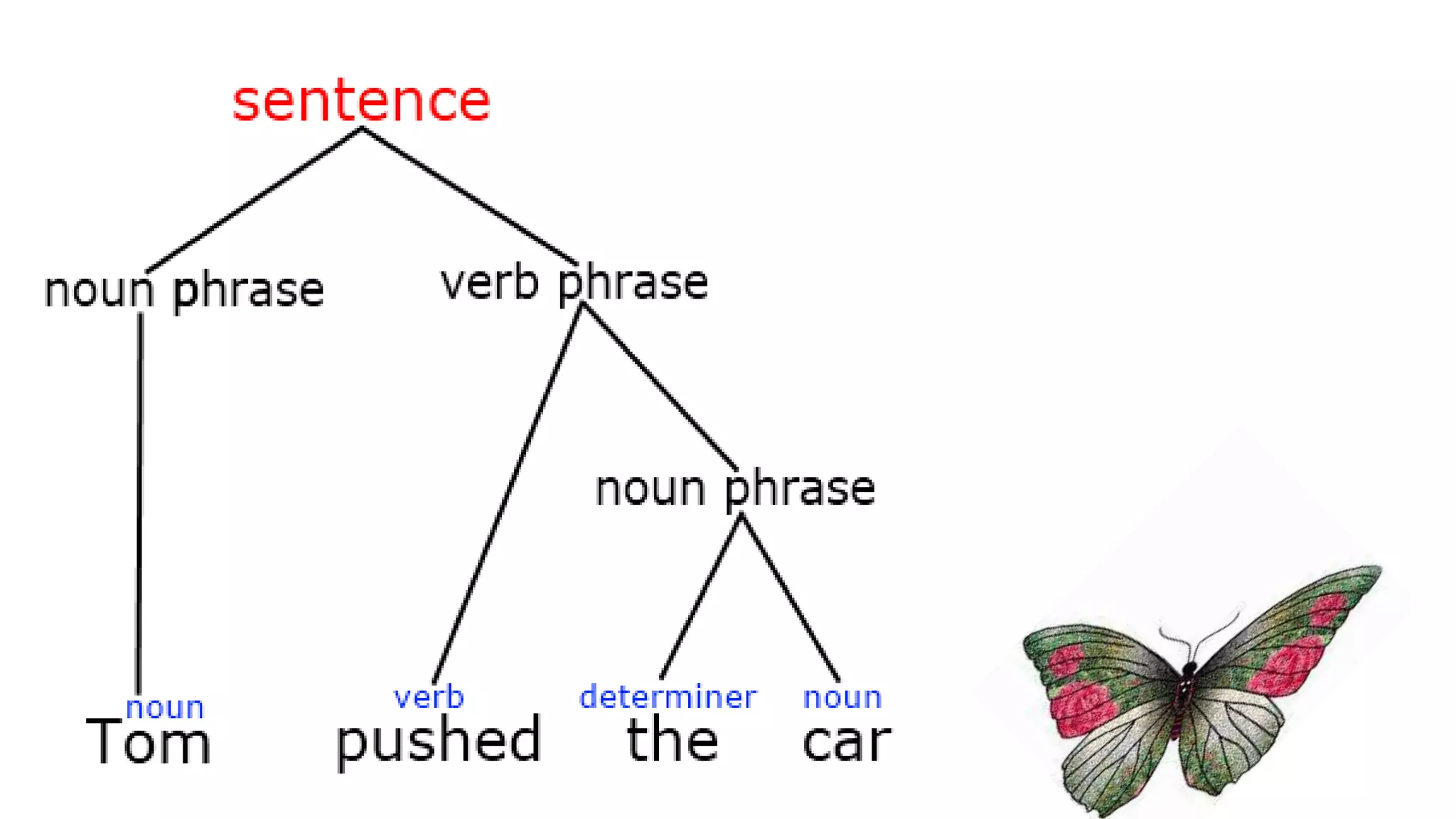
Language is a complex system of symbols and rules used for communication. It has several key characteristics - it is arbitrary, social, symbolic, vocal, generative, creative, unique and modifiable over time. The basic building blocks of language are sounds (phonemes), which combine to form meaningful units (morphemes) that can be arranged according to syntactic rules to form phrases and sentences. Language allows humans to learn, transmit information, express ideas and forge social identities and cultural ties.