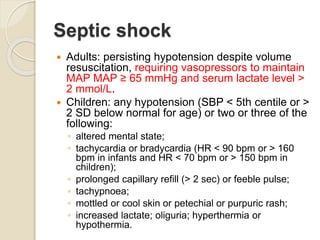
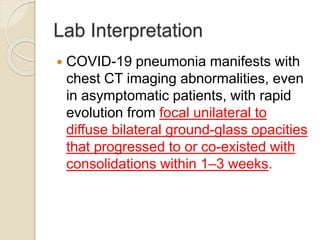
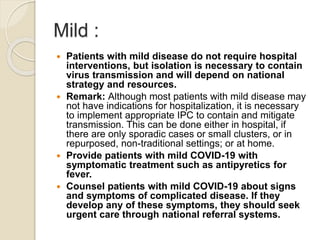
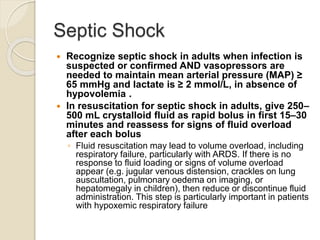
This document provides guidelines for the clinical management of COVID-19. It notes that while most cases are mild, approximately 14% of cases develop severe disease requiring hospitalization and oxygen support, and 5% require intensive care. Older age and comorbidities increase the risk of severe outcomes. For mild cases, isolation and symptomatic treatment is recommended, while severe cases may require oxygen therapy, fluid management, antimicrobials, and advanced support like mechanical ventilation for acute respiratory distress syndrome or vasopressors for septic shock. Testing for COVID-19 involves respiratory samples, and local protocols should be followed for patient isolation and discharge.