1. The document defines various types of companies under Indian law such as Indian company, domestic company, foreign company, and company in which the public are substantially interested.
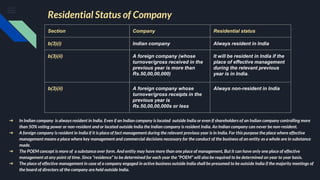
2. It explains the residential status of companies in India, noting that an Indian company is always resident in India regardless of control or location, while a foreign company's residence is determined by its place of effective management.
3. Tax planning tips are provided for the Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT) under section 115JB, such as recognizing revenue conservatively, using written down value depreciation, timing asset sales, writing off goodwill, and amortizing certain expenditures.










![● It may be noted that in respect of the following amounts debited to the statement of profit and loss, no adjustment is required under
section 115JB : a. any penalty or fine paid or payable under the Income-taxAct ; b. any tax, penalty or interest paid or payable under
the Wealth-taxAct ; c. any tax, penalty or interest paid or payable under the Gift-tax Act ; or d. any tax, penalty, or interest paid or
payable under the Companies (Profits) Surtax Act ; and e. any tax or duty which is not allowed as deduction while calculating taxable
income by virtue of section 43B f. securities transaction tax; g. banking cash transaction tax; and h. fringe benefit tax. The aforesaid
sums are not added to net profit in order to compute book profit for the purpose of section 115JB, though some of these expenses are
not allowed as deduction while calculating/ determining taxable income.
● Arrears of depreciation not provided in books in earlier years may be provided in the current year.
● Where the assessee has changed method of providing depreciation from straight line to written down value method which resulted in
shortfall in depreciation provided and resultant shortfall in depreciation is charged to statement of profit and loss for the current year,
the Assessing Officer is not justified in disallowing assessee’s claim of such additional depreciation while computing book profit on the
ground that such depreciation was not provided for in books of account of the assessee for the earlier years – CIT v. Farmson
Pharmaceuticals Gujarat Ltd. [ 2011] 241 CTR (Guj.) 568.
● Depreciation can be provided in books of account at rates higher than those specified in the Companies Act. Extra depreciation
(pertaining to earlier years) arising because of a bona fide change in depreciation method can be debitedto statement of profit and loss
for computing book profit.
● Guidance Note of ICAI indicates that depreciation also includes depletion of natural resources through process of extraction or use.
Book profit under section 115JB would be computed after allowing claim of depletion of natural resources.
● Refund of tax not credited to statement of profit and loss cannot be added to book profit.
● The Delhi High Court in CIT v. G E Power Services India Ltd. [2008] 171 Taxman 10 held that software expenditure debited to
statement of profit and loss is an allowable deduction in computing book profits. The Court refuted the argument of the revenue that
such expenditure would be capital in nature after amendment to section 32. The Court found such argument as unworthy, perhaps for
the reason that section 32 has no relevance as far as determination of book profits goes.
● This judgment thus provides a good tax planning method and, thus, an assessee can charge off software costs in accounts even while it
resorts to depreciation claim in tax computation after taking disallowance first. Before the statutory auditor, the assessee can take the
contention that the software in use has a short span of life and further it needs updating from time to time.
ASTHA JAIN 10557](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2ctpppt-221226142056-a628dc4c/85/corporate-tax-planning-pptx-12-320.jpg)

![Minimum Alternate Tax [Sec. 115JB]
➢ MAT is applicable when tax computed under normal provisions is less than tax computed under
Sec 115JB provisions.
➢ In the case of a company (may be domestic or foreign company), the income tax payable on its total
income (computed after applying all provisions of income tax except section 115JB) is less than
15% of book profits + surcharge (if applicable) + cess, then such book profits shall be deemed to be
total income.
➢ Book profit shall be calculated on the basis of profit and loss account prepared in accordance with
the provisions of schedule VI of the Companies Act.
➢ Exceptions - Life Insurance business, Shipping income liable to tonnage taxation
➢ In the following two cases, the Assessing Officer can rewrite the profit and loss account:
○ If profit and loss account is not prepared according to the Companies Act
○ If accounting policies, accounting standards or rates or method of depreciation are different](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2ctpppt-221226142056-a628dc4c/85/corporate-tax-planning-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![Determining Book Profit [Sec 115JB]
Negative Adjustments (Less)
● Income tax or any provision for Income tax
● Transfer to Reserve
● Provision for unascertained liability
● Dividends (whether proposed or paid)
● Loss/Provision for loss of Subsidiary company
● Provision for diminution in the value of assets
● Deferred tax or any provision for deferred tax
● Depreciation as per books of account
● Expenditure on income which are exempt u/s
10,11,12
● Expenditure relatable to income from share in
AOP or BOI.
● Amount standing in Revaluation reserve in
respect of an asset which has been sold or
disposed off but not credited to P&L A/c.
● Any Amount withdrawn from Reserves
● Depreciation as per books of account. (ignoring
revaluation)
● Amount withdrawn from provision for deferred
tax.
● Any amount of income which is exempt.
● Share of Profit from AOP/ BOI.
● Amount withdrawn from revaluation reserve
and credited to Profit and loss account to the
extent it doesn’t exceed the amount of
depreciation on account of revaluation.
● Amount of unabsorbed loss or unabsorbed
depreciation whichever is lower as per
Companies Act. (Aggregate Amount will be
considered not year wise amount.)
Positive Adjustments (Add)
Adjustments to Net Profit -](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2ctpppt-221226142056-a628dc4c/85/corporate-tax-planning-pptx-15-320.jpg)
![Tax Credit [Sec. 115JAA]
➢ The extra tax which the company has to pay because of MAT will be available for “tax credit” under
section 115JAA.
➢ Tax credit can be set off against future tax liability of the company but only in that year in which
the tax computed under normal provisions is more than MAT.
➢ The maximum amount which can be set off in respect of the brought forward tax credit shall be
allowed for any assessment year to the extent of the difference between the tax on the total
income and the tax which would have been payable under section 115JB for that assessment year.
➢ Tax credit can be carry forward up to a maximum of 15 years. For example, if MAT is paid in the
assessment year 2018-19, then 2033-34 is the last assessment year for adjustment of MAT credit.
➢ Carry forward and set off of MAT credit shall not apply to a limited liability partnership which has
been converted from a private company or unlisted public company](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2ctpppt-221226142056-a628dc4c/85/corporate-tax-planning-pptx-16-320.jpg)

![Alternate Tax Regime [Sec 115 BAA]
● Must be a domestic company.
● Disallowed deductions : Additional depreciated u/s 32(1)(iia), 10AA, 32AD, 33AB, 33ABA, 35(1)(ii),
35 (iia), 35(iii), 35(2AA), 35(2AB), 35AD, 35CCC, 35CCD, from 80C to 80U (excpt 80JJAA, 80LA,
80M)
● Adjustment of loss : Brought forward losses and unabsorbed depreciation are disallowed.
However, unadjusted additional depreciation in respect of block of asset which has not been given
full effect prior to A.Y. 2020-21, corresponding adjustment to be made to such block on 1st April,
2019(if 115BAA is opted)
● Depreciation allowed for taxation purposes, but restriction on availing additional depreciation.
● This option to avail 115 BAA can be exercised by domestic company by submitting Form No. 10-IC
on or before the due date of return filing u/s 139(1).
Conditions for availing benefit of lower tax :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2ctpppt-221226142056-a628dc4c/85/corporate-tax-planning-pptx-18-320.jpg)

![Alternate Tax Regime for Manufacturing cos.
[115BAB]
Conditions for availing benefit of lower tax :
● Must be a domestic company.
● Such company is set up on or after 1st October,2019( not formed by split or reconstruction
of already existing business) and commenced manufacturing / production on or before 31st
March, 2024.
● It includes manufacturing / production of any article(including generation of electricity), but
excludes the following business:
Development of computer software in any form
Conversion of marble blocks into slabs
Bottling of gas into cylinders
Printing of books / production of cinematographic films
Mining business
Any other business notified by Central govt.
● Company does not any plant / machinery , previously used for any other purpose
Exception : i) 20% of old plant / machinery permitted
ii) Second hand imported plant / machinery to be treated as new](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit2ctpppt-221226142056-a628dc4c/85/corporate-tax-planning-pptx-20-320.jpg)