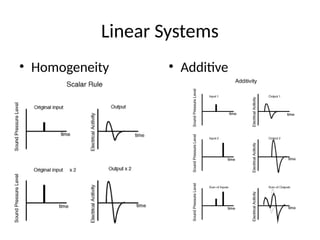
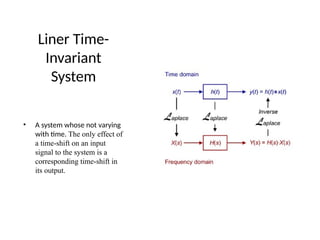
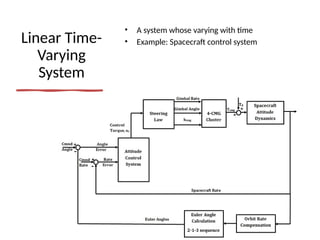
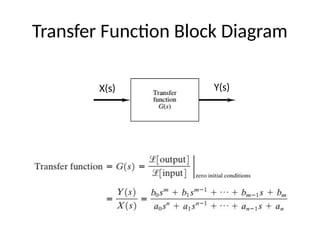
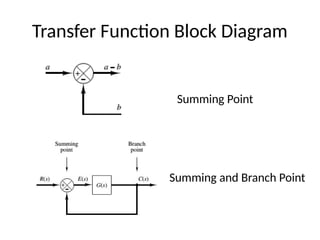
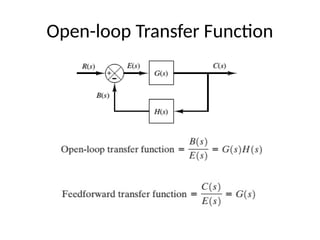
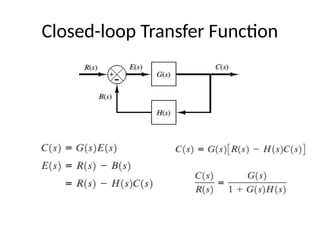
This document covers mathematical modeling in control systems, explaining that a mathematical model consists of equations that describe a system's input-output behavior. It distinguishes between linear and time-varying systems and introduces transfer functions, illustrating concepts with diagrams. Additionally, it outlines homework assignments based on the textbook by Ogata to reinforce these concepts.